CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 7 are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 7.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 7
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | XII |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 7 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 12 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme, as prescribed by the CBSE, is given here. Paper 7 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Chemistry is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time Allowed : 3 Hours
Max. Marks: 70
General Instructions
- All questions are compulsory.
- Question number 1 to 5 are very short answer questions and carry 1 mark each.
- Question number 6 to 10 are short answer questions and carry 2 marks each.
- Question number 11 to 22 are also short answer questions and carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 23 is a value based question and carry 4 marks.
- Question number 24 to 26 are long answer questions and carry 5 marks each.
- Use log table, if necessary. Use of calculators is not allowed.
Questions
Question 1.
Give the formula of an interhalogen compound which is isostructural with XeF4.
Question 2.
Is PCl5 an oxidising or a reducing agent? Justify your answer.
Question 3.
Write relationship of Freundlich’s adsorption isotherm.
Question 4.
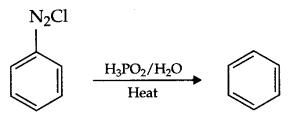
What happens when diazonium chloride is heated with H3PO2?
Question 5.
Write IUPAC name for the linkage isomer of [Pt(NH3)5NO2]+.
Question 6.
Name the crystal defect observed in following solid
- ZnO
- CsCl
Question 7.
Draw a curve representing variation Δm with √c (concentration) for acetic acid. Is it possible to find out limiting molar conductivity form this curve? Give reason for your answer.
Question 8.
Draw the structure of following compounds:
(i) BrO–3
(ii) IF3
Question 9.
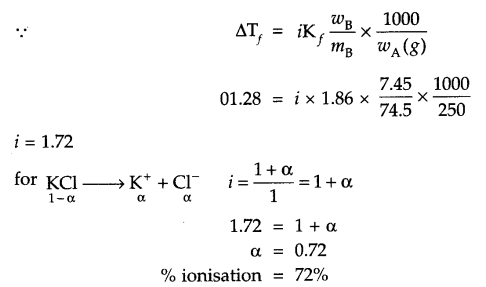
7.45 g of KCl was dissolved in 250 g of H2O and the solution froze at – 1.28°C. Calculate percentage dissociation of salt.
(Given Kf = 1.80 K kg mol-1, K = 39 u, Cl = 35.5 u)
OR
Find mass % of 10 m of aqueous solution of urea. If molar mass of urea is 60 g/mol and density of solution is 1.2 g cm-3.
Question 10.
Zinc crystallizes in bcc structure. Its atomic radii is 173.2 pm. Calculate its density if atomic mass of zinc is 65 g/mol. (NA = 6 x 1023 mol-1).
Question 11.
(a) Write short notes on:
(i) Wolff-Kishner Reduction
(ii) Esterification reaction
(b) Write mechanism of nucleophilic addition reaction by taking a suitable example.
OR
(a) Explain following terms by taking suitable example:
- Schiff’sbase
- Oxime
(b) Arrange according to increasing acidic strength
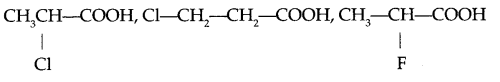
Question 12.
Give reasons for the following:
- NF3 is an exothermic compound, whereas NCl3 is not.
- BiCl5 acts as strong oxidising agent.
- F2 has lower bond enthalpy as compared to Cl2.
Question 13.
An aromatic compound (C7H6O2) on heating with aqueous ammonia forms compound ‘B’. ‘B’ on heating with Br2 and KOH yields compound ‘C’ of molecular formula (C6H7N). Write the reactions involved and structure of compound ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’.
Question 14.
Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram, write electronic configuration (in terms of eg and t2g orbitals) for central metal atom/ion and determine magnetic moment value in the following:
(i) [FeF6]4-
(ii) [CO(NH3)6]3+
Question 15.
- What happens when Fe(OH)3 is mixed with As2S3 sol? Give reason.
- What is shape selective catalysis?
- What is cottrell smoke precipitator?
Question 16.
(i) Predict the order of reactivity for SN1 reaction in case of isomers of bromobutane.
(ii) Arrange according to increasing hydrolysis reaction with aqueous KOH.
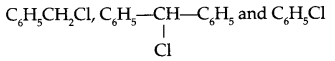
(iii) Which is a better nucleophile, a bromide ion or an iodide ion?
Question 17.
Define the following:
- Raoult’s law
- Osmotic pressure
- Mole fraction
Question 18.
Explain the role of
- Limestone in extraction of iron.
- Cresol and aniline in froth floatation process.
- SiO2 in extraction of copper from copper matte.
Question 19.
A solution of CuSO4 is electrolysed for 10 minutes with a current of 1.5 amperes. What is the mass of Cu deposited?
Question 20.
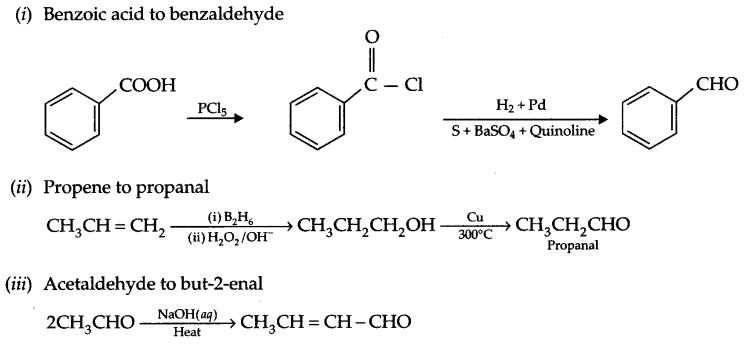
Carry out following conversions in not more than two steps:
(i) Benzoic acid to benzaldehyde
(ii) Propene to propanal
(iii) Acetaldehyde to but-2-enal
Question 21.
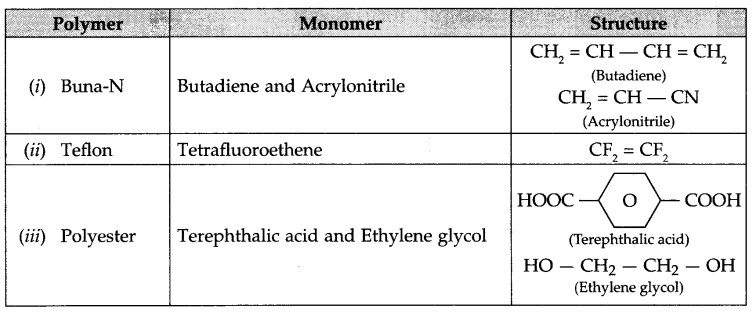
Write name and structure of monomers used for the following polymers:
(i) Buna-N
(ii) Teflon
(iii) Polyester (Dacron)
Question 22.
(a) Write a reaction of glucose which cannot be explained by its open chain structure.
(b) Explain the following:
- Peptide linkage
- Pyranose structure of a-D(+) glucose
Question 23.
Priya had stomach ache and hyper acidity she usually takes baking soda from kitchen to take relief, but her friend Roma asked her to discontinue taking baking soda and better consult a doctor.
- What values are associated with Roma?
- Why we should not take medicine without consulting a doctor?
- What are antacids. Give one example.
- Ranitidine is preferred over NaHCO3. Give reason.
Question 24.
(a) Distinguish following pairs of compound with a suitable chemical test
- Salicylic acid and phenol
- Methanol and ethanol
(b) Give reason for the following:
- Methoxy group present on benzene activates it for SE reaction at ortho, para position,
- Phenol is more acidic than cyclohexanol.
- Ethers having 2° and 3° alkyl group cannot be prepared by Williamson’s synthesis.
OR
(a) Complete the following reactions:
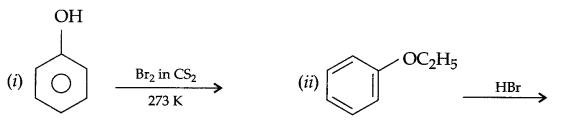
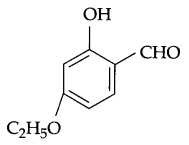
(b) Write IUPAC name for the following compound:
(c) While separating a mixture of ortho and para nitrophenol which is steam volatile and why?
Question 25.
(a) The half life for decay of radioactive 146C is 5730 years. An acheological artefact containing wood had only 80 % of 146C activity as found in a living tree. Calculate the age of the artefact.
(b) Write factors affecting rate of reactions.
OR
(a) Write differences (at least two) between order and molecularity of a reaction.
(b) For the reaction at 600 K
C2H5I(g) → C2H4(g) + HI(g)
the first order rate constant (k) is 1.6 × 10-5 s-1 and its activation energy is 209 KJ mol-1. Calculate the rate constant at 700 K.
Question 26.
- Which 3d series element should not be considered as transition metal?
- What happens when KMnO4 is heated?
- What is lanthanoid contraction?
- Why do transition elements are coloured?
- Transition metal acts as good catalyst explain.
OR
(a) Compare lanthanoids and actinoids with respect to
- atomic size
- oxidation state
(b) Write all reactions involved in preparation of K2Cr2O7.
(c) The reduction potential of Cu2+/Cu is positive. Give reason.
Answers
Answer 1.
IF–4 or ICl–4
Answer 2.
Phosphorus has five valence electrons so it cannot exceed its oxidation state beyond +5 so it cannot act as reducing agent but it can acquire lower oxidation state like +3 etc. Thus, PCl5 can act as oxidising agent only.
Answer 3.
Freundlich adsorption isotheron relation xm = kP1/n
where xm = mass of adsorbate per unit mass of adsorbent, P = pressure of gas, k = constant of adsorption, n = no. of layers of adsorption.
Answer 4.
Benzene will form
Answer 5.
Linkage isomer of [PtNH3)5NO2]+ is [Pt(NH3)5(ONO)]+
its IUPAC name is pentaamminenitrito-O-platinum(II) ion.
Answer 6.
- Metal excess defect due to the presence of extra cations at interstitial sites.
- Schottky defect.
Answer 7.
Curve between Δm Vs √c for acetic acid is as follows:
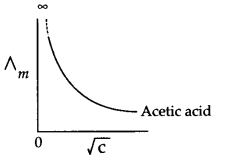
No, it is not possible to find out limiting molar conductivity from this curve reason being this curve is parallel to y-axis and hence meet only at infinity.
Answer 8.
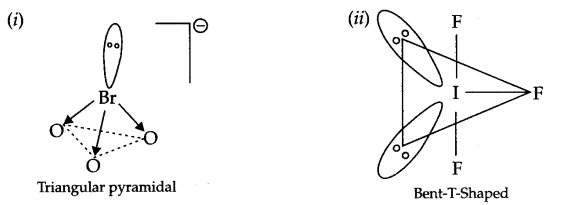
Answer 9.
Mass of solute (wB) = 7.45 g
Molar mass of solute (mB) = 74.5 g, wA = 250 g
ΔTf = 1.28°C = 1.28 K
i = ? α = ?
Kf = 1.86 K kg mol-1
OR
Since for x% by mass aqueous solution molality
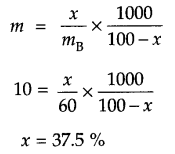
Answer 10.
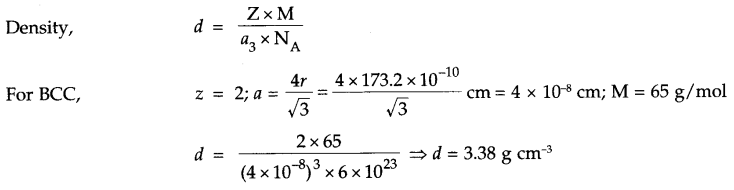
Answer 11.
(a) (i) Wolff-Kishner reduction: The carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones is reduced to CH2 group on treatment with hydrazine followed by heating with NaOH or KOH in ethylene glycol as solvent.
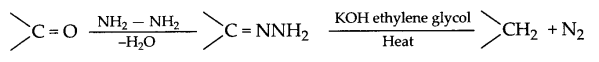
(ii) Esterification reaction: Acid on reaction with alcohol in presence of cone. H2SO4 gives ester so this reaction is known as esterification reaction.
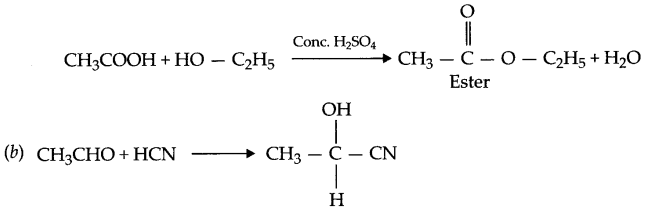
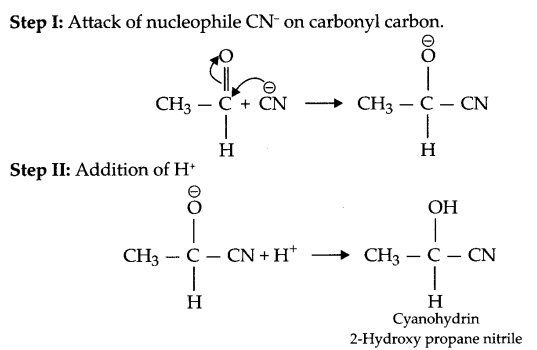
OR
(a)
- Schiff’s base: Schiff’s base are the compounds formed by condensation of primary amine with carbonyl compound such that carbonyl group is replaced by an imine or azomethine group. For example,
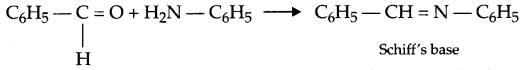
- Oxime: When an aldehyde or a ketone reacts with NH2OH (hydroxylamine), oximes are formed.
CH3CHO + NH2OH → CH3CH=NOH
(b) Increasing acidic strength
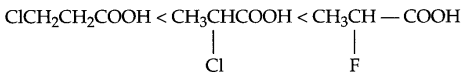
Halogen on α-carbon shows greater -I effect which stabilise the carboxylate ion to higher extent than that of β-carbon. Fluorine shows higher electron withdrawing property than chlorine.
Answer 12.
- Since bond dissociation energy of F2 is lower than Cl2 moreover fluorine forms stronger bond with nitrogen due to comparable size.
- Due to inert pair effect Bi in +3 state is more stable than +5 state. Therefore, in +5 oxidation state it accepts two electrons to get reduced to +3 state.
- Due to small size of fluorine, there is strong lone pair-lone pair repulsion between two F atoms hence its bond enthalpy is lower than Cl2.
Answer 13.
Since it is aromatic compound hence other than C6H5 there must be a COOH group to satisfy the molecular formula of C7H6O2 The reaction will be as under
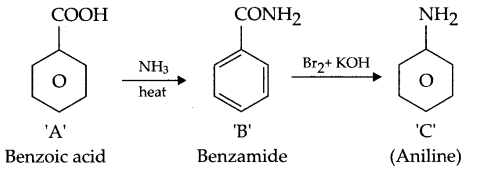
Answer 14.
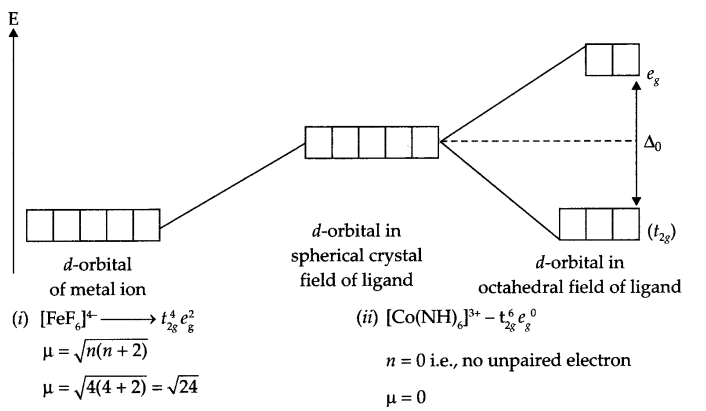
Answer 15.
- Fe(OH)3 is a positively charged sol and As2S3 is negatively charge sol hence on mixing coagulation will take place.
- Shape selective catalysis: The catalytic reaction which depends upon the pore structure on the surface of catalyst and the size of reactant and product is known as shape selective catalysis e.g. zeolite acts as shape selective catalyst.
- Cottrell smoke precipitator: It consists of plate with charge opposite to that of smoke particles which is fitted at the mouth of chimney. The charged plate neutralises the charge on smoke particles like arsenic compounds etc. and settle down them at the floor of the chamber.
Answer 16.
(i) Reactivity of isomenc forms of butane for SN1 reaction is:
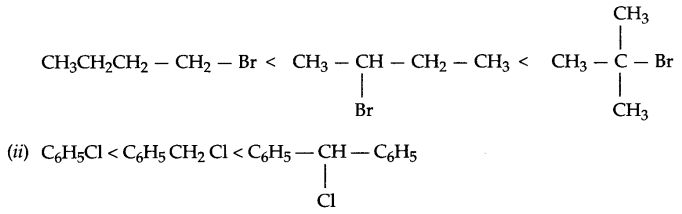
(iii) Iodide ion (due to its larger size it has higher polarizability thus, it is a better nucleophile).
Answer 17.
- Raoult’s law: It states than partial vapour pressure of a component of solution at a given temperature is directly proportional to its mole fraction in the solution i.e.
PA ∝ xA and PB ∝ xB or PA = P0AxA and PB = P0BxB
where A and B are two components of solution. - Osmotic pressure: It is pressure exerted on higher concentration side solution of semi permeable membrane so that there is no net flow of solvent in either side of membrane. It is represented by π.
π = CRT - Mole fraction: It is fraction of a component in each mole of solution i.e.
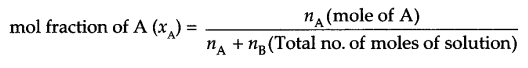
Answer 18.
- Umestone on heating decomposed in CaO and CO2. CaO combines with impurity (SiO3) to give slag and CO2 combines with C to form CO (reducing agent for reduction of FeO).
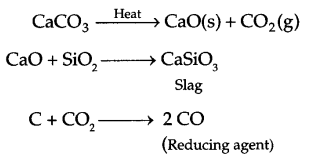
- Cresol and aniline behave as froth stabilizer i.e. stabilises froth in thick scum.
- SiO2 combines with FeO present in copper matte
- FeS + O2 → FeO + SO2
- FeO + SiO2 → FeSiO3
i.e. impurity of FeO can be eliminated as slag.
Answer 19.
Since in CuSO4, Cu2+ moves towards cathode
At cathode Cu2+ (aq) + 2e– → Cu(s)
Since,
m ∝ Q
m = ZQ and Q=lt
So m = ZIt and Z = MnF chemical equivalence of substance
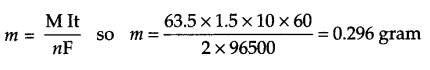
Answer 20.
Conversion
Answer 21.
Answer 22.
(a) D-glucose does not explain following reactions by its open chain structure.
- It does not respond to Schiff’s test or 2,4-DNP test.
- It does not react with NaHSO3 and NH3
- Glucose petaacetate does not react with NH2OH means there is absence of free -CHO group.
(b)
- Peptide linkage: The
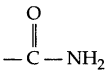
bond formed between carboxylic and amine groups of α-amino acids in protein is known as peptide linkage. - Pyranose structure of glucose
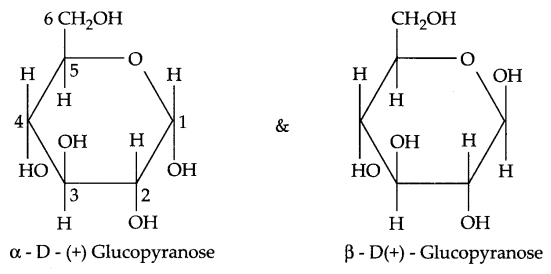
Answer 23.
- Critical thinking, awareness, helpful, concern for friend.
- The wrong medicine may be harmful because its small dose may prove fatal hence a doctor must be consulted before taking any medicine who prescribed medicine after observing the symptoms and conditions.
- Antacids: Chemical sustance which neutralizes excess acid present in stomach and raises the pH to appropriate level e.g. NaHCO3, Al(OH)3, Mg(OH)2, ranitidine etc.
- Ranitidine physiologically curtails formation of excess acid by preventing interaction of histamine with the receptors in the stomach wall while NaHCO3 makes the stomach alkaline which triggers even more production of acid and hence ranitidine is better than NaHCO3.
Answer 24.
(a) 1.
| Reagent | Salicylic acid | Phenol |
| NaHCO3 (aq) | Bubbles of CO2 gas evolves | No such gas evolution |
2.
| Reagent | Methanol | Ethanol |
| NaOH(aq) + I2 | No yellow ppt | Yellow precipitate of CHI3 will form |
(b)
- Due to resonance negative charge appears on ortho and para position to methoxy group hence methoxy group activates benzene ring on these positions for SE (electrophilic substitution) reaction.
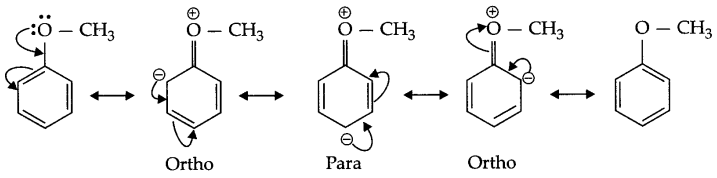
- Due to resonance stabilisation of phenoxide ion phenol is more acidic as compared to cyclohexanol.
- Ethers having 2° or 3° alkyl group cannot be prepared by Williamson’s synthesis reason being elimination reactions will take place and alkene will form.
OR
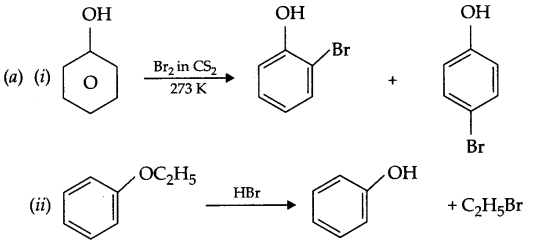
(b) 4-Ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde.
(c) o-Nitrophenol is steam volatile reason being their is intramolecular hydrogen bonding in it as a result, intermolecular force will be weaker. On the other hand, p-nitrophenol possess intermolecular hydrogen bonding so it has high b.pt.
Answer 25.
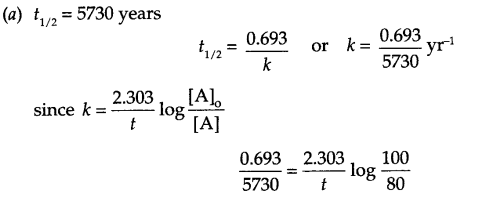
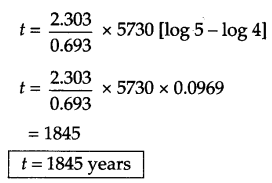
(b) Factors affecting rate of reactions are
- Temperature
- Pressure
- Physical state of reactants
- Catalyst
- Concentration of reactants
OR
(a) Difference between order and molecularity
| Order | Molecularity | ||
| (i) | It is sum of the powers of reactants in rate law expression. | It is sum of powers of reactant present in law of mass action equation. | |
| (ii) | It is determined experimentally. | It is determined from balanced chemical reaction. | |
| (iii) | It can be positive, negative, zero or fraction. | It can be positive integer only. | |
| (iv) | It is applicable for all reaction. | It is applicable only for elementary reaction. | |
(b) Since
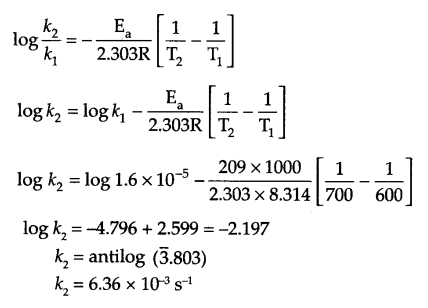
Answer 26.
- Zn
- 2KMnO4 heat→ K2MnO4 + MnO2 + O2
- Lanthanoid contraction: The contraction in size from La (Lanthanum) to Lu (Lutetum) due to filling of electrons in 4f orbital which has poor shielding is known as lanthanoid contraction.
- Due to presence of unpaired electrons in valence shell of transition metals and d-d transitions are responsible for colour of transition metals and their compounds.
- Due to variable oxidation state, high charge density and large surface area transition metals acts as good catalyst.
OR
(a)
- Atomic size: Element to element contraction in size in case of actinoids is more than lanthanoids due to poor shielding of 5f orbital as compared to 4f orbital.
- Oxidation state: Lanthanoid shows +3 as general oxidation state. Some of the elements like Eu and Yb shows +2 and Ce, Gd, Ho shows +4 oxidation state.
But in actinoids variable OAidation state from +3 to +7 are known due to comparable energy of 5f, 6d and 7s orbitals.
(b) Reactions involved in preparation of K2Cr2O7
- 4FeCr2O4 + 8Na2CO3 + 7O2 Roasted→ 8Na2CrO4 + 2Fe2O3 + 8CO2
- 2Na2CrO4 + H2SO4 → Na2Cr2O7 + Na2SO4 + H2O
- Na2Cr2O7 + 2KCl → K2Cr2O7 + 2NaCl
(c) High ionisation enthalpy of Cu (g) to Cu2+ (g) is not balanced by its hydration enthalpy as a result its reduction potential Cu2+ to Cu is positive.
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 7 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 7, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
