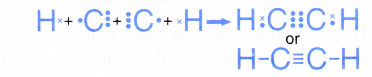How is covalent bond is formed?
A. Formation of a single covalent bonds
Formation of chlorine molecule, Cl2
- A chlorine atom has an electron arrangement of 2.8.7. It has seven valence electrons.
- Each chlorine atom needs one more electron to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement (similar to argon).
- As a result, two chlorine atoms will combine with each other. Each of these two chlorine atoms contributes one electron to each other for sharing.
- By doing so, the two chlorine atoms share one pair of electrons that bind them together, called a single covalent bond, as shown in Figure.
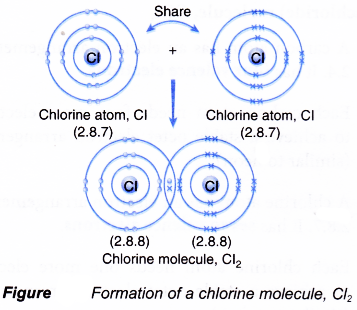
- Hence, a covalent molecule with a single covalent bond is formed. It has the molecular formula of Cl2.
- The formation of the chlorine molecule can be represented by the Lewis structure as shown below.

Formation of a water molecule, H2O
- An oxygen atom has an electron arrangement of 2.6. It has six valence electrons.
- Each oxygen atom needs two more electrons to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement (similar to neon).
- A hydrogen atom has an electron arrangement of 1 and one valence electron.
- Each hydrogen atom needs one more electron to achieve a stable duplet electron arrangement (similar to helium).
- As a result, two hydrogen atoms will combine with one oxygen atom through the sharing of electrons. Each of the two hydrogen atoms contributes one electron and one oxygen atom contributes two electrons for sharing.
- By doing so, one oxygen atom is bonded to each of the two hydrogen atoms by a shared pair of electrons so that all the three atoms achieve in stable noble gas electron arrangements, as shown in Figure.
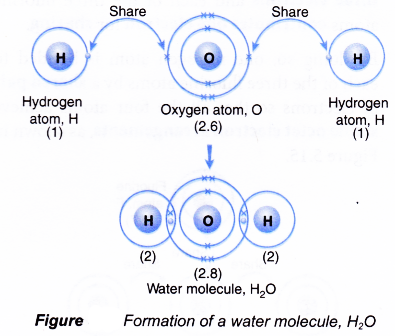
- Hence, a covalent molecule, H20, with two single covalent bonds is formed.
- The formation of the water molecule can be represented by the Lewis structure as shown below.
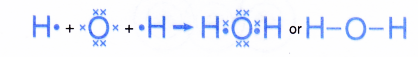
People also ask
- Chemical Bonding and Compound Formation
- Chemical Bonding
- What is Covalent Bond?
- Describe how to write a formula for a covalent compound
- What causes ions to form ionic bonds?
- Explain the formation of ionic bonds with examples
- Properties of Ionic and Covalent Compounds
- How do you write the formula for ionic compounds?
- How do you Name an Ionic Compound?
Formation of a nitrogen trifluoride molecule, NF3
- A nitrogen atom has an electron arrangement of 2.5. It has five valence electrons.
- Each nitrogen atom needs three more electrons to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement (similar to neon).
- A fluorine atom has an electron arrangement of 2.7. It has seven valence electrons.
- Each fluorine atom needs one more electron to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement (similar to neon).
- As a result, one nitrogen atom will combine with three fluorine atoms through the sharing of electrons. One nitrogen atom contributes three electrons and each of the three fluorine atoms contributes one electron for sharing.
- By doing so, one nitrogen atom is bonded to each of the three fluorine atoms by a shared pair of electrons so that all the four atoms achieve stable octet electron arrangements, as shown in Figure.
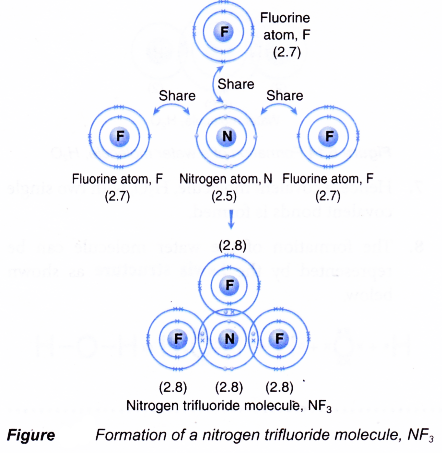
- Hence, a covalent molecule NF3 with three single covalent bonds is formed.
- The formation of the nitrogen trifluoride molecule can also be represented by the Lewis structure as shown below.
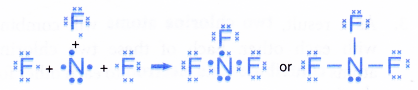
Formation of a tetrachloromethane (carbon tetrachloride) molecule, CCl4
- A carbon atom has an electron arrangement of 2.4. It has four valence electrons.
- Each carbon atom needs four more electrons to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement (similar to neon).
- A chlorine atom has an electron arrangement of 2.8.7. It has seven valence electrons.
- Each chlorine atom needs one more electron to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement (similar to argon).
- As a result, one carbon atom will combine with four chlorine atoms through the sharing of electrons. One carbon atom contributes four electrons and each of the four chlorine atoms contributes one electron for sharing.
- By doing so, one carbon atom is bonded to each of the four chlorine atoms by a shared pair of electrons so that all the five atoms achieve stable octet electron arrangements, as shown in Figure.
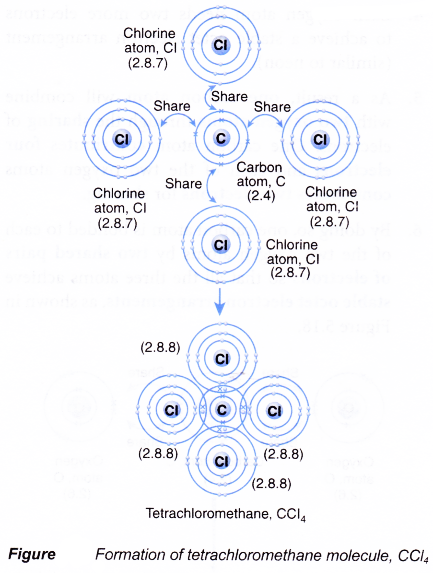
- Hence, a covalent molecule, CCl4, with four single covalent bonds is formed.
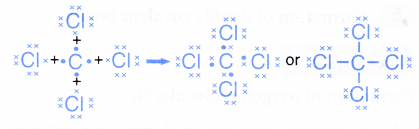
- The formation of the tetrachloromethane molecule can also be represented by the Lewis structure as shown.
B. Formation of double covalent bonds
Formation of oxygen molecule, O2
- An oxygen atom has an electron arrangement of 2.6. It has six valence electrons.
- Each oxygen atom needs two more electrons to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement (similar to neon).
- As a result, two oxygen atoms will combine with each other. Each of these two oxygen atoms contributes two electrons to each other for sharing.
- By doing so, the two oxygen atoms share two pairs of electrons that bind them together, called a double covalent bond, as shown in Figure.
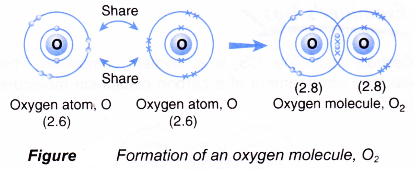
- Hence, a covalent molecule with the molecular formula O2 is formed.
- The formation of the oxygen molecule can be represented by the Lewis structure as shown below.

Formation of a carbon dioxide molecule, CO2
- A carbon atom has an electron arrangement of 2.4. It has four valence electrons.
- Each carbon atom needs four more electrons to achieve a stable octet eletron arrangement (similar to neon).
- An oxygen atom has an electron arrangement of 2.6. It has six valence electrons.
- Each oxygen atom needs two more electrons to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement (similar to neon).
- As a result, one carbon atom will combine with two oxygen atoms through the sharing of electrons. One carbon atom contributes four electrons and each of the two oxygen atoms contributes two electrons for sharing.
- By doing so, one carbon atom is bonded to each of the two oxygen atoms by two shared pairs of electrons so that all the three atoms achieve stable octet electron arrangements, as shown in Figure.
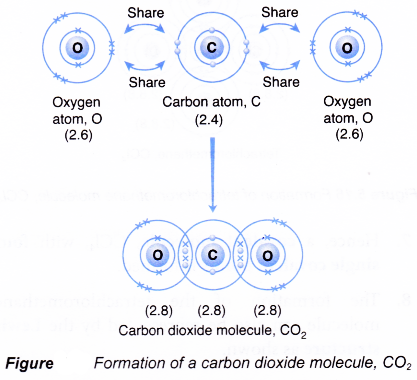
- Hence, a covalent molecule, CO2, with two double covalent bonds is formed.
- The formation of the carbon dioxide molecule can be represented by the Lewis structure as shown below.
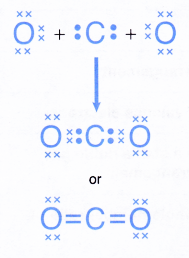
C. Formation of triple covalent bonds
Formation of nitrogen molecule, N2
- A nitrogen atom has an electron arrangement of 2.5. It has five valence electrons.
- Each nitrogen atom needs three more electrons to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement (similar to neon).
- As a result, two nitrogen atoms will combine with each other. Each of these two nitrogen atoms contributes three electrons to each other for sharing.
- By doing so, the two nitrogen atoms share three pairs of electrons that bind them together, called a triple covalent bond, as shown in Figure.
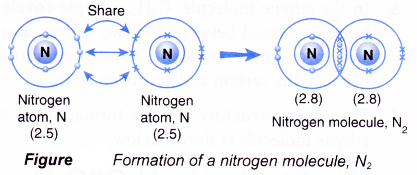
- Hence, a triple covalent bond is formed in the nitrogen molecule with the molecular formula N2.
- The formation of the nitrogen molecule can be represented by the Lewis structure as shown below.

Formation of an ethyne molecule, C2H2
- A carbon atom has an electron arrangement of 2.4. It has four valence electrons.
- Each carbon atom needs four more electrons to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement (similar to neon).
- A hydrogen atom has an electron arrangement of 1. It has one valence electron.
- Each hydrogen atom needs one more electron to achieve a stable duplet electron arrangement (similar to helium).
- Two carbon atoms and two hydrogen atoms can combine to form an ethyne molecule, C2H2 so that all the four atoms can achieve stable noble gas electron arrangements, as shown in Figure.
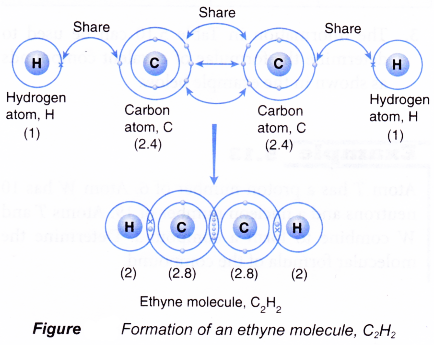
- In the ethyne molecule, C2H2, a triple covalent bond is formed between the two carbon atoms and two single covalent bonds are formed between the carbon and hydrogen atoms.
- The Lewis structure for the formation of the ethyne molecule is shown below.