CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physics Paper 1 are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physics. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physics Paper 1.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physics Paper 1
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | XII |
| Subject | Physics |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 1 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
- All questions are compulsory. There are 26 questions in all.
- This question paper has five sections: Section A, Section B, Section C, Section D and Section E.
- Section A contains five questions of 1 mark each. Section B contains five questions of 2 marks each. Section C contains twelve questions of 3 marks each. Section D contains one value based question of 4 marks and Section E contains three questions of 5 marks each.
- There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in 1 question of 2 marks, 1 question of 3 marks and all the 3 questions of 5 marks weightage. You have to attempt only 1 of the choices in such questions.
- You may use the following values of physical constants wherever necessary :
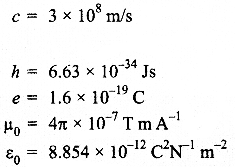

Questions
SECTION : A
Question 1.
How does the electric flux due to a point charge enclosed by a spherical Gaussian surface get affected when its radius is increased?
Question 2.
![]()
A point charge +Q is placed at point O as show in the figure. Is the potential difference VA – VB positive, negative or zero?
Question 3.
Why are microwaves considered suitable for radar systems, used in aircraft navigation?
Question 4.
Define ‘quality factor‘of resonance in series LCR circuit. What is its SI unit?
Question 5.
Write the underlying principle of a moving coil galvanometer.
SECTION : B
Question 6.
Plot a graph showing variation of de-Broglie wavelength X versus 1/\(\sqrt { V } \),, where V is accelerating potential for two particles A and B carrying same charge but of masses m1m2. Which one of the two represents a particle of smaller mass and why?
Question 7.
A nucleus with mass number A = 240 and BE/A =7.6 MeV breaks into two fragments each of A = 120 with BE/A =8.5 MeV. Calculate the released energy.
OR
Calculate the energy in fusion reaction :
![]()
Question 8.
Explain the terms
(i) Attenuation and
(ii) Demodulation used in Communication System.
Question 9.
State Brewster’s law. The value of Brewster angle for a transparent medium is different for light of different colour. Give reason.
Question 10.
Write three characteristic features in photoelectric effect which cannot be explained on the basis of wave theory of light, but can be explained only using Einstein’s equation.
SECTION : C
Question 11.
(a) Write the expression for the magnetic force acting on a charged particle moving with velocity v in the presence of magnetic field B.
(b) A neutron, an electron and an alpha particle moving with equal velocities, enter a uniform magnetic field going into the plane of the paper as shown. Trace their paths in the field and justify your statement.
Question 12.
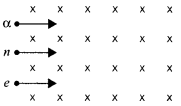
Two parallel plate capacitors X and Y have the same area of plates and same separation between them. X has air between the plates while Y contains a dielectric medium of εr = 4.
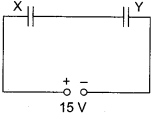
(i) Calculate capacitance of each capacitor if equivalent capacitance of the combination is 4 pF.
(ii) Calculate the potential difference between the plates of X and Y.
(iii) Estimate the ratio of electrostatic energy stored in X and Y.
Question 13
(i) Define mutual
(ii) A pair of adjacent coils has a mutual inductance of 1. 5 H. If the current in one coil changes from 0 to 20 A in 0.5 s, what is the change of flux linkage with the other coil?
Question 14.
(a) Explain any two factors which justify the need of modulating a low frequency signal.
(b) Write two advantages of frequency modulation over amplitude modulation.
Question 15.
Two long straight parallel conductors carry steady current I, and I2 separated by a distance d. If the currents are flowing in the same direction, show how the magnetic field set up in one produces an attractive force on the other. Obtain the expression for this force. Hence define one ampere.
Question 16.
Draw a schematic ray diagram of reflecting telescope showing how rays coming from a distant object are received at the eyepiece. Write its two important advantages over a refracting telescope.
Question 17.
How are e.m. weaves produced by oscillating charges? Draw a sketch of linearly polarized e.m. waves propagating in the Z-direction. Indicate the directions of the oscillating electric ‘ and magnetic fields.
OR
Write Maxwell’s generalization of Ampere’s Circuital Law. Show that in the process of charging a capacitor, the current produced within the plates of the capacitor is
![]()
is the electric flux produced during charging of the capacitor plates.
Question 18.
A charge is distributed uniformly over a ring of radius V. Obtain an expression for the electric intensity E at a point on the axis of the ring. Hence show that for points at large distances from the ring, it behaves like a point charge.
Question 19.
(i) Write the functions of three segments of a transistor.
(ii) Draw the circuit diagram for studying the input and output characteristics of n-p-n transistor in common emitter configuration. Using the circuit, explain how input, output characteristics are obtained.
Question 20.
(a) Calculate the distance of an object of height h from a concave mirror of radius of curvature 20 cm, so as to obtain a real image of magnification 2. Find the location of image also,
(b) Using mirror formula, explain why does a convex mirror always produce a virtual image.
Question 21.
(i) State Bohr’s quantization condition for defining stationary orbits. How does de-Broglie hypothesis explain the stationary orbits?
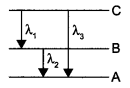
(ii) Find the relation between the three wavelengths λ1 λ2 and λ3 from the energy level diagram shown below:
Question 22.
Two cells of emf 1.5 V and 2.0 V having internal resistances 0.2 O and 0.3 Q respectively are connected in parallel. Calculate the emf and internal resistance of the equivalent cell.
SECTION : D
Question 23.
Meeta’s father was driving her to the school. At the traffic signal she noticed that each traffic light was made of many tiny lights instead of a single bulb. When Meeta asked this question to her father, he explained the reason for this.
Answer the following questions based on above information:
- What answer did Meeta’s father give?
- What are the tiny lights in traffic signals called and how do these operate?
- What were the values displayed by Meeta and her father?
SECTION : E
Question 24.
(i) Define the term drift velocity.
(ii) On the basis of electron drift velocity, derive an expression for resistivity of a conductor in terms of number density of free electrons and relaxation time. On what factors does resistivity of a conductor depend?(iii) Why alloys like constantan and manganin are used for making standard resistors?
OR
(i) State the principle of working of a potentiometer.
(ii) In the following potentiometer circuit AB is a uniform wire of length 1 m and resistance 10 Ω. Calculate the potential gradient along the wire and balance length AO (= l).
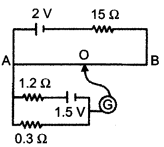
Question 25.
(i) An a.c. source of voltage V = V0 sin at is connected to a series combination of L, C and R. Use the phasor diagram to obtain expressions for impedance of the circuit and phase angle between voltage and current. Find the condition when current will be in phase with the voltage. What is the circuit in this condition called?
(ii) In a series LR circuit XL = R and power factor of the circuit is P1. When capacitor with capacitance C such that XL = Xc is put in series, the power factor becomes P2.Calculate P1/P2.
OR
(i) Write the function of a transformer. State its principle of working with the help of a diagram. Mention various energy losses in this device.
(ii) The primary coil of an ideal step up transformer has 100 turns and transformation ratio is also 100. The input voltage and power are respectively 220V and 1100 W Calculate:
(a) number of turns in secondary.
(b) current in primary.
(c) voltage across secondary.
(d) current in secondary.
(e) power in secondary.
Question 26.
(i) In Young’s double slit experiment, deduce the condition for (a) constructive, and (b) destructive interference at a point on the screen. Draw a graph showing variation of intensity in the interference pattern against position V on the screen.
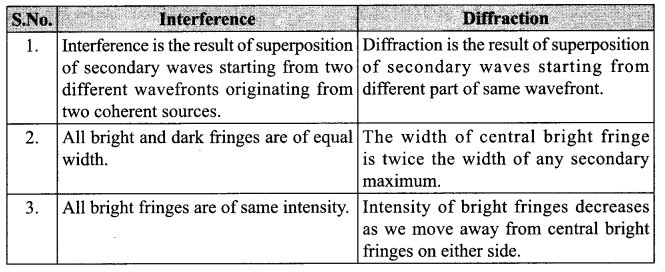
(ii) Compare the interference pattern observed in Young’s double slit experiment with single slit diffraction pattern, pointing out three distinguishing features.
OR
(i) Plot a graph to show variation of the angle of deviation as a function of angle of incidence for light passing through a prism. Derive an expression for refractive index of the prism in terms of angle of minimum deviation and angle of prism.
(ii) What is dispersion of light? What is its cause?
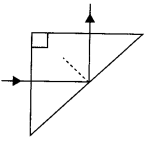
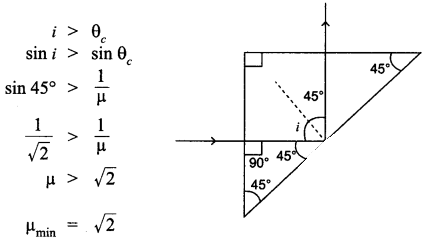
(iii) A ray oflight incident nonnally on one face ofa right isosceles prism is totally reflected as shown in. What must be the minimum value of refractive index of glass? Give relevant calculations.
Answers
SECTION : A
Answer 1.
According to Gauss’s law :
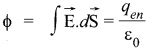
Flux depends only on the charge enclosed.
Hence, the electric flux remains constant.
Answer 2.
Potential at a distance r from a given point charge Q is given by
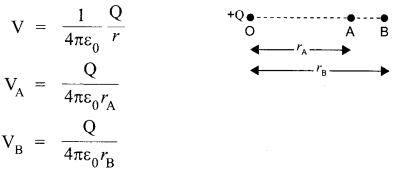
rA < rA ⇒ VA > VB
Since
Hence , VA – VB is positive
Answer 3.
Microwaves of frequency 1 GHz to 300 GHz bounces from even the smallest aircraft so that they are suitable to avoid getting bombed. Microwaves can penetrate through clouds also.
Answer 4.
The Q factor of series resonance circuit is defined as the ratio of the voltage developed across the inductor or capacitor at resonance to the applied voltage, which is the voltage across R.
![]()
It is dimensionless, hence it has no units.
Answer 5.
When a current carrying coil is placed in magnetic field then it experiences a torque.
NIAB = kα
![]()
N = The number of turns,
I = Current
A = Area of the loop,
B = Magnetic field
k = Torsional constant of the wire,
α = Angle of deflection
SECTION : B
Answer 6.
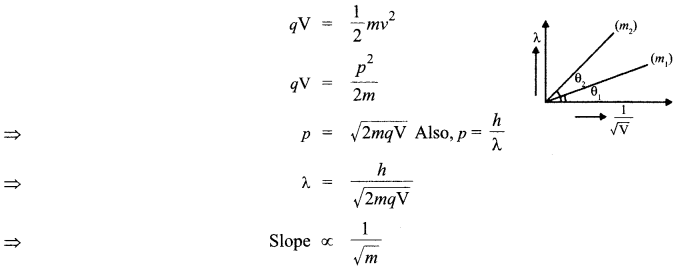
Lesser mass, greater slope, i.e. of mass m2.
Answer 7.
Gain in binding energy for nucleon is about 0.9 MeV.
Binding energy of the nucleus, B1= 7.6 x 240 = 1824 MeV
Binding energy of each product nucleus, B2 = 8.5 x 120 = 1020 MeV. Then, energy released as the nucleus breaks.
E = 2B2-B1= 2 x 1020 – 1824 = 216 MeV
![]()
OR
ΔE = (7.73) – 2(2.23) = 7.73 – 4.46 = 3.27 MeV
Answer 8.
(i) Attenuation :
The loss of strength of a signal while propagating through a medium is known as attenuation.
(ii) Demodulation :
The process of retrieval of information from the carrier wave at the receiver is termed demodulation. This is the reverse process of modulation.
Answer 9.
Brewster’s law :
The law states that the tangent of the polarising angle of incidence of a transparent medium is equal to its refractive index. The light incident at this angle when reflects back is perfectly polarised.
p = tan ip
The refractive index of a material depends on the colour or wavelength of light. As the polarising angle depends on refractive index (p = tan ip), so it also depends on wavelength of light.
Answer 10.
(i) Existence of threshold frequency :
According to wave theory, there should not exist any threshold frequency but Einstein’s theory explains the existence of threshold frequency.
(ii) Dependence of kinetic energy on frequency of incident light :
According to wave theory, the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons should depend on intensity of incident light and not on frequency whereas Einstein’s equation explains that it depends on frequency and not on intensity.
(iii) Instantaneous emission of electrons :
According to wave theory there should be time lag between emission of electrons and incident of light whereas Einstein’s equation explains why there is no time lag between incident of light and emission of electrons.
SECTION : C
Answer 11.
(a) A charge particle having charge q is moving with velocity V in a magnetic field strength ‘B’ then the force acting on it is given by the formula F = q (\(\vec { v } \) x \(\vec { B } \)) and F = qv B sin 0 (where 0 is the angle between velocity vector and magnetic field).
Direction of force is given by the cross product of velocity and magnetic field.
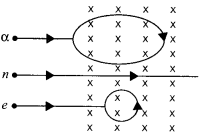
(b) α particle will trace circular path in clockwise direction as it’s deviation will be in the direction (\(\vec { v } \) x \(\vec { B } \))
i .e, perpendicular to the velocity of particle. neutron will pass without any deviation as magnetic field does not exert neutral particle.
Electron will trace circular path in anticlockwise direction as its deviation will be in the direction opposite to (\(\vec { v } \) x \(\vec { B } \)) with a smaller radius due to large charge/mass ratio as r = mv/qB
Answer 12.
(i) Let capacitance of X be C1 and capacitance of Y be C2.
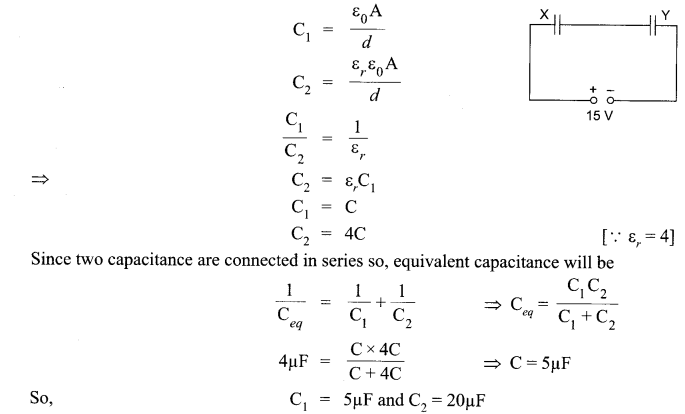
(ii)
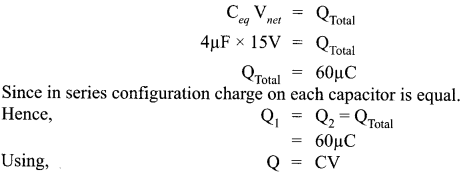
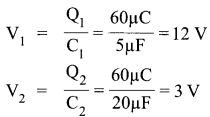
(iii)
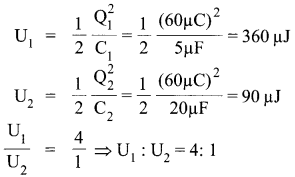
Answer 13
(i) Mutual induction is the phenomenon of production of induced emf in one coil due to change of current in the neighbouring coil. The coil in which the current changes is called primary coil and the coil in which emf is induced is called the secondary coil.
(ii)
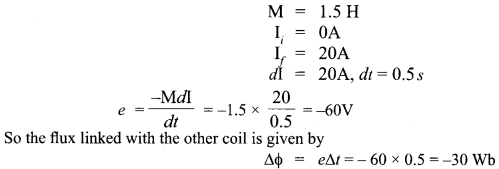
Answer 14.
(a)
(i) Size of Antenna :
The size of antenna required will be of order of λ/4. When frequency is small, the height of antenna will be large, so audio frequency signal would be modulated over a high frequency carrier wave.
(ii) Effective power radiated by an Antenna :
As power radiated μ 1/ λ2 —, hence when frequency is increased then the power radiated will be more.
(b) Advantage of frequency modulation over amplitude modulation.
(i) Noise can be reduced
(ii) Transmission efficiency is more because the amplitude of an FM wave is constant.
Answer 15.
Magnetic field produced on the wire (carrying current I2) due to I1 will be.
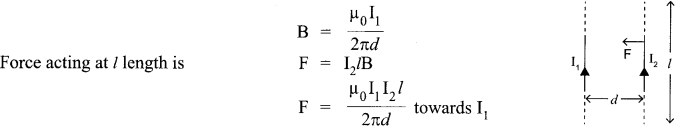
⇒ Attractive force between wires
If l = 1 m, d = I m, I1 = I2 = I and F = 2 x 10-7 N
⇒ I = I A
So one ampere is defined as the current, which when maintained in two parallel infinite length conductors, held at a separation of one metre will produce a force of 2 x 10-7 N per metre of each conductor.
Answer 16.
Reflecting Telescope :
The reflecting telescope uses concave mirror as objective. The rays of light coming from distant object are incident on the objective (parabolic reflective). After reflection the rays of light meet at a point where another convex mirror is placed. This mirror focusses light inside the telescope tube. The final image is seen through the eye piece.
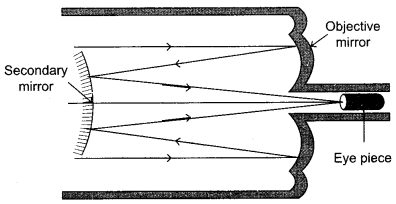
The images produced by the reflecting telescope is very bright and its resolving power is high.
Advantages :
- The resolving power (the ability to observe two object distinctly) is high, due to the large diameter of the objective.
- There is no chromatic aberration as the objective is a mirror.
Answer 17.
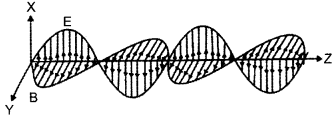
Oscillating charges would give rise to oscillating magnetic field. This oscillating magnetic field, according to Faraday’s Law, will induce an emf, i.e., it produces an oscillating electric field. The electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular to each other and are also perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave. E is the envelope of electric intensity vector and B is the envelope of magnetic intensity vector.
OR
Correction in Amperes Circuital law (Modified Ampere’s law): Maxwell removed the problem of current continuity and inconsistency observed in Ampere’s Circuital law by introducing the concept of displacement current, Displacement current arises due to change in electric flux with time and is given by
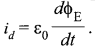
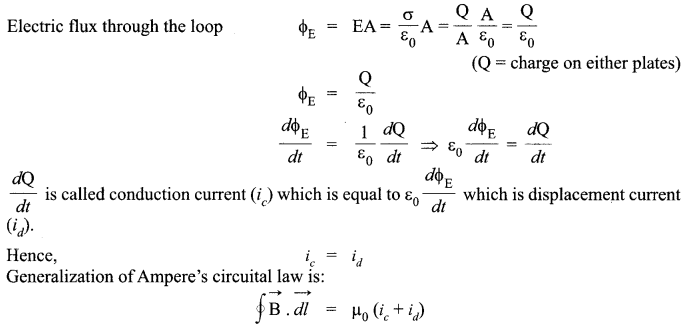
Conduction current is because of flow of charges but displacement current is not because of flow of charges but because of change in electric flux.
Answer 18.
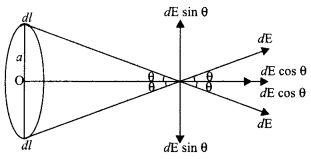
Suppose we have a ring of radius ‘a’ that carries a uniformly distributed positive charge q. As the total charge q is uniformly distributed, the charge dg on the element dl is
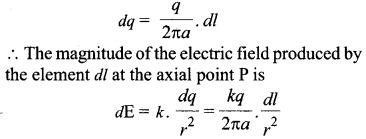
- The axial component is dE cos θ and
- The perpendicular component is dE sin θ.
Since the perpendicular component of any two diametrically opposite elements are equal and opposite, they cancel out in pairs. Only the axial components will add up to produce the resultant field.
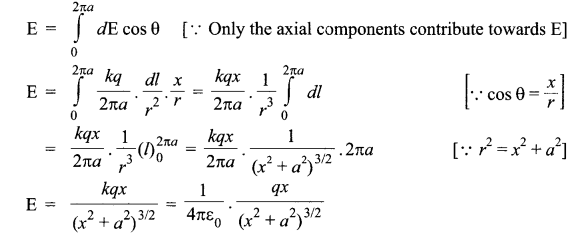
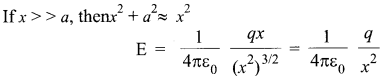
Answer 19.
(i) Three segments of transistor are:
- Emitter
- Base
- Collector
Emitter :
It is of moderate size and heavily doped, it supplies a large number of majority carriers which flow through the transistor.
Base :
It is very thin and lightly doped and it separates emitter and collector region of transistor and controls the flow of charge carriers.
Collector :
This segment is moderately doped and larger in size as compared to emitter. It collects a major portion of majority carriers supplied by the emitter.
(ii)
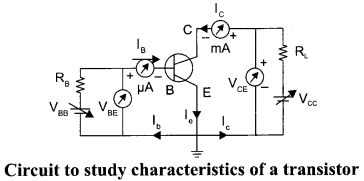
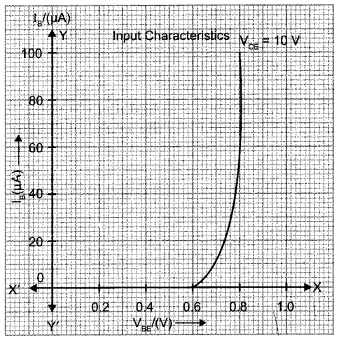
For input characteristics, base current IB versus base emitter voltage VBE is plotted while collector base voltage VCB is kept constant. VCB is kept large, that is 3V to 20V. Input characteristics for various values of VCB gives almost same curves.
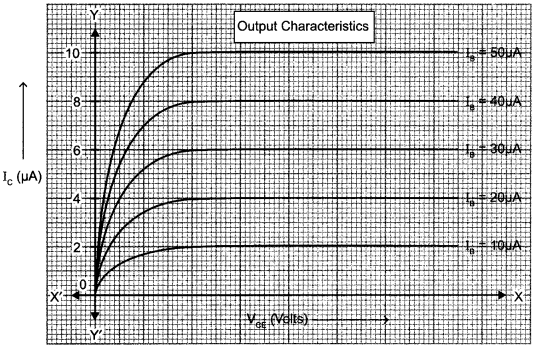
Output characteristics is obtained by varying Ic with VCE keeping IB constant. Different curves are obtained for different values of IB.
Answer 20.
(a) Given,
Height of object = h0
Radius of curvature = 20 cm
Magnification, m = 2
Object distance, u = ?
Image distance, v = ?
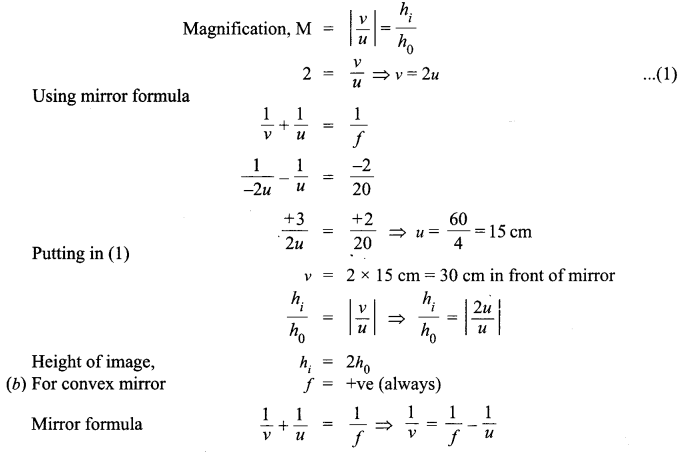
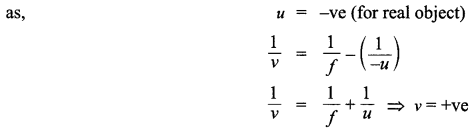
Hence, it will always form virtual image.
Answer 21.
(i) Quantization condition :
Of all possible circular orbits allowed by the classical theory, the electrons are permitted to circulate only in those orbits in which the angular momentumof

Where L, m, and v are the angular momentum, mass and speed of the electron, r is the radius of the permitted orbit and n is positive integer called principal quantum number. The above equation is Bohr’s famous quantum condition. When an electron of mass m 4 is confined to move on a line of length λ with velocity v, the de-Broglie wavelength X associated with electron is:

(ii) In the given energy level diagram, energy increases from level A to B and then B to C. The wavelength corresponds to lowest energy transition is λ2. Then the wavelength λ1 corresponds to higher energy transition and wavelength λ3 corresponds to highest energy transition.
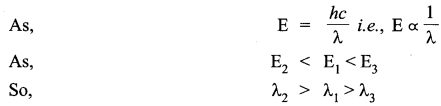
Answer 22.
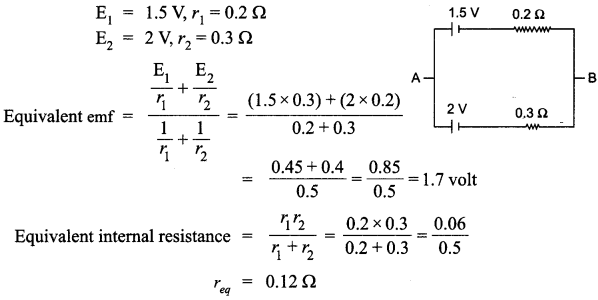
SECTION : D
Answer 23.
- Meeta’s father said that these are LED light which consume less power and have high reliability.
- The tiny lights in traffic signals are Light Emitting Diode. These are operated by connecting the pn-junction diode in forward biased condition.
- Values displayed by Meeta were a good observer, curious and her father shows awareness for energy conservation, power saving and have knowledge about such electrical devices.
SECTION : E
Answer 24.
(i) Drift velocity is defined as the average velocity which the electrons are drifted towards the positive terminal under the effect of applied electric field.
![]()
(ii) We know that the current flowing through the conductor is :
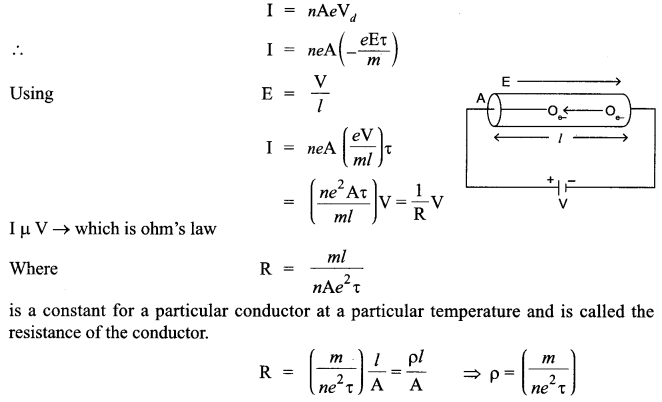
Where p is the specific resistance or resistivity of the material of the wire. It depends on number of free electron per unit volume and temperature.
(iii) They are used to make standard resistors because :
- They have high value of resistivity.
- Temperature coefficient of resistance is less.
- They are least affected by temperature.
OR
(i) Principle :
When a constant current flows through a wire of uniform cross sectional area then the composition of the potential drop across any length of the wire is directly proportional to that length. Let V be the potential difference across the portion of the wire of length l whose resistance is R.
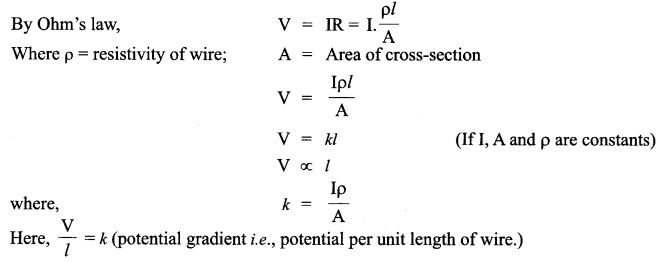
(ii) Total resistance of the primary circuit
15 + 10 = 25 Ω, emf = 2V
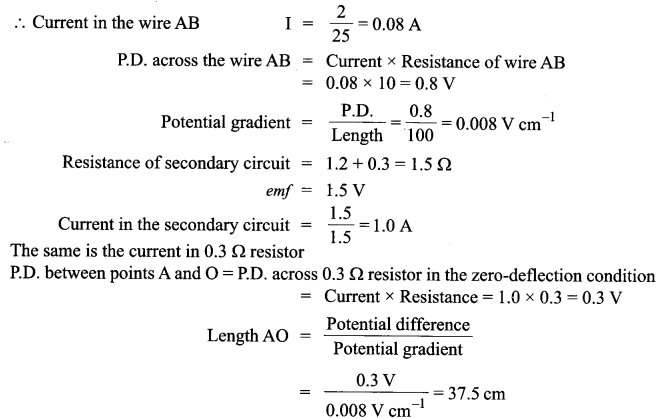
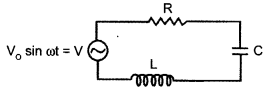
Answer 25.
(i) Let a, series LCR circuit is connected to an ac source V. We take the voltage of the source to be
V = V0 sin ωt.
The AC current in each element is the same at any time, having the same amplitude and phase. It is given by,
I = I0 sin (ωt + Φ)
Let VL, VR, Vc and V represent the voltage across the inductor, resistor, capacitor and the source respectively.
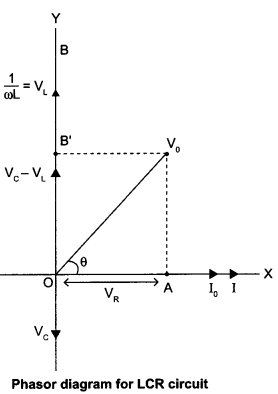
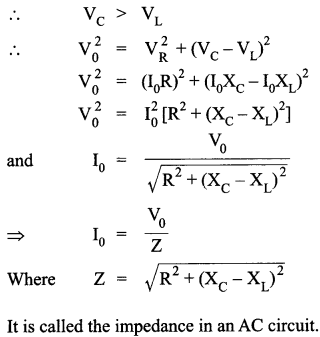
Condition :
The current will be in phase with the voltage at resonance condition. At resonance condition
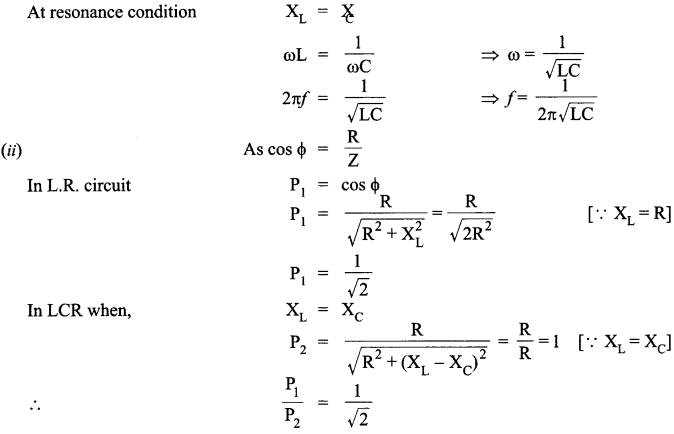
OR
(i) A transformer is an electrical device for converting an alternating current at low voltage into that at high voltage or vice-versa.
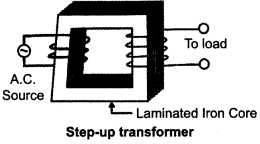
- If it increases the input ac voltage, it is called step up transformer.
- If it decreases the input ac voltage, it is called step down transformer.
Principle :
It works on the principle of mutual induction i.e., When a changing current is passed through one of the two inductively coupled coils, an induced emf is set up in the other coil.
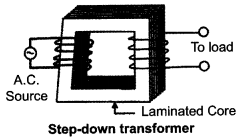
Working Theory :
As the AC flows through the primary coil, it generates an alternating magnetic flux in the core which passes through the secondary coil.
Let N1 = No. of turns in primary coils
N2 = No. of turns in secondary coils
This changing flux set up an induced emf in the secondary, also a self induced emf in the primary.If there is no leakage of magnetic flux, then flux linked with each turn of the primary coil will be equal to that linked with each of the secondary coil. According to Faraday’s law of induction.
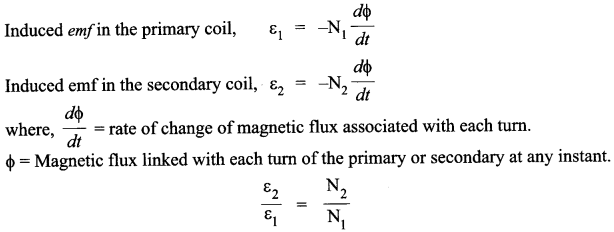
Various energy losses in transformer are :
- Copper loss :
Some energy is lost due to the heating of copper wires used in the primary and secondary windings. This power loss (P = I2R) can be minimised by using thick copper wires of low resistance. - Eddy current loss :
The alternating magnetic flux induces eddy current in the iron core which leads to some energy loss in the form of heat. This loss can be reduced by using laminated iron core. - Hysteresis loss :
The alternating current carries the iron core through cycles of magnetisation and demagnetisation. Work done in each of these cycles and is lost as heat. This is called hysteresis loss and can be minimised by using core material having narrow hysteresis loop. - Flux leakage :
The magnetic flux produced by the primary may not fully pass through the secondary. Some of the flux may leak into air. This loss can be minimised by winding the primary and secondary coils over one another.
(ii) Given , N1 = 100, k = 100, V1 = 220V, P1 = 1100W
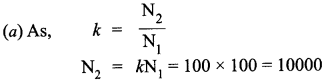
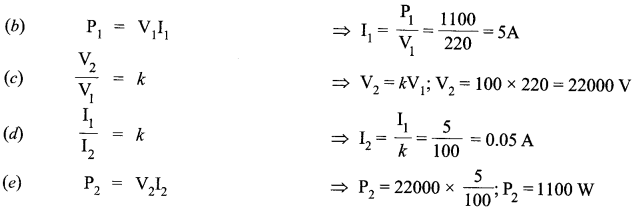
Answer 26 .
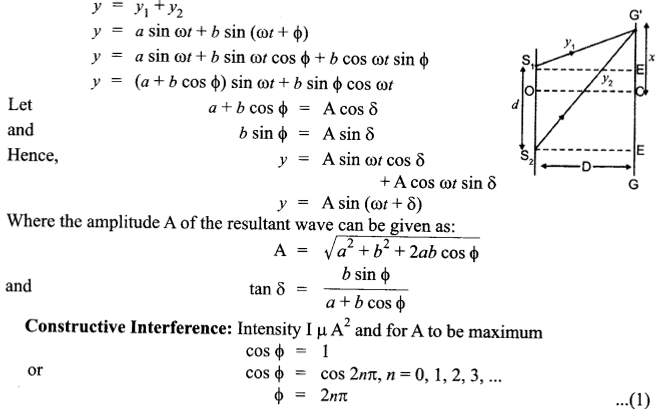
(i) Let the two waves arising from the slits A and B have the amplitudes
a and b and the phase difference Φ. Such that y1 = a sin ωt and y2 = b sin(ωt +Φ).
The resultant displacement is given as :
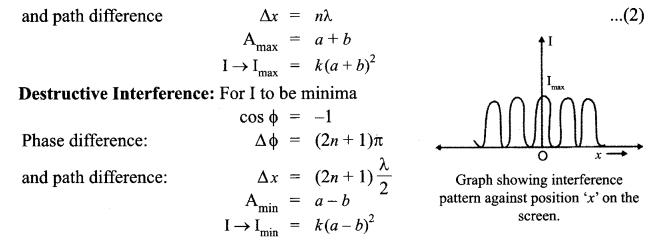
(ii) Comparison of interference pattern observed in Young’s double slits and the single slits diffraction:
OR
(i) Angle of deviation is the angle through which the incident rays is deviated on passing through a prism i.e., angle between the incident ray and emergent ray. It is denoted by δ.
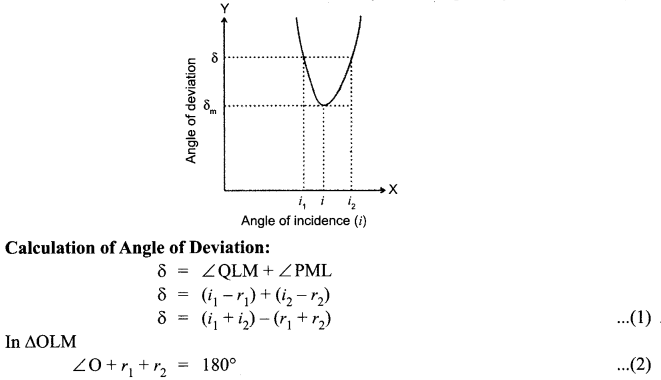
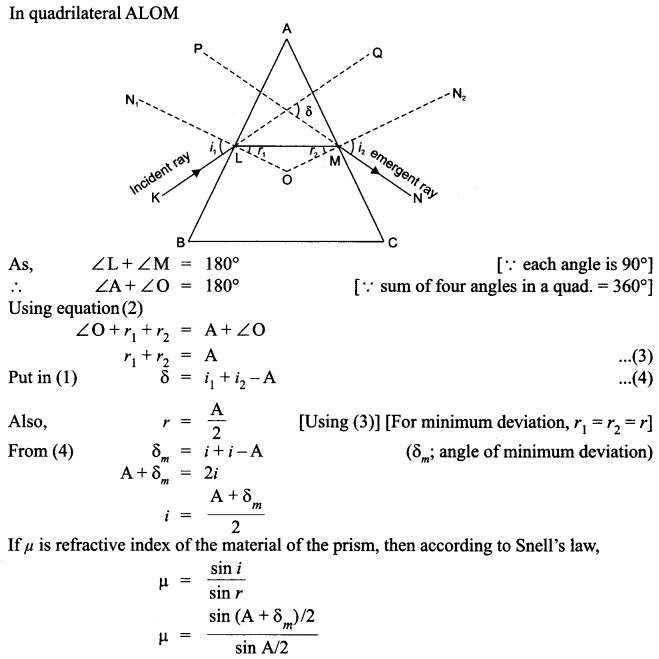
(ii) Dispersion of light :
Upon passing through the prism, the white light is separated into its component colours : red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet. The separation of visible light into its different colours is known as dispersion. Dispersion occurs because for different colour of light a transparent medium will have different refractive indices (p).
(iii) For total internal reflection :
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physics Paper 1 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physics Paper 1, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
