Classification of Solutions
Solutions are of Three types.
- True Solutions
- Suspension
- Colloids
1. True Solutions :
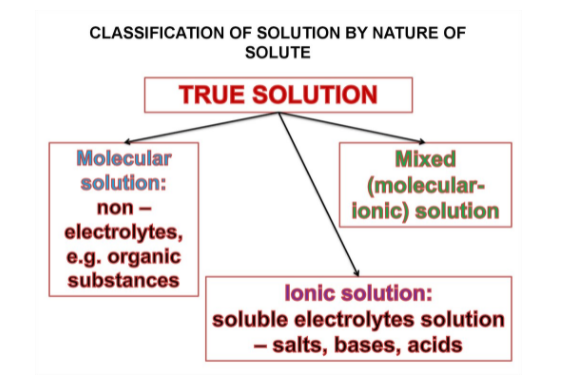
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more pure substances. A solution is made up of two parts i.e., a solute and a solvent. Usually the component which is present in larger amount is called solvent and the other is called solute.
Ex. In case of solution of sugar and water, sugar is the solute and water is the solvent.
Aqueous solutions
The solutions made by dissolving various solutes in water are called aqueous solutions.
Properties of solutions
- A solution is homogeneous in nature.
- The solute particles in a solution easily pass through a filter paper. Thus, a true solution passes through a filter paper.
- The solute particles in a solution cannot be seen by naked eyes.
- The properties of solute are retained in the true solution. Thus a sugar solution is sweet in taste and a solution of salt in water is saline in taste.
- A true solution does not scatter light and hence does not show tyndall effect. In other words, solutions are transparent to light.
- The solute particles in a solution do not settle on keeping.
- The diameter of solute particles in a solution is about 10–9 m.
Types of solutions
- Solution of solid in a solid : Metal alloys are the solutions of solids in solids.
Ex. Brass is a solution of zinc in copper. Brass is prepared by mixing molten zinc with molten copper and cooling their mixture. - Solution of solid in a liquid : This is the most common type of solutions. Sugar solution and salt solution are the solutions of solids in liquids. A solution of iodine in alcohol called ‘tincture of iodine’ is also a ‘solid in a liquid’ type of solution. This is because it contains a solid (iodine) dissolved in a liquid (alcohol) solution.
- Solution of liquid in a liquid : Vinegar is a solution of acetic acid (ethanoic acid) in water.
- Solution of gas in a liquid : Soda-water is a solution of carbon dioxide gas in water.
- Solution of gas in a gas : Air is a solution of gases like oxygen, argon, carbon dioxide and water vapour, etc., in nitrogen gas. Nitrogen is the solvent in air and all other gases are solutes.
2. Suspensions :
A suspension is a heterogeneous mixture in which the small particles of a solid are spread throughout a liquid without dissolving in it.
Ex. Chalk-water mixture, Muddy water, Milk of magnesia, Sand particles suspended in water, and Flour in water.
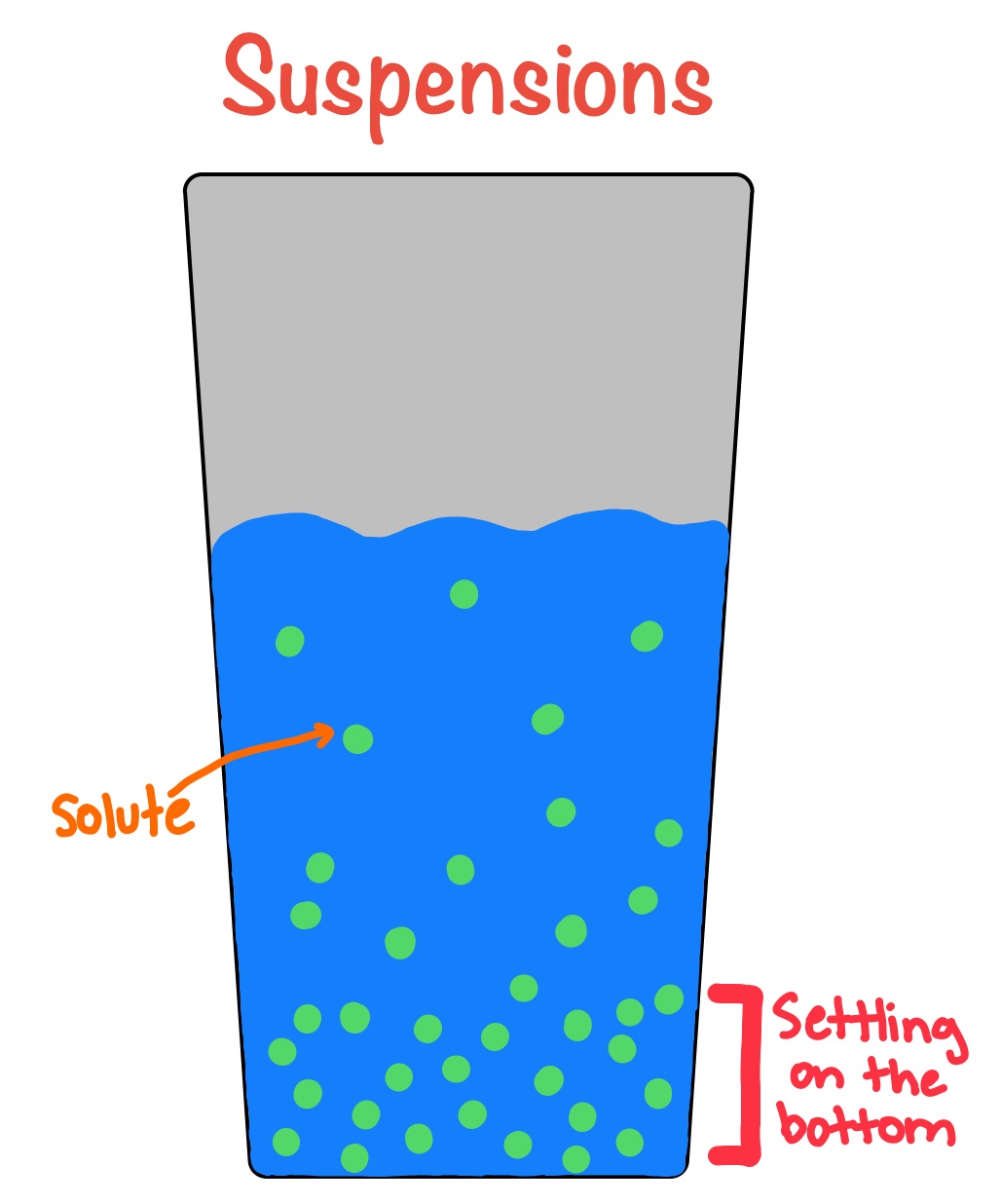
Properties of suspensions
- A suspension is a heterogeneous mixture.
- The particles of a suspension do not pass through a filter paper. Hence, it is possible to separate them by ordinary filtration.
- The particles of suspension can be seen with naked eyes or with the help of a simple microscope.
- The particles of suspension settle down when a suspension is left undisturbed. Thus, a suspension is unstable.
- The size of particles in a suspension is greater than 100 nm in diameter.
- A suspension is not transparent to light.
3. Colloids :
A colloid is a kind of solution in which the size of solute particles is intermediate between those in true solutions and those in suspensions. The size of solute particles in a colloids is bigger than that of a true solution but smaller than those of a suspension.
