Chemical Reactions
The processes in which a substance or substances undergo change to produce new substances with new properties are known as chemical reactions. for example, when calcium carbonate is heated, calcium oxide (lime) and carbon dioxide are formed. The breaking up of calcium carbonate into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide is, thus, a chemical reaction because calcium carbonate changes into new substances, calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
Reactant :
The substance which takes part in a chemical reaction is called reactant. For example, in the breaking up of calcium carbonate into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide, calcium carbonate is the reactant. Similarly, sodium and water are the reactants when they react.
Product :
A product is a new substance formed in a chemical reaction. For example, hydrogen and sodium hydroxide are the products of the reaction between sodium and water.
![]()
Similarly, in the breaking up of calcium carbonate, calcium oxide and carbon dioxide are the products.
![]()
You know, atoms in a molecule are held together by a force of attraction called bond. The molecules do not participate directly in a chemical reaction. First they break down into atoms and these atoms then take part in the reaction. New bonds are formed between the atoms to form the products. That is, there take place rearrangement or regroupings of atoms in various ways to give products. For example, when ammonium cyanate is heated, different bonds in ammonium cyanate molecules are broken and new bonds are formed to produce urea.
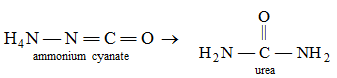
Here, we see that the molecular formulae of both ammonium cyanate and urea are the same, but their properties are quite different and they are two different compounds. Such compounds are known as isomers of each other and the reactions that produce such isomers are called isomerization reactions.
Valency :
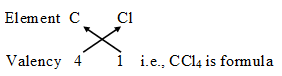
The number of electrons shared by an atom is called its valency. It is also called the combining capacity of an atom, e.g., Cl atom can share one valence electron, its valency is 1, Oxygen can share two valence electrons, its valency is 2. Nitrogen can share 3 valence electrons, its valency is 3, Carbon can share 4 valency electrons, therefore its valency is 4 and so on.
It means if carbon combines with Chlorine, Carbon will share four valence electrons with four chlorine atoms, therefore the molecular formula of the covalent compound will be
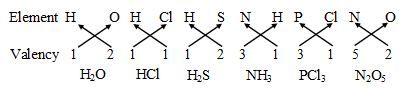
Some more examples are :
Some Common Monoatomic Ions
| +1 Charge | Formula | +2Charge | Formula | +3 Charge | Formula |
| Name of ion | Name of ion | Name of ion | |||
Copper ion | Cu+ | Barium ion Cobalt ion | Ba2+ Co2+ | Aluminium ion Auric ion | Al3+ Au3+ |
| Potassium ion | K+ | Strontium ion | Sr2+ | Chromium (III) ion | Cr3+ |
| Silver ion | Ag+ | Iron (II) ion (Ferrous ion) | Fe2+ | Iron (III) ion (Ferric ion) | Fe3+ |
| Sodium ion | Na+ | *Copper (II) ion | Cu2+ | Scandium ion | Sc3+ |
| Lithium ion | Li+ | *Lead (II) ion | Pb2+ | Arsenic ion | As3+ |
| Cadmium ion | Cd2+ | Bismuth ion | Bi3+ | ||
| Magnesium ion | Mg2+ | Antimony ion | Sb3+ | ||
| Aurous | Au+ | Manganese (II) ion | Mn2+ | ||
| *Mercury (I) ion | |||||
| Zinc ion | Zn2+ |
| – 1 Charge | Formula | – 2Charge | Formula | – 3 Charge | Formula |
| Name of ion | Name of ion | Name of ion | |||
| Bromide ion | Br– | Oxide ion | O2– | Nitride ion | N3– |
| Chloride ion | Cl– | Sulphide ion | S2– | Phosphide ion | P3– |
| Fluoride ion | F– | Boride ion | B3– | ||
| Iodide ion | I– |
These elements show more than one valency. So a Roman numeral shows their valency in a bracket.
Some Common Polyatomic Ions
| – 1 Charge | Formula | – 2Charge | Formula | – 3 Charge | Formula |
| Name of ion | Name of ion | Name of ion | |||
| Hydrogen carbonate or bicarbonate ion | HCO3– | Carbonate ion Manganate ion | CO32- MnO42- | Phosphate ion Arsenate ion | PO43- |
Hydrogen sulphate | HSO4– | Thiosulphate ion Silicate ion | S2O32- SiO32- | Arsenite ion | AsO33- |
| Hydroxide ion | OH– | Sulphate ion | SO42- | Phosphite ion | PO33- |
| Nitrate ion | NO3– | Sulphite ion | SO32- | ||
| Chlorate ion | ClO3– | Chromate ion | CrO42- | Borate ion | BO33- |
| Nitrite ion | NO2– | Dichromate ion | Cr2O72- | Ferricyanide ion | [Fe(CN)6]3– |
| Permanganate ion | MnO4– | Hydrogen phosphate ion | HPO42- | ||
| Acetate ion | CH3COO– | Oxalate ion | C2O42- | ||
| Cyanide ion | CN– | ||||
| Hypophosphite ion | H2PO2– | – 4 Charge | |||
| Meta aluminate ion | AlO2– | Carbide ion | C4– | ||
| +1 Charge | Ferrocyanide ion | [Fe(CN)6]4– | |||
| Ammonium ion | NH4+ |
Tests of Chemical Reaction :
A chemical reaction must satisfy the following :
(i) There must be either evolution or absorption of heat, i.e., a chemical reaction must be accompanied with change in temperature.
(ii) The reaction must occur between fixed quantities of the reactants.
(iii) There must not be either gain or loss of matter, i.e., a chemical reaction should follow the law of conservation of mass.
(iv) The products obtained as a result of chemical reaction must have properties different from those of the reactants.
