Which Components form the Structure of the Plasma Membrane
Ultra Structure of Cells
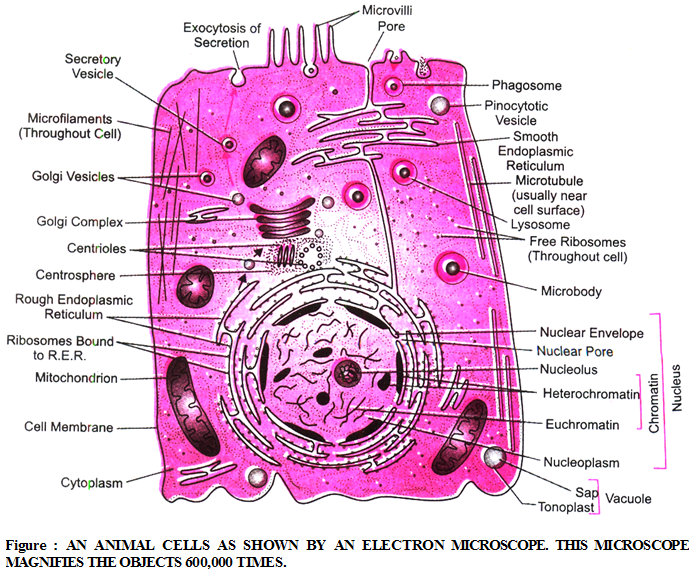
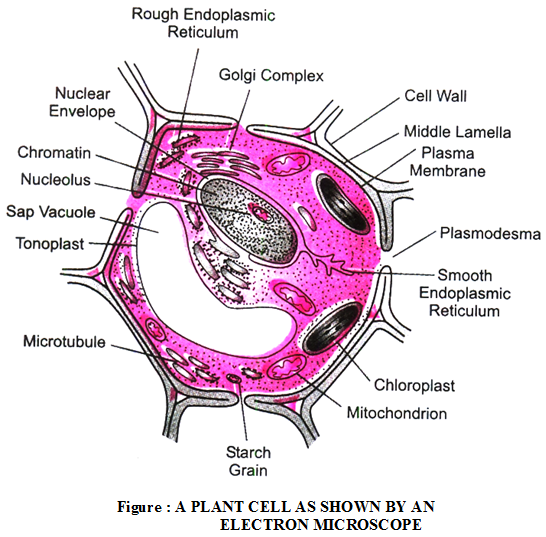
Plasma Membrane :
Introduction :
Cell surface in all the cells is enclosed by a living membrane which is called cell membrane by
C. Nageli and C. Kramer (1855).
Historical Account :
J.Q. Plower (1931) coined the term Plasmalemma for cell membrane.
Ultrastructure :
- Plasma membrane forms outer covering of each cell.
- It is present in both plant and animal cells.
- Plasma membrane is a living, thin, delicate elastic, selectively permeable membrane.
- It separates contents of a cell from the surrounding medium.
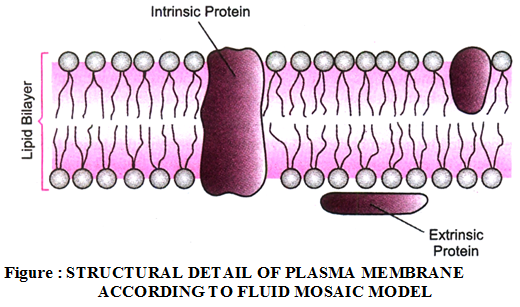
Fluid Mosaic Model :
- In 1972, Singer Nicolson proposed this model. According to this, cell membrane consists-two layers of phospholipid molecules, phospholipid & protein molecules are arranged as a mosaic.
- Phospholipid molecules have their polar heads directed outward non polar tail pointing inward.
- The proteins are of two types :
- Peripheral and integral. Peripheral proteins are located superficially while integral proteins are embeded in the phospholipid matrix. The protein monolayer have elasticity & mechanical support to the lipid matrix.
Functions of Plasma Membrane :
- The main function of plasma membrane is to regulate the movement of molecules inside and outside the cell.
- It allow the movement of gaseous substance from high concentration to low concentration which known as diffusion.
- Water also obeys the low of diffusion . The movement of water molecule through a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis.
- The flexibility of cell membrane also enables the cell to engulf in food, which is also known as endocytosis. For example – in Amoeba
Cell wall :
In plants, one another rigid is called ‘Cell wall’. It is made up of cellulose which provide structural strength to plant.
Function of cell wall :
- It maintains the shape of cell.
- It protect the cells from mechanical injury & prevents their desication.
- It provide mechanical support against gravity. It is due to rigid cell walls that the aerial part of plant are able to keep erect & expose their leaves to sunlight.
- Cell walls permit the cells to with stand very dilute external media without bursting.
Nucleus : It is the most important part of cell which control all the activities of cell.
Structure of Nucleus :
- The nucleus has a double layered covering called nuclear membrane.
- The nuclear membrane has pores inside the nucleus to its outside, that is, to the cytoplasm.
- The nucleus contains chromosomes, which are visible as rod-shaped structures only when the cell is about to divide.
- Chromosomes are composed of DNA and protein.
- Functional segments of DNA are called genes.
- In a cell which is not dividing, this DNA is present as part of chromatin material.
Function of nucleus :
- It play a important role in cellular reproduction.
- DNA contain the information necessary for constructing & organizing cells.
- Nucleoid – In some organisms nuclear region of cell may be poorly defined due to the absence of nuclear membrane. Such an undefined nuclear region called nucleoid.
Note :
- Prokaryotic cell – Cell which do not have well defined nuclear region . called prokaryotic cells. Pro – Primitive Karyon – nucleus
- Eukaryotic cells – Cells which have well defined nuclear region, called eukaryotic cells.
- Along with nucleus membrane, prokaryotic cells lack most of cell organells.
Cytoplasm :
The fluid & semifluid matrix of a cell between the nucleus & the plasma membrane, containing various organelles is called cytoplasm.
Cell organelles :
Small membrane bound structures, which perform a lot of chemical activities to support the function & structure of a cell, called cell organelles –
