CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Paper 5 are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Paper 5.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Paper 5
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | IX |
| Subject | Science |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 5 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 9 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme as prescribed by the CBSE is given here. Paper 5 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 9 Science is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time Allowed : 3 Hours
Max. Marks: 80
General Instructions
- The question paper comprises of two Sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections.
- All questions are compulsory. How ever an internal choice will be provided in two questions of 3 marks each and one question of five marks.
- All questions of Section A and all questions of Section B are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 2 in Section A are one-mark questions. These are to be answered in one word or in one sentence.
- Question numbers 3 to 5 in Section A are two-marks questions. These are to be answered in about 30 words each.
- Question numbers 6 to 15 in Section A are three-marks questions. These are to be answered in about 50 words each.
- Question numbers 16 to 21 in Section A are five-marks questions. These are to be answered in about 70 words each.
- Question numbers 22 to 27 in Section B are two-marks questions based on practical skills. These are to be answered in brief
Questions
SECTION-A
Question 1.
Name the plastid which stores starch, oils and protein granules.
Question 2.
A person in the moving train tosses a coin over his head which falls behind him. What is the principle involved in it.
Question 3.
Name the appendages used for movement by organisms belonging to Protista kingdom.
Question 4.
Give one example when work done on an object is negative.
Question 5.
What happens when petrol is kept on our palm?
Question 6.
What is an Echo? State two necessary conditions for echo to be heard. Bats cannot see still they catch their prey. Explain.
Question 7.
- Define evaporation.
- How does increase in surface area affects the rate of evaporation? Support your answer with an example.
Question 8.
- It was diagnosed that Preeti suffers from Japanese encephalitis, which organ of Preeti’s body is effected?
- How are antibiotics effective in the treatment of some diseases?
- Will they help in curing Preeti’s disease? Why or why not?
OR
- Discuss briefly the principle of immunisation.
- Mention any two diseases that can be prevented by immunisation.
Question 9.
Distinguish between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures. Classify the following mixtures as homogeneous and heterogeneous:
- Tincture of iodine
- Smoke
- Brass
- Sugar solution
Question 10.
A stone dropped from a window reaches the ground in 0.5 seconds:
(i) Calculate its speed just before it hits the ground.
(ii) What is its average speed during 0.5 s?
(iii) Calculate the height of window from the ground.
OR
- State Newton’s first law of motion.
- Look at the diagrams given below and answer the following questions:
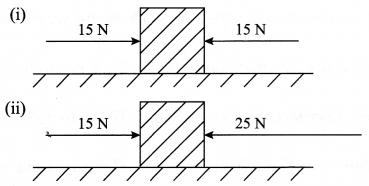
In which case will the object move and in which direction? Give reason in support of your answer. .
Question 11.
- Identify two features possessed by all Chordates.
- In which class would you place an organism which has
- A scaly exoskeleton and a bony endoskeleton.
- A scaly exoskeleton and lay eggs outside water.
Question 12.
Give the functions of the following:
nuclear membrane, mitochondria, ribosomes
Question 13.
You are given an element 3517X
- Find the number of protons, electrons and neutrons in element X.
- What is the valency of X?
- Write down the chemical formulae of the compound formed when it combines with carbon and sodium.
Question 14.
Define osmosis. In which way it is different from diffusion.
Question 15.
A flask contains 4.4 g of CO2 gas. Calculate
(a) How many moles of CO2 gas does it contain?
(b) How many molecules of CO2 gas are present in the sample?
(c) How many atoms of oxygen are present in the given sample?
[Atomic mass of C = 12 u, O = 16 u]
Question 16.
Define ‘Power’.
State and define its S.I. Unit. Two children A and B both weighing 32 kg start climbing up a rope separately and reaches a height of 8 m, ‘A’ takes 15 s and ‘B’ takes 20 s to reach that level. Calculate the amount of work done by A and B. Which of the two has more power? Show by calculation, [g = 10 m/s2]
Question 17.
- Draw a plant cell and label seven important organelles found in it.
- Name one organelle that can make some of the proteins in a plant cell and mention one function of it in the plant cell.
Question 18.
How can you separate the following mixtures:
- Sand + iron
- Cream from milk
- Salt + water
- Ammonium chloride + NaCl
- Copper sulphate and water
- Rice and dal (uncooked)
- Gases from air
- Petrol and diesel form crude oil
- Drugs from blood
- Acetone from water.
Question 19.
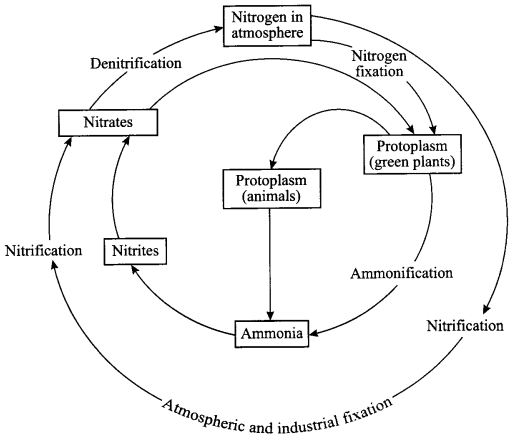
Explain nitrogen cycle in nature and define all the terms involved in it.
Question 20.
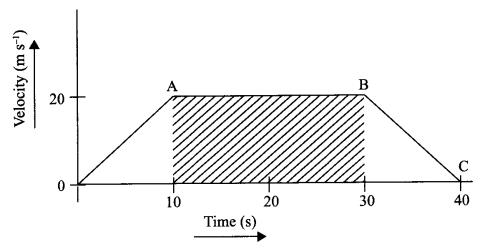
The velocity time graph of a body is given as follows:
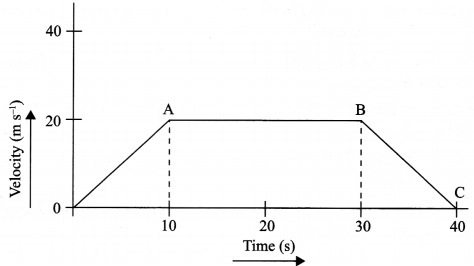
(i) State the kind of motion represented by OA; AB.
(ii) What is the velocity of the body after 10 s and after 40 s?
(iii) Calculate the retardation of the body.
(iv) Calculate the distance covered by the body between 10th and 30th second.
Question 21.
Explain Rutherford’s a-particle scattering experiment and give its observation and conclusion drawn.
OR
(a) Atomic mass exists as a whole number, then why do we write the atomic mass of chlorine as 35.5 u?
(b) Give the differences between isotopes and isobars.
SECTION-B
Question 22.
In the reaction between copper sulphate and sodium sulphide solutions, when 15.9 g copper sulphate completely reacts with 7.8 g of sodium sulphide, it is observed that 9.5 g of copper sulphide is formed. What mass of sodium sulphate solution is formed?
Question 23.
How can you calculate the minimum distance for echo?
Question 24.
Name four different adulterants commonly used in food items.
Question 25.
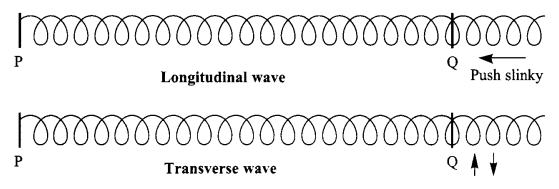
With the help of a diagram show what kind of wave motion can be produced by a slinky?
Question 26.
In a chemical reaction 0.096 g of boron combines with 0.144 g of oxygen to form a compound. Calculate the mass of the compound formed.
Question 27.
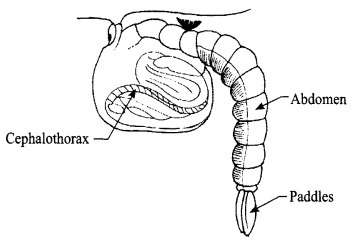
Explain the Pupa stage of mosquito with the help of a diagram. Why is the this stage also called ‘tumblers’?
Answers
SECTION-A
Answer 1.
Leucoplast
Answer 2.
Inertia of motion
Answer 3.
- Paramecium – Cilia
- Euglena – Flagella
- Amoeba – Pseudopodia
- Microtubules – Movement within the cell body
Answer 4.
When a person is walking down the stairs with load on its head, the work done is negative as the force applied on the load is in opposite direction to its displacement.
Answer 5.
Petrol is highly volatile and it starts evaporating on from our palm by gaining energy from our palm and gives a cooling effect.
Answer 6.
Echo: Sound heard after reflection from an obstacle in a confined space.
Conditions:
- Time interval between the original sound and reflected sound must be at least 0.1 s.
- Minimum distance of the obstacle from the source of sound must be 17.2 m at 22°C which is approximately equal to 17 – 18 m at room temperature.
Bats can produce ultrasonic waves. These signals are received by them after reflection from the prey and later interpreted by their brain accordingly.
Answer 7.
- It is the phenomenon of change of a liquid into vapours form at any temperature below its boiling point.
- Increase in surface area of evaporating substance increases the rate of evaporation.
Example, while putting clothes for drying up in Sim, we spread them out.
Answer 8.
- Brain
- They block biochemical pathway. As a result of which the harmful bacteria are unable to make cell-walls and so they die without causing the disease or harming any part of our body.
- No, Japanese encephalitis is a viral disease.
OR
- Our immune system responds against the microbe or any foreign particle when it enters the body for the first time and remembers it specifically.
The next time the same microbe/ foreign particle tries to enter our body, the immune system recognise it and responds vigorously, thus eliminating the infection. - Diphtheria/ pertussis/ mumps/ tetanus/ measles/ polio. (Any two)
Answer 9.
| Homogeneous Mixtures | Heterogeneous Mixtures |
| (i) Uniform composition throughout the mass. | Does not have a uniform composition throughout its mass. |
| (ii) No visible boundaries of separation between the constituents. | Visible boundaries of separation between the constituents. |
- Homogeneous
- Heterogeneous
- Homogeneous
- Homogeneous
Answer 10.

OR
- Every object in this universe continues to be in the state of rest or of uniform motion in a . straight line, unless acted upon by some external unbalanced force to change that state.
- Case I: Object will remain static because of equal and opposite forces acting upon it.
Case II: Object will move towards the left, in the direction of 25 N force. This is because an unbalanced force of 25 – 15 = 10 N is acting in this direction.
Answer 11.
- Presence of notochord/ dorsal nerve chord/ paired gill pouches/ bilaterally symmetrical body/ triploblastic/ coelomate. (any two)
- Class Pisces
- Class Reptilia
Answer 12.
- Nuclear membrane: It is a membrane made up of double layer of lipid molecules and is also called as the envelope protecting the nucleus in the cell.
- Mitochondria: It is called the powerhouse of the cell as it stores energy in the form of ATP. It regulates the overall metabolism of the cell.
- Ribosomes: They help in making of proteins in the cell. Proteins are needed for many cell functions such as repairing, damage or directing the chemical processes inside the cell.
Answer 13.
- Protons = 17, Electrons = 17 and Neutrons = 18
- Valency of X is 1.
- CX4 and NaX
Answer 14.
- Osmosis: Movement of water from region of higher concentration to the region of lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane is called osmosis. It is applicable only for the movement of a solvent/ liquid.
- Diffusion: It is the movement of particles from one medium to another from higher concentration to lower concentration. It is applicable for any medium. Semipermeable membrane is not required.
Answer 15.
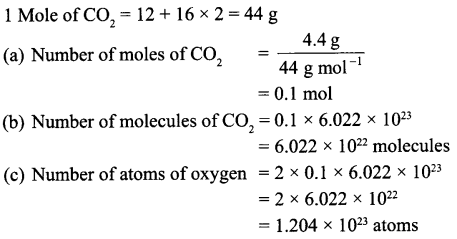
Answer 16.
- Power is rate of doing work/rate of transfer of energy.
- S.I. unit of power is Watt
- 1 watt is the power of an agent which does work at the rate of ljoule per second/ when the rate of consumption of energy is 1 joule per second.
For A:
W = mgh
= 32 kg × 10 m/s2 × 8 m
W = 2560 J
Both have the same mass and climb up the same height.
So, Work done by B = 2560 J
PA = (2560J15s) = 170.7 W
PB = (256020s) = 128 W
∴ ‘A’ has more power than ‘B’.
Answer 17.
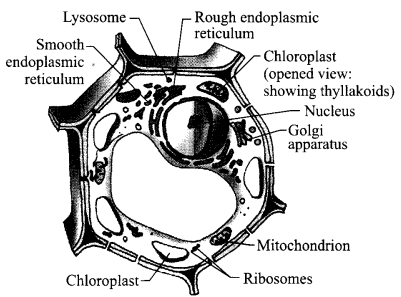
- Seven labels:
- Chloroplast
- Ribosomes
- Mitochondrion
- Golgi apparatus
- Lysosome
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Nucleus
- Mitochondrion: It releases energy- required for various chemical activities needed for life.
Answer 18.
- Magnetic separation
- Centrifugation
- Evaporation
- Sublimation
- Crystallisation
- Hand picking
- Distillation
- Fractional distillation
- Chromatography
- Distillation
Answer 19.
Terms involved in nitrogen-cycle are
- Nitrogen fixation: Plants cannot use free nitrogen present in the air. This nitrogen molecule is converted into nitrates and nitrites which can be taken up and used to make the required molecule. This is called nitrogen fixation, which can be done by the bacteria that live in the root nodules of leguminous plants.
- Nitrification: By physical process i.e. during lightning, the high temperature and pressure created in the air converts nitrogen into oxides of nitrogen which dissolve in water and came down along with the rain. This is called nitrification.
- Ammonification: The nitrogen compounds formed after nitrificaiton are taken by the plants to form proteins which are further converted into ammonia.
- Denitrification: The nitrates and nitrites of nitrogen are acted upon by some group of microbes, e.g. Pseudomonas bacteria, which converts these compounds into free nitrogen gas.
Nitrogen cycle:
- Free nitrogen from atmosphere is converted into nitrates by bacteria or by lightning.
- Nitrates mixes with soil and is absorbed by the plants to make proteins.
- The proteins in plants and animals are converted into amino acids and ammonia.
- Ammonia is converted into nitrates and then these nitrates and nitrites present in soil is acted upon by a group of bacteria called denitrifying bacteria. This process is called denitrification. Nitrates are converted into free nitrogen and is released back to the atmosphere.
Answer 20.
(i) OA – uniform acceleration, AB – zero acceleration/constant velocity.
(ii) 20 ms-1 ; zero/body comes to rest.
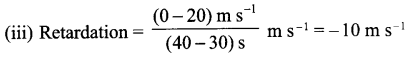
(iv) Distance between 10th and 30th second = area of the figure shaded
= (30 – 10)s × 20 ms-1
= 20 s × 20 m s-1
= 400 m
Answer 21.
Rutherford’s α-particle scattering experiment:
Fast moving α-particles having +2 charge, 4 u mass and considerable amount of energy were made to fall on a thin gold foil.
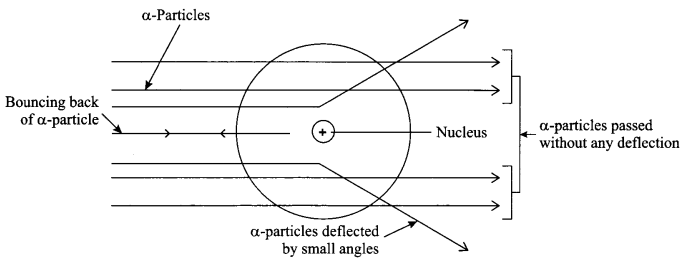
Observations:
- Most of the a-particles passed straight through the foil without any deflection.
- Some of the a-particles were deflected by small angles when passed through the foil.
- One out of every 20,000 particles were rebounded.
Conclusion from the observations:
- Most of the space inside an atom foil is empty.
- Positive charge of the atom occupies very less space and lies within the centre of the atom.
- Mass of the atom is concentrated in the centre with all positive charge concentrated in a small volume called nucleus of the atom.
OR
(a) Chlorine has two isotopes and the mass of an atom is taken as the average-mass of all the naturally occurring isotopes of that element.
This is obtained by knowing the percentage of each isotopic form and then the average mass is calculated, e.g. Cl = 35 × 75% and Cl = 37 × 25%
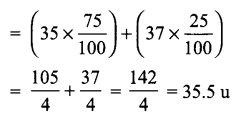
(b)
| Isotopes | Isobars |
| Atoms of the same element. | Atoms of different elements. |
| Have same atomic number. | Have different atomic number. |
| Have different mass number. | Have same mass number. |
| Number of protons and electrons are same in these atoms. | Number of protons and electrons are not same in these atoms. |
SECTION-B
Answer 22.
Mass of (copper sulphate + sodium sulphide) = Mass of (copper sulphide + sodium sulphate)
(15.9 + 7.8) g = (9.5 + x)g
x = 23.7g
Answer 23.
Speed of sound = DistanceTime
344 m/s = Distance0.1s
∴ Distance = 34.4 m
This is the total distance, hence half of 34.4 m = 17.2 m is the required minimum distance for echo.
Answer 24.
The commonly used adulterants in food are
- Black pepper – dry seeds of papaya
- Honey – jaggery
- Red chili powder – red brick powder
- Mustard seed – argemone seeds
Answer 25.
A slinky can produce both longitudinal and transverse wave motion.
Answer 26.
Boron + Oxygen → Compound of Boron and Oxygen
0.096 g + 0.144 g → 0.240 g
This can be accounted on the basis of law of conservation of mass.
Answer 27.
The pupa of a mosquito is formed from its larva, it floats in water. It takes up the oxygen through its two breathing tubes called ‘trumpets’. When the water is disturbed the pupa tumbles down and floats back on surface of water, so it is also called “Tumblers”. This is a hibernating stage, where pupa does not eat and only rest/sleep. This stage lasts for 1-4 days.
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Paper 5 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Paper 5, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
