CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Paper 2 are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Paper 2.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Paper 2
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | IX |
| Subject | Science |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 2 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 9 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme as prescribed by the CBSE is given here. Paper 2 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 9 Science is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time Allowed : 3 Hours
Max. Marks: 80
General Instructions
- The question paper comprises of two Sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections.
- All questions are compulsory. How ever an internal choice will be provided in two questions of 3 marks each and one question of five marks.
- All questions of Section A and all questions of Section B are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 2 in Section A are one-mark questions. These are to be answered in one word or in one sentence.
- Question numbers 3 to 5 in Section A are two-marks questions. These are to be answered in about 30 words each.
- Question numbers 6 to 15 in Section A are three-marks questions. These are to be answered in about 50 words each.
- Question numbers 16 to 21 in Section A are five-marks questions. These are to be answered in about 70 words each.
- Question numbers 22 to 27 in Section B are two-marks questions based on practical skills. These are to be answered in brief
Questions
SECTION-A
Question 1.
What is plasma membrane made up of?
Question 2.
What is the charge and mass of a neutron?
Question 3.
- Illustrate with an example that physical and chemical changes can takes place simultaneously.
- Which of the following are chemical changes:
- Mixing of iron filling and sand
- Growth of plant
- Rusting of iron
- Freezing of water
Question 4.
What are the positions on the earth where the value ‘g’ is (i) maximum, (ii) minimum? Justify your answer.
Question 5.
What is endoplasmic reticulum? Name the two types of endoplasmic reticulum. Write its main functions.
Question 6.
- Differentiate between epidermal and cork cells.
- Why are they called protective tissues?
Question 7.
- Name the compound formed on heating a mixture of iron filing and sulphur.
- If dilute HCl is added to the above compound, then name the gas evolved and write down its two properties.
OR
How can we separate a mixture of two immiscible liquids? Describe the process.
Question 8.
List three characteristics of particulate nature of matter.
Question 9.
How are diseases spread through water?
Question 10.
Define velocity and acceleration. Is it possible for a body to have a zero velocity but constant acceleration. Justify your answer.
OR
State three characteristics of action-reaction forces.
Question 11.
List any three human activities which would lead to the increase in carbon dioxide content the air.
Question 12.
- State the law of Constant Proportion.
- In the formation of a compound, carbon and oxygen react in the ratio 3 : 8 by mass to form carbon dioxide. What mass of oxygen is required to react completely with 9 g of carbon?
Question 13.
List any three ways of preventing the spread of airborne diseases.
Question 14.
Plot velocity-time graph for a body whose initial velocity is 5 m/s and is moving with a constant retardation of 1 m/s2. Also calculate the distance covered by it.
Question 15.
Write the given statement after filling the blanks?
- Pila and Unio have an external shell and belong to the phylum _____ .
- Free living marine animals with water driven tube system are in the phylum _____ .
- Sponges belong to the phylum _____ .
Question 16.
Which separation techniques you will apply for the separation of the following mixtures?
- Oil from water
- Camphor from sand
- Sodium chloride from its solution in water
- Metal pieces from engine oil of a car
- Cream from milk
Question 17.
Complete the following flow chart:
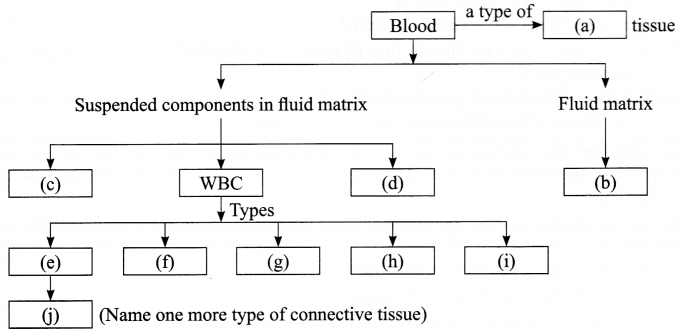
Question 18.
An element “X” has 13 protons, 13 electrons and 14 neutrons.
Answer the following questions:
- What is the atomic number of ‘X’?
- Identify the element.
- What is its valency? What is the number of valence electron in ‘X’?
- What is the type of ion formed by ‘X’? Why?
- Name the scientist who discovered electrons and protons.
Question 19.
The following graph describes the motion a girl going to meet her friend who stays 50 m away from her house.
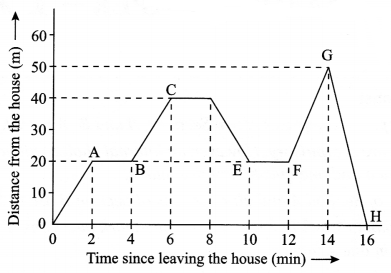
- How much time will she take to reach her friend’s house?
- What is the distance travelled by the girl during the time interval 0 to 12 min?
- During which time interval she is moving towards her house?
- For how many minutes she was at rest, during the entire journey?
- Calculate the speed by which she returned home.
Question 20.
(a) What are the greenhouse gases?
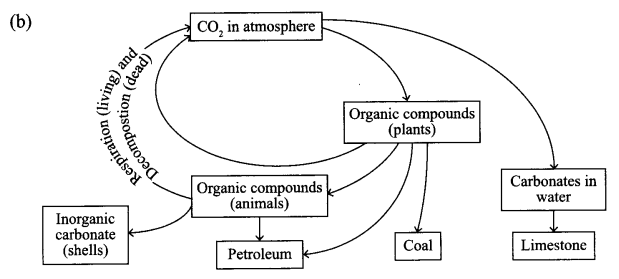
(b) Give a diagrammatic representation of carbon cycle in nature.
Question 21.
(a) Derive an expression for the potential energy of a body.
(b) When do you say that work is done?
(c) A porter lifts a luggage of 15 kg from the ground and puts on his head 1.5 m above the ground. Calculate the work done by him in lifting the luggage.
OR
(a) Derive an expression for kinetic energy of a moving body.
(b) Name the type of energy possessed by
(i) Flowing water
(ii) Stretched rubbed band
(c) A car weighing 2000 kg is accelerated from rest and covers a distance of 40 m in 6 seconds. Calculate the work done by the car.
SECTION-B
Question 22.
In an experiment 14 g of sodium hydrogen carbonate was allowed to react with 10g of acetic acid. After the reaction was completed it was found that only 16.67 g solution was left. What conclusion can you draw from this observation.
Question 23.
Write the difference between male and female cones of Pinus?
Question 24.
Why does the temperature remain unchanged until the entire solid changes into liquid even if we are heating the solid at the melting point?
Question 25.
Two bottles of equal volume are filled with glycerine and water respectively. Which of the bottles will be heavier? Give reason for your answer.
Question 26.
What happens when dilute sulphuric acid is added to a compound of iron and sulphur?
Question 27.
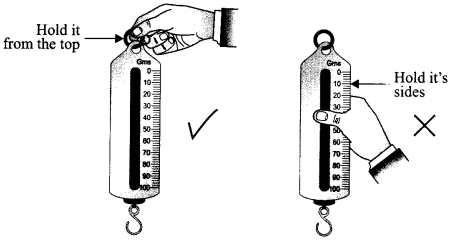
What precautions will you take while holding the spring balance to find the weight of a body?
Answers
SECTION-A
Answer 1.
Proteins and Lipids
Answer 2.
Neutron does not have any charge, i.e. charge is zero.
Its mass is 1.675 × 10-27 kg.
Answer 3.
- One example in which both physical and chemical changes take place simultaneously is burning of candle. Burning of wick of the candle forming CO2 and emitting light and heat energy is a chemical change. Simultaneously melting of wax also takes place which, is a physical change.
- Chemical changes: Growth of plant, rusting of iron.
Answer 4.
- On earth value of g is maximum at poles and minimum at the equator.
- At poles radius of earth is slightly less, so value of g is more while at equator the radius of earth is slightly more, so the value of g is less, g = 1R
Question 5.
- Endoplasmic reticulum is a membranous network enclosing a fluid-filled lumen.
- The two types of endoplamic reticulum are Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) and Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER).
- RER has ribosomes attached to its surface. These ribosomes take part in protein synthesis.
- SER does not have any ribosomes on it and secretes lipids. Some proteins and lipids synthesised in ER are used for producing new cellular parts, specially the cell membrane by biogenesis.
Answer 6.
1.
| Epidermal Cells | Cork Cells |
| Single layered | Multi layered |
| Living | Non-living |
| Secrete cutin | Secrete suberin |
| Present in younger plants. | Present in older plants. |
2. They are called protective tissues because
- They protect the plants from mechanical injury and infection.
- They prevent loss of water.
Answer 7.
- Iron sulphide
- Hydrogen sulphide gas
Properties –- It is colourless.
- It has the smell of rotten eggs.
OR
Distillation is the process employed to obtain pure liquid from its solution. It can be defined as the conversion of impure liquid into vapours by evaporation and then condensation of the vapours to get back the liquid in pure form.
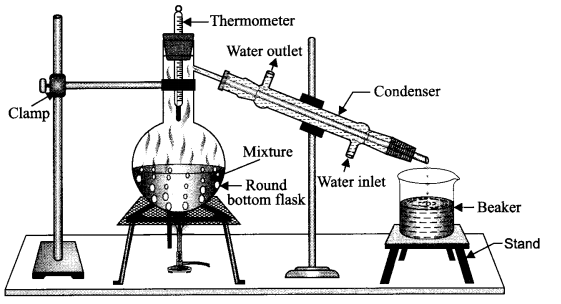
This method is a generally used for the separation of components of a mixture containing two immiscible liquids that boil without decomposition and their boiling points are quite different (more than 25 – 30°C).
Answer 8.
- Particles of matter have spaces between them.
- Particles of matter are continuously moving.
- Particles of matter attract each other.
Answer 9.
- Diseases spread through water when the excreta from someone suffering from an infectious disease such as cholera, gets mixed with drinking water used by people living nearby.
- The Cholera causing microbes will enter the new hosts through water they drink and cause diseases in them. Such diseases are more likely to spread in the absence of safe supply of drinking water.
Answer 10.
Velocity: Rate of change of displacement.
Acceleration: Rate of change of velocity.
Yes, when the body is just released during free fall, u = 0 but g = 10 m/s2
OR
- Equal in magnitude.
- Opposite in direction.
- Act simultaneously on two different bodies.
Answer 11.
- Burning of fossil fuels such as petrol, diesel uses transportation and industrial purposes.
- Burning of wood and charcoal for heating and cooking.
- Cutting of trees /deforestation.
Answer 12.
- In a chemical substance the elements are always present in definite proportion by mass,
- For 3 g of carbon, 8 g of oxygen is needed.
For 1 g of carbon, 83 g of oxygen is needed.
For 9 g of Carbon, 83 g × 9 g = 24 g of oxygen is needed.
Answer 13.
- Avoiding direct contact with the infected person.
- Not sharing articles used by infected person.
- Use of mask/ gloves/ handkerchief.
Answer 14.
Given, u = 5 m/s and a = -1 m/s2
Using, v = u + at
For, v = 0 m/s
0 = 5 – 1 × t or t = 5 s
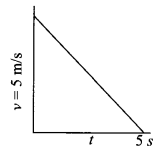
Distance, s = Area under the graph
=12 × 5 × 5 = 12.5 m2
Answer 15.
- Mollusca
- Echinodermata
- Porifera
Answer 16.
- Separating funnel
- Sublimation
- Evaporation
- Filtration
- Centrifugation
Answer 17.
(a) Connective
(b) Plasma
(c) RBC
(d) Platelets
(e) Neutrophils
(f) Eosinophils
(g) Basophils
(h) Lymphocytes
(i) Monocytes
(j) Bone or ligament or tendon
Answer 18.
- 13
- Al
- Valency is 3, the number of valence electrons = 3
- Ion formed by X = Cation as it need to lose 3 electrons to acquire an octate electronic configuration.
- Discoverer of proton is Goldstein and that of electron was JJ Thomson.
Answer 19.
- 14 minutes
- 60 m
- 8 to 10 minutes and 14 to 16 minutes
- 6 minutes
- 25 m/min
Answer 20.
(a) Greenhouse gases: The gases whose increasing percentage in the atmosphere would cause the increase ¡n the average temperature of the earth. A few examples of greenhouse gases are CO2, CH4, and NO2, etc.
Answer 21.
(a) Let there be an object of mass, m kept at (or raised through) a height, h above the ground. Now, the minimum force acting on the object at a height, h above the ground is equal to the weight, w of the object.
∵ W = mg …(i)
Now, work done on the object to raise it (or keep it) at a height, h above the ground is equal to the potential energy (P.E.) of the object.
∵ Work done = Force × Displacement
= mg × h [Using Equation (i)]
= mgh
∵ P.E. (or Ep) = mgh
(b) Work is said to be done if force is applied on an object and it shows some displacement.
(c) Mass of object, m = 15 kg, Displacement, s = 1.5 m
Work done F × s = mg × s
1.5 × 10 × 1.5 =225 J
OR
(a) Let there be an object of mass, m at rest, i.e. initial velocity, u = 0
From Newton’s Ilnd Law of Motion, we have
v2 – u2 = 2as
Where, v = Final velocity;
u = Initial velocity;
s = Displacement of an object
a = Acceleration
Let the object at rest be moved by displacement, s.
Let ‘v’ be the final velocity on moving the object, and ‘a’ be the acceleration produced. Now, from Newton’s IIIrd Law of Motion, we know that force acting on the object,
W = F.s
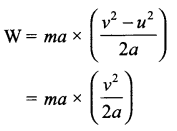
∴ W = mv22 or 12 mv2
Here, work done is equal to the change in the kinetic energy of the object.
Kinetic Energy, K.E. = 12 mv2
(b) (i) Kinetic energy
(ii) Elastic potential energy
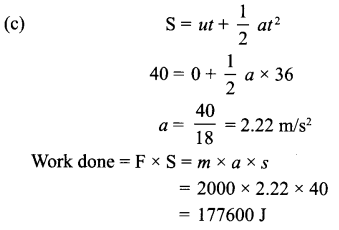
SECTION-B
Answer 22.
A gaseous product has escaped into the atmosphere. The gas that escapes is CO2.
Answer 23.
- Female cones are large and woody.
- Male cones are smaller and tender.
Answer 24.
The temperature remains unchanged until the entire solid changes into liquid even if we are heating the solid; it is because the heat is used up by the molecules in overcoming the forces of attraction while state of matter is changing from solid to liquid.
Answer 25.
- The bottle with glycerine would be heavier because its mass is greater than water. The density of the substance is directly proportional to the mass of the body.
- The density of glycerine is 1.26 g/cc and that of water is 1 g/cc.
Answer 26.
- Iron sulphide is the product formed on mixing iron and sulphur.
- It reacts with dilute sulphuric acid to form hydrogen sulphide gas. It is a colourless gas with the smell of rotten eggs.
Answer 27.
The spring balance should be held only at the hook from the top end. Never hold the spring balance from its sides.
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Paper 2 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Paper 2, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
