What did Dalton Contribute to the Understanding of the Atom
Dalton’s atomic theory:
On the basis of laws of chemical combination John Dalton, an English school teacher in Manchester, proposed that behaviour of matter could be explained using an atomic theory. He published his work about atomic theory in 1808. The main points of Dalton’s atomic theory are:
- All the matter is made up of very small particles called “atoms”.
- Atoms cannot be divided.
- Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed.
- Atoms are of various kinds. There are as many kinds of atoms as are elements
- All the atoms of a given element are identical in every respect, having the same mass, size and chemical properties.
- Atoms of different elements differ in mass, size and chemical properties.
- Chemical combination between two (or more) elements consists in the joining together of atoms of these elements to form molecules of compounds.
- The “number” and “kind” of atoms in a given compound is fixed.
- During chemical combination, atoms of different elements combine in small whole numbers to form compounds.
Atoms of the same elements can combine in more than one ratio to form more than one compounds.
People also ask
- How would you describe the Structure of an Atom
- What was Rutherford’s Original Hypothesis
- What did Bohr Contribute to the Theory of an Atom
- What are the Characteristics of Electron, Proton and Neutron
- Explain Bohr Bury rules for Distribution of Electrons into Different Shells
- What are the Isotopes, Isobars and Isotones of an Element
- What is the Definition of Atom and Molecule
- What is Atomic Mass
- How has the Model of the Atom Changed Over the Years?
Drawbacks of Dalton’s atomic theory
Some of the drawbacks of the Dalton’s atomic theory of matter are given below :
- One of the major drawbacks of Dalton’s atomic theory of matter is that atoms were thought to be indivisible (which cannot be divided). We now know that under special circumstances, atoms can be further divided into still smaller particles called electrons, protons and neutrons. So, atoms are themselves made up of three particles : electrons, protons and neutrons.
- Dalton’s atomic theory says that all the atoms of an element have exactly the same mass. it is, however, now known that atoms of the same element can have slightly different masses.
- Dalton’s atomic theory said that atoms of different elements have different masses. it is, however, now known that even atoms of different elements can have the same mass.
- It failed to explain how atoms of different elements differ from each other, i.e., it did not tell anything about internal structure of the atom.
- It could not explain how and why atoms of different elements combine with each other to form compound atoms or molecules.
- It failed to explain the nature of forces that hold together different atoms in a molecule.
- It did not make any distinction between ultimate particle of an element that takes part in reactions (atom) and ultimate particle that has independent existence (molecule).
In order to represent the elements, instead of using full lengthy names, scientists use abbreviated names. These abbreviated names of the elements are known as symbols. Thus, symbol may be defined as the abbreviation used for the name of an elements.
Dalton’s symbols of elements
Dalton was the first scientist to use the symbols to represent elements in a short way.
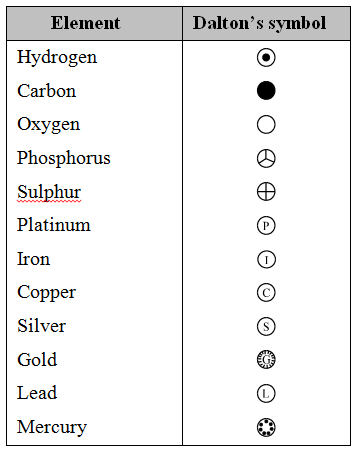
Dalton’s symbols for elements were difficult to draw and inconvenient to use. So, Dalton’s symbols are only of historical importance. They are not used at all.
Modern symbols of elements
IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) approves names of elements. The symbols of elements are generally either the first letter or the first two letters or the first and the third letters of the name of the elements. The symbols of the following elements are the first letter of the name of that elements.
Element | Symbol |
| Hydrogen Carbon Nitrogen Oxygen Fluorine Phosphorus Sulphur Iodine | H C N O F P S I |
Some symbols derived from the first two letters of the names of the elements.
Element | Symbol |
| Aluminium Barium Lithium Beryllium Neon Silicon Argon Calcium Nickel | Al Ba Li Be Ne Si Ar Ca Ni |
Some symbols derived from the first and the third letters of the names of the elements.
Element | Symbol |
| Arsenic Magnesium Chlorine Chromium Manganese Zinc Rubidium | As Mg Cl Cr Mn Zn Rb |
Some symbols derived from the latin names of the elements are given below.
Element | Latin name | Symbol |
| Iron Gold Copper Potassium Sodium Silver Mercury Tin Lead Antimony | Ferrum Aurum Cuprum Kalium Natrium Argentum Hydragyrum Stannum Plumbum Stibium | Fe Au Cu K Na Ag Hg Sn Pb Sb |
It is important to note that the first letter of every chemical symbol is capital letter but, if the symbol consists of two letters, the second letter is not capital letter.
Example: Symbol for aluminum is Al and not AL and Symbol for lead is Pb and not PB
Significance of the symbol of an element
- Symbol represents name of the element.
- Symbol represents one atom of the element.
- Symbol also represents one mole of atoms of the element. That is, symbol also represents 6.022 × 1023 atoms of the elements
- Symbol represents a definite mass of the element (equal to atomic mass expressed in grams)
