CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Paper 6 are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Paper 6.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Paper 6
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | IX |
| Subject | Science |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 6 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 9 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme as prescribed by the CBSE is given here. Paper 6 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 9 Science is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time Allowed : 3 Hours
Max. Marks: 80
General Instructions
- The question paper comprises of two Sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections.
- All questions are compulsory. How ever an internal choice will be provided in two questions of 3 marks each and one question of five marks.
- All questions of Section A and all questions of Section B are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 2 in Section A are one-mark questions. These are to be answered in one word or in one sentence.
- Question numbers 3 to 5 in Section A are two-marks questions. These are to be answered in about 30 words each.
- Question numbers 6 to 15 in Section A are three-marks questions. These are to be answered in about 50 words each.
- Question numbers 16 to 21 in Section A are five-marks questions. These are to be answered in about 70 words each.
- Question numbers 22 to 27 in Section B are two-marks questions based on practical skills. These are to be answered in brief
Questions
SECTION-A
Question 1.
State the relation between commercial unit of energy and joules.
Question 2.
Name the man made component which is responsible for the depletion of ozone layer.
Question 3.
List in tabular form, the differences between mass and weight.
Question 4.
List two ways in which water is useful to living organisms.
Question 5.
Differentiate between transverse and longitudinal waves and give one example of each.
Question 6.
A source of sound produces 20 compressions and 20 rarefactions in 0.2 seconds. The distance between a compression and the next (consecutive) rarefaction is 50 cm. Find the wavelength, frequency and time period of the wave.
Question 7.
Classify the following animals into their phyla giving one reason:
- Earthworm
- Scorpion
- Starfish
Question 8.
Define power. Name its S.I. Unit. An electric bulb is rated 15 watts. What does it mean? What is the energy consumed in joules, if it is used for 10 minutes?
Question 9.
- Name the plant tissues found in the husk of a coconut and also identify the chemical which is responsible for its stiffness.
- Give one way in which it differs from parenchymatous cells.
Question 10.
State the universal of law of Gravitation.
The mass of Sun is 2 × 1030 kg and that of Earth is 6 × 1024 kg. If the average distance between the Sun and Earth is 1.5 × 1011 m, calculate the force exerted by the sun on the earth and also by the earth on the sun.
OR
A ball is thrown vertically upwards and returns to the thrower after 6 seconds. Find :
(a) The velocity with which it was thrown up.
(b) The maximum height that it reaches. [Take g = 9.8 m/s2]
Question 11.
Distinguish between density and relative density of a substance. The relative density of silver is 10.8. If the density of water is 103 kg/m3 find the density of silver.
Question 12.
What is acid rain? Give its harmful effects.
Question 13.
- Under which category of mixtures will you classify alloys and why?
- A solution is always a liquid. Comment.
- Can a solution be heterogeneous? Justify
Question 14.
Why is excess use of fertilisers harmful for environment?
Question 15.
- State the law of constant proportion.
- Taking the example of water explain the law of constant proportion.
- Which postulate of Dalton’s Atomic Theory explains this law?
OR
Write the electronic configuration and valency of the following:
- Fluorine
- Potassium
- Silicon
Question 16.
Explain ‘Potential energy’ in your own words and give an example of it. State the S.I. unit of potential energy. Derive an expression for potential energy of an object of mass ‘m ’ that has been raised to a height ‘h’ from the ground.
A body of mass 20 kg is lifted up by 10 meters. Calculate its potential energy. If this body is allowed to fall, find its kinetic energy just before it touches the ground. [Take g = 10 m/s2]
Question 17.
- Draw a neat and labelled diagram of the apparatus used to separate the components of blue-black ink. Name the process and state the principle involved.
- Identify the physical and chemical changes from the following:
- Burning of magnesium in air.
- Tarnishing of silver spoon.
- Sublimation of iodine.
- Electrolysis of water.
Question 18.
- State one difference and one similarity between boiling and evaporation.
- What is sublimation. Name two substances that show this property?
- Using kinetic molecular theory give differences between solid and liquid particles.
Question 19.
Explain how animals in Vertebrata are classified into further subgroups.
Question 20.
(a) List any 3 situations in your daily life where you can say work has been done.
(b) What work is said to be done to increase the velocity of a car from 15 km/h to 30 km/h, if mass of the car is 1000 kg?
OR
- State Archimedes’principle.
- What are fluids? Why is Archimedes’ principle applicable only for fluids? Give three applications of Archimedes’ principle.
Question 21.
(a) Derive the formula for universal law of gravitation.
(b) Give the differences between ‘g’ and ‘G’.
SECTION-B
Question 22.
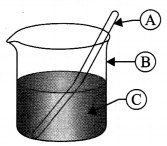
For preparing a true solution, the given set up was done. What is ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’?
Question 23.
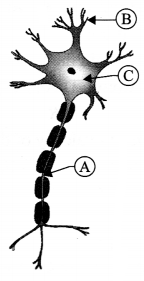
The following diagram gives the structure of a nerve cell. Identify the parts labelled as A, B and C respectively.
Question 24.
Give two functions of osmosis.
Question 25.
Represent a wave with low and high amplitude.
Question 26.
How the presence of an air bubble in the liquid taken in the measuring cylinder can affect the volume of the solid?
Question 27.
A rectangular body has dimensions x and y (l and b). If its dimensions get doubled, what will happen to its volume?
Answers
SECTION-A
Answer 1.
Commercial Unit of Energy : Kilowatt hour
1 kilowatt hour = 3.6 × 106 Joules
Answer 2.
CFC (Chloro Fluoro Carbon)
Answer 3.
| Mass | Weight |
| (i) Mass of an object is the quantity of matter contained in it. | Weight of an object is the force with which it is attracted towards the centre of the Earth. |
| (ii) It remains constant everywhere. | It changes from place to place with the value of ‘g’. |
| (iii) It can never be zero. | It can be zero. |
| (iv) Its S.I. unit is kg. | Its S.I. unit is newton. |
Answer 4.
- All cellular processes takes place in water as a medium. The reactions that take place within our body cells occur between the substances that are dissolved in water.
- Water is an excellent solvent. Substances are also transported from one part of the body to the other part in dissolved form.
Answer 5.
Transverse waves are the waves in which particles of the medium vibrates at right angle to the direction of propagation of wave.
Example: Water waves/waves set up in a rope whose one end is fixed and the other is jerked. (Or any other appropriate example)
On the contrary longitudinal waves are those waves in which particles of the medium vibrates in the same direction as that of the wave.
Example: Compressed spring. (Or any other appropriate example)
Answer 6.
No. of waves = 20
Distance between a compression and the next rarefaction is half of the wavelength.

Answer 7.
- Earthworm: Annelids, as its body is segmented.
- Scorpion: Arthropoda, as it has joint appendages.
- Starfish: Echinodermata, as it has calcareous skeleton and tubefeet.
Answer 8.
Power is the rate of doing work, i.e. the amount of work done per unit time.
S.I. unit: Watt
If a bulb is rated 15 watts, it means it consumes 15 joules energy per second.
Therefore, Power = EnergyTime
So, Energy = Power x Time
Therefore, energy consumed by the bulb = 15 × (10 × 60)
= 15 × 600
= 9000 Joules or 9 kJ
Answer 9.
- Sclerenchyma
- Lignin
- Sclerenchyma consists of dead cells/with very thick walls/provides strength to plant parts. Parenchyma consists of living cells/with thin cell walls/stores food.
Answer 10.
Universal law of gravitation states that every body in this universe attracts every other body with an the force of gravitation is directly proportional masses of two interacting bodies and is inversely proportional to the square of distance (d2) between them.
Force of sun on earth is,
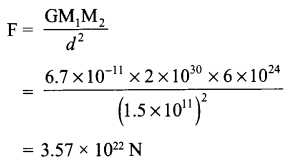
Force of the earth on the sun is the same.
OR
(a) Time of ascent is equal to the time of descent. The ball takes a total time of 6 seconds for its upward and downward journey.
Hence, it has takes 3 seconds to attain the maximum height.
Final velocity of the ball at maximum height, v = 0
Acceleration due to gravity, g = – 9.8 ms-2
As per the equation of motion, v = u + gt
⇒ 0 = u + (- 9.8 × 3)
u= 9.8 × 3
= 29.4 ms-1
Hence, the ball was thrown upwards with a velocity of 29.4 ms-1
(b) Let the maximum height attained by the ball be h.
Initial velocity during the upward journey, u = 29.4 ms-1
Final velocity, v = 0
Acceleration due to gravity, g = – 9.8 ms-2
s = ut + (12)at2
From the equation of motion,
h = 29.4 × 3(12)x – 9.8 × (3)2 = 44.1 m
Answer 11.
| Density | Relative Density |
| (i) It is defined as mass per unit volume. | (i) It is defined as the ratio of density of the substance to the density of water at 4°C. |
| (ii) Its value is different in different systems of measurement. | (ii) Its value remains the same in all systems of measurement. |
| (iii) Its units are g cm-3 and kg m-3. | (iii) It has no units. |
Relative density of silver =10.8
Density of water = 103 kg m-3
RD = DensityofsilverDensityofwater
Hence, Density of silver = RD × Density of water
= 10.8 × 103 kg m3 = 1.08 × 104 kg m-3
Answer 12.
The gases released due to combustion of fossil fuels are SO2, NO2, CO2, etc. These gases remain suspended in the air.
And when it rains the rain water mixes with these gases to form sulphuric acid, nitrous acid, carbonic acid and came down on the surface of the earth in the form of rain called the acid rain.
Harmful effects of acid-rain:
- It corrodes statues, monuments of marble, building etc.
- It makes the soil acidic.
- It damages crops, plantations.
Answer 13.
- Alloys are classified in the category of homogeneous mixtures as the combined constituents cannot be easily distinguished.
- A solution obtained when a solute (solid/liquid or gas) dissolves in the liquid solvent is a liquid solution. However, it is not always true. For instance, in the formation of alloys solids are mixed to form a solution.
- No, as a solution is formed by dissolving one substance into another substance.
Answer 14.
- It changes the nature of the soil.
- It lowers the water holding capacity of soil.
- The chemical enters the food chain, as it is an inorganic chemical which not used by animals, so it gets accumulated in the top most consumers leading to biological magnification. This can cause various harmful diseases, e.g. cancer.
Answer 15.
- In a chemical substance the elements are always present in definite proportion by mass.
- Example – H2O
Mass ratio of H : O in water is always 2 : 16 or 1 : 8
Whatever may be the source of water 9 g of H2O when decomposed always give 1 g of hydrogen gas and 8 g of oxygen gas. - The postulate is the relative number and kind of atoms present in a compound is always constant.
OR
- Flourine: Atomic number = 9; Electronic configuration = 2,7 and Valency =1
- Potassium: Atomic number =19; Electronic configuration = 2, 8, 8, 1 and Valency = -1
- Silicon: Atomic number = 14; Electronic configuration = 2, 8, 4 and Valency = 4
Answer 16.
‘Energy possessed by object by virtue of its position or configuration’ – to be explained in candidate’s own words.
Example: Stretched string of bow/ a stone lifted to a certain height (or any other appropriate example).
S.I. unit — joule
Let an static object of mass, m be raised to a height h above the ground.
Then, Force required to raise the object = Weight of the object
= mg
Now, Work done on the object, W = Force × displacement
= mg × h
This work done is the stored potential energy of the object,
∴ P.E. = mgh
As the object falls down, m = 20kg; g=10m/s2; h = 10m
∴ P.E. = mgh = 20 kg × 10 m/s2 × 10 m
P.E. = 2000 J
Its P.E. gets converted to K.E.
Kinetic energy just before it touches = 2000 J
Answer 17.
1.
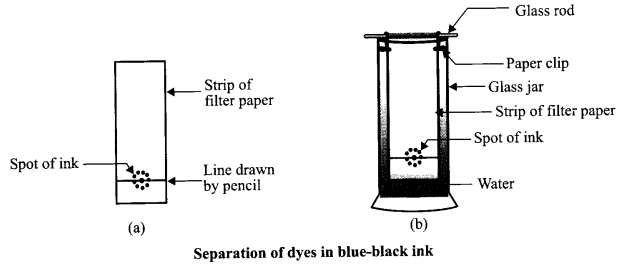
Process: Chromatography
Principle: The coloured component that is more soluble in a solvent rises faster and in this ‘ way, the constituent colours of different dyes present in an ink gets separated.
- Chemical change
- Chemical change
- Physical change
- Chemical change
Answer 18.
1. Similarity: Liquid state is changed into gaseous state in both the processes.
| Evaporation | Bolling |
| It is a surface phenomenon, i.e., water molecules at the surface gain energy to change their state. | It is a bulk phenomenon. All (bulk) the water molecules of water gain energy to change their state. |
| Can take place at all temperatures. | Take place at a fixed temperature. |
2. The transfer of solids directly into gaseous phase without attaining the liquid state is called sublimation.
Camphor, naphthalene, dry ice.
3. In solids, particles are closely packed with less intermolecular spaces but there are very strong forces of attraction.
In liquids the molecules are far from each other with kinetic energy that enables them to keep moving past each other, however they have less forces of attraction and more intermolecular spaces.
Answer 19.
Vertebrata is divided into two superclasses, viz. Pisces and Tetrapoda. Animals belonging to Pisces subclass have streamlined body with fins and tails to assist in swimming. Animals belonging to Tetrapoda subclass have fore limbs for locomotion.
Tetrapoda subclass is further classified into the following classes:
- Amphibia: These are adapted to live in water and on land. They can breathe oxygen through skin, when under water and through lungs, when on land.
- Reptilia: These are crawling animals. Their skin is hard to withstand extreme temperatures.
- Aves: Their forelimbs are modified into wings to assist in flying. Beaks are present. Their body is covered with feathers.
- Mammalia: These have mammary glands present to nurture the young ones. Their skin is covered with hair. Most of the animals are viviparous.
Answer 20.
(a) 3 situations where work can be said to be done are:
- If a pebble lying on a surface is pushed, the pebble moves through a distance. In this situation work is said to be done as the applied force moves the body through some distance.
- If a girl pulls a trolley and the trolley moves through a distance. In this situation work is said to be done.
- When a book is lifted upto a certain height, a force is applied and the book rises up, therefore work is said to be done.
(b) w = 15 km/h; v = 30 km/h; Mass = 1000 kg; W = ?
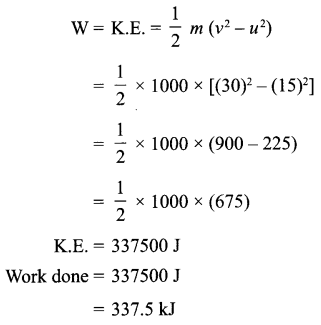
OR
- Archimedes’ principle – When a body is immersed fully or partially in a fluid, it experiences an upward force that is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it.
It is used in designing of ships and submarines. - Fluids are the substances which can flow, e.g. gases and liquids are fluids.
Archimedes’ principle is based on the upward force exerted by the fluid on any object immersed in it. Hence it is applicable only for fluids.
Applications of Archimedes’ principle:- It is used in designing of ship and submarines.
- It is used in designing lactometer which is used to determine the purity of milk.
- To make hydrometer that is used to determine the density of liquid.
Answer 21.
(a) Let two objects ‘A’ and ‘B’ of masses M and m, lie at a distance d from each other as shown in the figure.
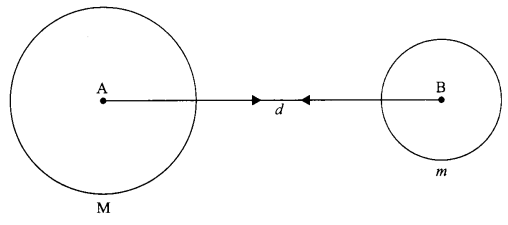
Let the force of attraction between the two objects be F.
According to the universal law of gravitation, the force between two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses.
F α Mm …(i)
Also force between the two objects is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them,
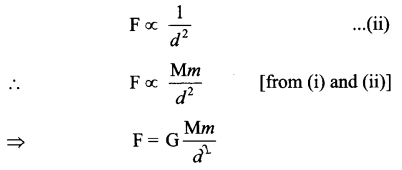
Where G = Universal gravitational constant
(b)
| ‘g’ | ‘G’ |
| (i) It is defined as acceleration due to gravity. | It is defined as universal gravitational constant. |
| (ii) Value of g = 9.8 | Value of G = 6.67 × 10-11 |
| (iii) Unit = m/s2 | Unit = Nm2/kg2 |
| (iv) It changes from place to place. At poles value of ‘g’ is more than at equator. | It remains constant throughout the universe. |
SECTION-B
Answer 22.
- A – Glass rod,
- B – Beaker and
- C – Solution
Answer 23.
- A – Axon,
- B – Dendrite
- C – Cytoplasm/ Cell body/ Cyton.
Answer 24.
- Plant root cells absorb water by osmosis.
- The unicellular organisms like amoeba takes in the required material by osmosis.
Answer 25.
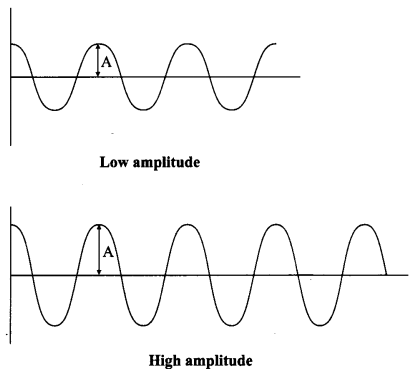
Answer 26.
The air bubble in the liquid taken in the measuring cylinder for an experiment will affect the volume of the solid because air bubble occupies some space in the liquid and this increases the volume of the liquid.
Answer 27.
Suppose the dimensions of a rectangular solid is 1, then
V= 1 × 1 × 1 (l, b and h are taken as 1)
V = 13
If it gets doubled, then Vn = 23
Vn = 8 times × V
Hence volume will increase by 8 times.
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Paper 6 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Paper 6, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
