CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Paper 4 are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Paper 4.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Paper 4
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | IX |
| Subject | Science |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 4 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 9 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme as prescribed by the CBSE is given here. Paper 4 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 9 Science is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time Allowed : 3 Hours
Max. Marks: 80
General Instructions
- The question paper comprises of two Sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections.
- All questions are compulsory. How ever an internal choice will be provided in two questions of 3 marks each and one question of five marks.
- All questions of Section A and all questions of Section B are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 2 in Section A are one-mark questions. These are to be answered in one word or in one sentence.
- Question numbers 3 to 5 in Section A are two-marks questions. These are to be answered in about 30 words each.
- Question numbers 6 to 15 in Section A are three-marks questions. These are to be answered in about 50 words each.
- Question numbers 16 to 21 in Section A are five-marks questions. These are to be answered in about 70 words each.
- Question numbers 22 to 27 in Section B are two-marks questions based on practical skills. These are to be answered in brief
Questions
SECTION-A
Question 1.
Define the commercial unit of electrical energy.
Question 2.
Name the plastid involved in the conversion of a green tomato into a red.
Question 3.
Give the difference in mass and weight. Find the mass and weight of a boy on Moon if his weight on Earth is 520 kg.
Question 4.
What are antibiotics. Name one antibiotic.
Question 5.
Which object will exert more force, a body with mass 5 kg and acceleration 6 m/s2, or a body with mass 6 kg and acceleration 5 m/s2?
Question 6.
What information do you get from the figure given below about the atomic number, mass number and valency of atoms X, Y, and Z?
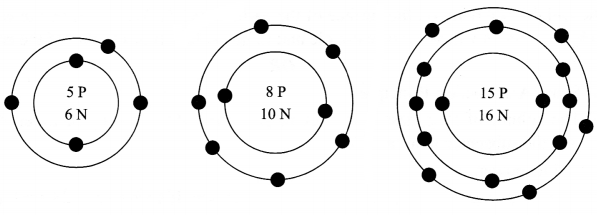
Give your answer in tabular form.
Question 7.
Differentiate between monocots and dicots. Give two differences and one example of each?
Question 8.
- On which characteristics of sound wave do the following properties depend?
- Loudness
- Pitch
- Calculate the time for which the sensation of sound persists in our brain if the minimum distance of the obstacle from the source of sound is 17.2 m (speed of sound in air = 344 m/s)
Question 9.
- Calculte the number of molecules present in 4.4 g of CO2
[At Mass: C = 12 u, O = 16 u, NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol-1] - What are polyatomic ions? Give one example.
OR
- What mass of sodium sulphate will react with 5.22 g of barium chloride to produce 6.10 g of sodium chloride and 2.80 g of barium sulphate?
- On the basis of which law did you calculate your answer?
Question 10.
- What are the necessary conditions for work to be done?
- An electric bulb of 60 W is lighted for 10 hours a day. What is the amount to be paid in a month of 30 days, if one unit of electricity of costs ₹ 3.50?
Question 11.
How are the following related to each other?
- Chromatin network and chromosomes
- Chloroplast and chlorophyll
- Genes and DNA
Question 12.
- What is motion?
- State types of motion.
- Derive the unit for acceleration.
Question 13.
Surbhi along with her younger sister Vibha loved going to the field with parents. She helped taking out certain plants from the field using khurpi. She told Vibha that only selected plants need to be uprooted. Vibha asked her why only specific plants need to be pulled out Surbhi explained that these were weeds which are not desired along with the crop.
- Why is it essential to remove weeds?
- Name two common weeds?
- What values are exhibited by Surbhi here?
Question 14.
The weight of a body on the surface of the earth is 392 N. What will be the weight of this body on a planet whose mass is double and radius is four times to that of the earth?
OR
(i) State ‘Archimedes’ Principle’.
(ii) The volume of 50 g mass of a substane is 20 cm3. If the density of water is 1 gm cm-3, will the substance float or sink?
Question 15.
- Define power.
- A body of mass 45 kg climbs up 20 steps in 20 sec. If each step is 25 cm high, calculate the power used in climbing. Take g= 10 m/s2.
Question 16.
Write your observations when the following processes take place:
- An aqueous solution of sugar is heated to dryness.
- A saturated solution of potassium chloride prepared at 60° C is allowed to cool at room temperature.
- a mixture of iron filings and sulphur powder is heated strongly.
- A beam of light is passed through a colloidal solution.
- Dil. HCl is added to the mixture of iron and sulphur.
Question 17.
Explain the necessity of the crop variety improvement in food production, giving five reasons.
Question 18.
Give five points of differences between prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell.
Question 19.
- Prove that if Earth attracts two bodies placed at the same distance from the centre of Earth with equal force; then their masses will be the same.
- Mathematically express the acceleration due to gravity that is expressed by a free falling object.
- Why is ‘G’ called a universal constant?
Question 20.
The following graph describes the motion of a girl going to meet her friend who stays 50 m away from her house.
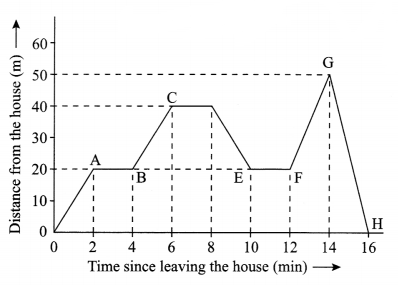
- How much time did she take to reach her friend’s house?
- What is the distance travelled by the girl during the time interval-0 to 12 min?
- During which time interval is she moving towards her house?
- For how many minutes she was at rest, during the entire journey?
- Calculate the speed by which she returned home.
Question 21.
(a) Explain the following:
- An object increases its energy when raised through a height.
- Energy is neither created nor destroyed then from where do we get energy.
- When we push the wall, the wall does not move and no work is done.
(b) State and explain one example where
- Kinetic energy is present in a body and is used; and
- Potential energy is present in a body and is used.
OR
(a) Explain law of conservation of energy.
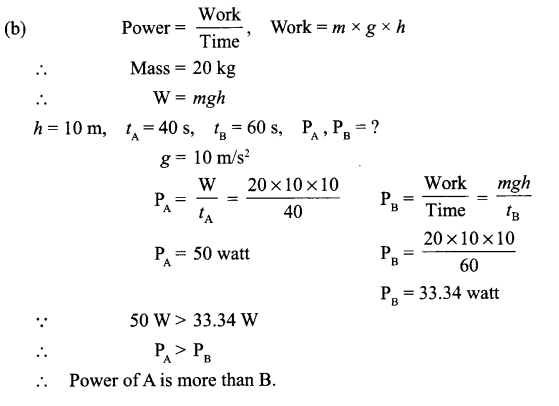
(b) Two boys A and B were given a task to carry 20 kg load from ground level to height 10 m. A completed the work in 40 s and B in 60 s. Calculate the power in both the cases. Who has greater power?
SECTION-B
Question 22.
Give two examples where multiple reflection is used.
Question 23.
A measuring cylinder has 5 marks between 10 mL to 20 mL. What is its least count?
Question 24.
Give two examples of semi-permeable membrane.
Question 25.
What is your observation when you bum magnesium ribbon in air? What would happen if you place zinc metal in copper sulphate solution?
Question 26.
Why do we use stain for mounting the slide? Give the use of glycerine in slide preparation.
Question 27.
Why does plastic bottle float on water? What is the downward force acting on the bottle immersed in water?
Answers
SECTION-A
Answer 1.
Kilowatt hour is the commercial unit of electrical energy.
When 1000 watt power is used for one hour it is 1 kW h.
(1000 watt) × (3600 seconds) i.e., 3600000 joules = 3.6 × 106 J
3.6 × 106 J is defined as 1 kW h
Answer 2.
Chromoplastid
Answer 3.
Mass: It is the matter present in a body. It remains constant and its S.I. unit is kg.
Weight: The force of gravity acting on an object with a certain mass is called weight. It keeps changing with place to place and its S.I. unit is Newton.
The mass of a body will remain the same, i.e. 520 kg , its weight on moon will be:

Answer 4.
Antibiotics are the drugs that blocks the biochemical pathways important for bacterial growth. 1 These are used to cure diseases caused by bacteria, e.g. Pencillin.
Answer 5.
f=m × a; 5 × 6 = 30 N
f= m × a; 6 × 5 = 30 N
Both the objects will exert the same force.
Answer 6.
| Atoms | Atomic No. | Mass No. | Valency |
| X | 5 | 11 | 3 |
| Y | 8 | 18 | 2 |
| Z | 15 | 31 | 3,5 |
Answer 7.
- Monocots: One cotyledon/ parallel venation/ fibrous roots, e.g. wheat, maize, rice.
- Dicots: Two cotyledons/ reticulate venation/ tap root, e.g. green gram, pea.
Answer 8.
- Loudness depends on the amplitude of sound wave.
- Pitch depends on the frequency of sound wave.
- 2 d = v × t
2 × 17.2 = 344 × 7
t = 34.4344 = 0.1 s
Answer 9.
- 1 mole of CO2 = 6.023 × 1023 molecules
44 g = 6.023 × 1023 molecules
Hence, 4.4 g = 6.023 × 1022 molecules - The ions which contains more than one atomic species in it are called polyatomic ions.
Example: SO2-4, Sulphate ion is a polyatomic ion.
OR
- Mass of sodium sulphate = xg
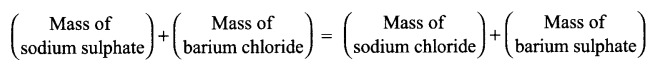
x g + 5.22 g = 6.10 g + 2.80 g
xg= 8.90 – 5.22
= 3.68 g - For calculation Law of conservation of mass is used.
Answer 10.
- Two conditions that are need to be satisfied for work to be done:
- Force should act on the object, and
- The object must be displaced.
- P = 60 W, t= 10 hours
E = P × t
= 60 × 10 = 600kWh
= 6.0 kWh
Bill to be paid =0.6 × 3.5 × 30 = ₹ 63
Answer 11.
- On cell division, chromatin network organise themselves into chromosomes.
- Chloroplast is a plastid which contains the green pigment called chlorophyll, which is required for the photosynthesis process.
- The segments of DNA are called genes.
Answer 12.
- Motion: An object is said to be in motion when its position changes with time. We describe the location of an object by specifying a reference point. Motion is a relative quantity.
The total path covered by an object is said to be the distance travelled by it. - There are two types of motion: Uniform motion and non-uniform motion.
Uniform motion: When an object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time, it is said to be in uniform motion.
Non-uniform motion: Motion where an object covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time. - Acceleration, ‘a’ is change in velocity per unit time.
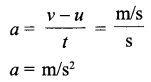
Answer 13.
- Weeds take up nutrients and reduce the growth of crop.
- Xanthium, Parthenium, Common ragweed (Any two)
- Values associated: Family bonding, sharing knowledge/work.
Answer 14.
Let mass of the earth be ‘M’ and its radius be ‘R’
Then the acceleartion due to gravity (g) = GMR2 = 9.8 m/s2, where G is the Gravitational Constant
Now, Mass of the planet = 2 M
Radius of the planet = 4 R

OR
(i) Archimedes principle states that when a body is immersed fully or partially in a fluid (liquid) it experiences an upward force that is equal to the weight of the fluid (liquid) displaced.
(ii) In the present problem, density of water
pw = 1 gm cm-3
Mass of substance = 50 gm
Volume of substance = 20 cm3

Answer 15.
- Power: ability to do the work by a body in given time. Its S.I. unit is Watt.
- Height of each step = 25 cm
No. of steps = 20
Total height = 25 × 20 = 500 cm = 5 m
Work done = m × g × h = 45 × 10 × 5 = 2250 J
Power = WorkdoneTime = (225020) = 112.5 Watt
Answer 16.
- Sugar remains as residue in the form of a solid mass.
- Potassium chloride crystallises out.
- A black coloured compound, FeS (iron sulphide) is formed.
- The path of the light becomes visible.
- A colourless gas is evolved.
Answer 17.
Five main reasons to explain the necessity of crop variety improvement are:
- Higher yield
- Improved quality
- Biotic and abiotic resistance
- Change in maturity duration
- Desirable agronomic traits (or any five traits relevant to it)
Answer 18.
| Characters | Prokaryotic Cell | Eukaryotic Cell |
| (i) Size | 1-10 pm diameter | Diameter 5-100 pm |
| (ii) Nucleus | No true nucleus, single chromosome, nuclear membrane is absent. | True nucleus, nuclear membrane is present, more than one chromosome is present. |
| (iii) Organelles | Membrane-bound organelles are absent. | Membrane-bound organelles are present. |
| (iv) Ribosomes | Ribosomes are 70 S type and are randomly scattered. | Ribosomes are 80 S type and they can be free or attached to ER. |
| (v) Cell division | Cell divides by simple fission. | Cell divides by mitosis or by meosis. |
Answer 19.
- (a) Let mass of first body be m1
Let mass of second body be m2
Force on 1st body = Force on 2nd body
GMm1R2 = GMm2R2
G and G cancel, M and M cancel R2 and R2 cancel
This leaves
m1 = m2
Hence proved. - g = GMR2
- Its value is constant throughout the universe.
Answer 20.
- 14 min
- 60 m
- 8 to 10 min or 14 or 16 min
- 6 min
- 25 m/min
Answer 21.
(a)
- An object has some mass ‘M’, when it is raised through a certain height, energy is applied on it, this energy gets transformed and is gained by the stone. Hence its energy increases.
- Energy is present in every object in some or the other form, it exist in Sun, planet, wind, water etc. Energy gets transformed and because of its transformation we get it into different form.
For example, Sun ‘s energy Converted→byplants Food Oneating→ Energy to our body. - Work is said to be done, when force is applied on the body and it moves to a certain distance. When a wall is pushed there is no displacement and we say that work done is zero.
(b) Kinetic energy is the energy present in a body by virtue of its motion. When water is stored in a dam at particular height, we say it has maximum potential energy as the water is present at a height.
When this water is allowed to fall down from a certain height, it is said to have kinetic energy. When water falls on the turbine, the paddle wheels rotates to rotate the turbine. Hence kinetic energy of water is used to push or rotate the turbine which is further used to produce the electricity.
OR
(a) Law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but it can be transferred from one form to another. The total energy before and after transformation remains the same.
Let the body be at position A from the ground level. It has the potential energy, PE. When the body falls down and reaches in the middle, P.E. = K.E. and when the body is just about to touch the ground its K.E. > P.E. This shows that P.E. is getting transferred into kinetic energy.
SECTION-B
Answer 22.
In megaphones, curved ceilings or walls of the concert hall are some examples where multiple reflection of sound is used.
Answer 23.
20 mL – 10 mL = 10 mL
∴ 5 × 2 = 10
Each mark is of 2 mL value.
Answer 24.
Tissue, layer of cells, cell wall, plasma membrane. (Any two)
Answer 25.
- It catches fire, bums with dazzling white flame and forms white powdery mass of magnesium oxide.
- Zinc metal reacts with copper sulphate solution to form zinc sulphate, colourless zinc sulphate solution and copper metal is deposited.
Answer 26.
- The stain makes cell wall, nucleus, cell membrane visible as they take up the stain.
- Glycerine prevents the drying of specimen. The material remains wet and do not dry.
Answer 27.
- When upward force acting on the bottle is more than the downward force acting on the bottle, then it will float.
- The downward force is the gravitational pull of the earth.
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Paper 4 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Paper 4, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
