Classification of Hydrocarbons
The compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen in their molecules are called hydrocarbons.
Hydrocarbons are classified into two categories known as open chain hydrocarbons and closed chain hydrocarbons. Open chain hydrocarbons are also called aliphatic hydrocarbons or acyclic hydrocarbons.
Open and closed chain hydrocarbons
Let us observe the following structural formulae of different hydrocarbons.
1) CH3–CH2–CH2–CH2–CH3 n-pentane, a straight chain compound.
2) 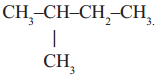 Iso pentane, a branched chain compound
Iso pentane, a branched chain compound
3) 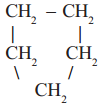 cyclo pentane, a cyclic compound or a ring compound
cyclo pentane, a cyclic compound or a ring compound
In the first example you will notice that all carbons are linked to one another resulting a linear structure, where as in the second example four carbons are linked in linear way and the fifth carbon is linked to the parent chain resulting a branch. In the third example we find that carbon chain is closed to form a ring. So, it is a closed chain hydrocarbon or ring hydrocarbon.
All hydrocarbons (both Aliphatic and cyclic hydrocarbons) are again classified as Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes:
1) Hydrocarbons containing only single bonds between carbon atoms are called Alkanes.
2) Hydrocarbons containing atleast one double bond between carbon atoms are called Alkenes, and
3) Hydrocarbons containing atleast one triple between carbon atoms are called Alkynes.
Saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons
The hydrocarbons containing only C–C single bonds are known as saturated hydrocarbons. All alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons. The hydrocarbons that contain at least one double bond (C=C) or contain atleast one triple bond (C ≡ C) between the two carbon atoms are called unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes and Alkynes are the examples for unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Straight chain, branched chain and closed chain hydro carbon compounds may be saturated or unsaturated. See the following examples.
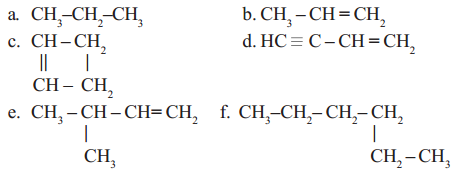
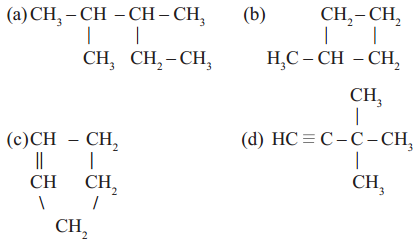
Read More:
- Binding of Carbon with other Elements
- Homologous Series of Hydrocarbons
- Allotropes of Carbon
- Catenation in Carbon
- sp3 Hybridized Carbon atom
- Hybridization of the Carbon atoms in Acetylene
- Versatile Nature of Carbon
- What are the Characteristics of Compounds
- Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
- Nomenclature of Carbon Compounds
People also ask
- What are carbon compounds?
- Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
- How are alkanes formed?
- What is an alkene in chemistry?
- What is an isomerism?
- What is alcohol and how is it made?
- How are carboxylic acids formed?
- How esters are formed?
- What are fats and oils?
- How palm oil is extracted?
- Order in Homologous Series
- What is the monomer of natural rubber?
- Which acid is used for coagulating rubber from latex?
- What is the homologous series of hydrocarbons?
- Properties and Uses of Ethanol
- Properties and Uses of Ethanoic Acid
