What is the Conductivity of Water
Electrical Conductivity
The measure of the ability of a substance to allow the flow of an electric current is called electrical conductivity. Substances that are good conductors have high electrical conductivity as compared to substances that are poor conductors (i.e., insulators). Some liquids, but not all, are good conductors. Let us discuss the electrical conductivity of some common liquids.
Electrical Conductivity of Water
Pure water is a poor conductor. But, the water that we use in our homes is not pure. Generally, tap water, pond water, and well water, etc., contain a lot of impurities, most of which are usually dissolved salts. The presence of even a small amount of impurities makes water a good conductor. Remember, getting an electric shock could result in very serious consequences, even death. So, always take care while operating electrical appliances. One is more likely to get an electric shock upon touching an electrical appliance with wet hands than with dry hands. This is because wet skin has many times more conductivity than dry skin.
Electrical Conductivity of Other Liquids
Most acids and bases dissolved in water are good conductors of electricity. To test the electrical conductivity of two common acids, lemon juice and vinegar, let us perform an activity.
Activity
Aim: To test the electrical conductivity of lemon juice and vinegar
Materials needed: Lemon juice, vinegar, insulated copper wire, battery, and a light-emitting diode (LED)
Method: Arrange the set-up as shown in the figure below. Take a small amount of lemon juice in a plastic bottle cap and dip the two free ends of the copper wire into it, as shown in the figure. Take care that the free ends of the wire do not touch each other. Repeat this procedure with vinegar.
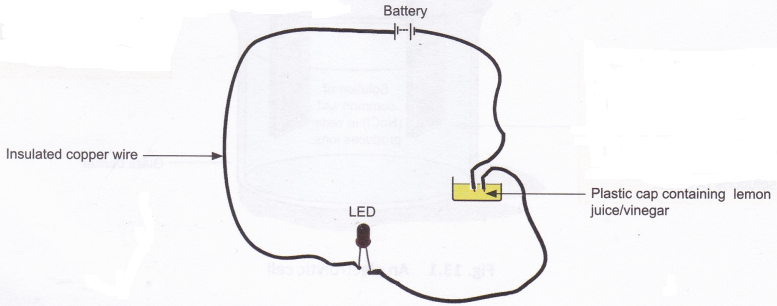
Observation: The LED will glow in each case.
Conclusion: Lemon juice and vinegar are good conductors.
Note: Adult supervision required.
When salts like sodium chloride (common salt), potassium iodide, etc., are heated, the molten salts so obtained are good conductors. However, most substances that exist as liquids at room temperature, like alcohol, oils, etc., are bad conductors. When substances like salts, acids, and bases are dissolved in water, the resultant solutions are fairly good conductors.
Let us find out why this happens.
Effect of Impurities on Electrical Conductivity of Water
As we discussed earlier, an electric current requires freely moving charged particles.
Moving charged particles are also referred to as charge carriers. In metals, which are good conductors, the charge carriers are a type of particles called electrons. In liquids, the charge carriers are generally ions. Atoms or a group of atoms with a positive or a negative charge are called ions. When impurities (like salts) dissolve in water, they form ions, and these ions make it possible for an electric current to pass through the solution.
Suppose we dissolve a small quantity of common salt (sodium chloride, NaCl) in pure water. When salt dissolves in water, it forms ions of sodium and chlorine. If we take this salt solution in a beaker and set it up as shown in Figure, an electric current will flow in the circuit. Such an arrangement is called an electrolytic cell. Pure water does not form enough ions to conduct electricity. That is why pure water is a poor conductor of electricity.
Unlike the dry cell you are familiar with, an electrolytic cell does not use chemical reactions to generate electric current. In fact, it does the opposite. An electrolytic cell uses electric current to produce a chemical reaction.
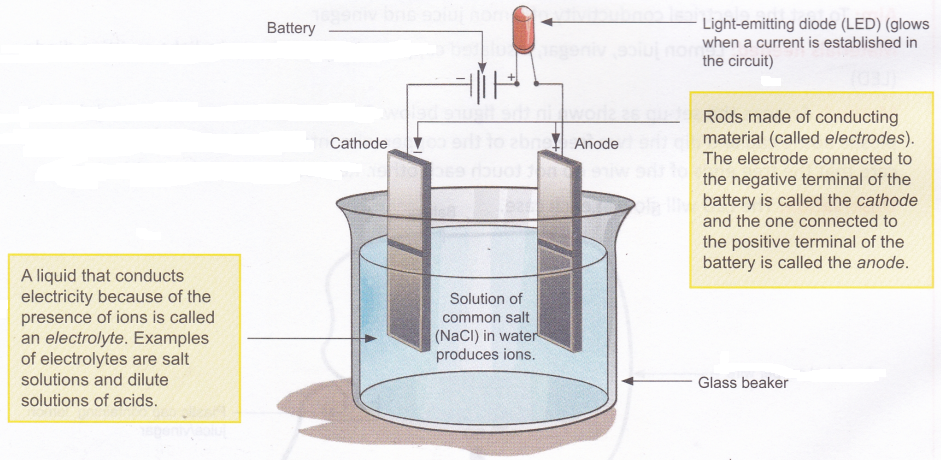
A process called electrolysis occurs in an electrolytic cell when a current is passed through the electrolyte.
