CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 6 are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 6.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 6
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | XII |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 6 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 12 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme, as prescribed by the CBSE, is given here. Paper 6 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Chemistry is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time Allowed : 3 Hours
Max. Marks: 70
General Instructions
- All questions are compulsory.
- Question number 1 to 5 are very short answer questions and carry 1 mark each.
- Question number 6 to 10 are short answer questions and carry 2 marks each.
- Question number 11 to 22 are also short answer questions and carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 23 is a value based question and carry 4 marks.
- Question number 24 to 26 are long answer questions and carry 5 marks each.
- Use log table, if necessary. Use of calculators is not allowed.
Questions
Question 1.
Draw structure of p-nitroanisole.
Question 2.
What causes Brownian movement?
Question 3.
Write IUPAC name of the following complex
[Cr(CN)2(CH3NH2)2(NO)2]Cl
Question 4.
Write reaction between phenol and bromine water.
Question 5.
For the reaction, C2H4 + H2 \(\underrightarrow { Ni } \) C2H6 the rate constant is 3 × 10 mol L-1 s-1. Predict the order of reaction.
Question 6.
What are colligative properties? Give example of any two colligative properties.
Question 7.
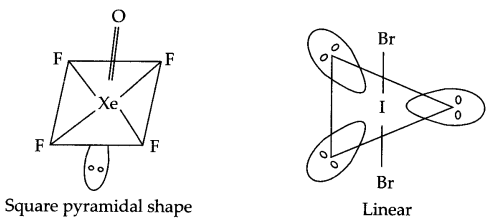
Draw the structure of the following compounds:
(i) XeOF4
(ii) IBr–2
Question 8.
Give reasons for the following:
- Transition metals show variable oxidation states.
- Actinoids show variable oxidation states.
Question 9.
Define the following terms:
- Anisotropic solid
- Ferromagnetic solid
Question 10.
Write definitions of the following:
- Enantiomers
- Chiral compounds
OR
What are ambident nucleophiles? Give an example.
Question 11.
Give one difference in each of the following pairs:
- Hormones and enzymes
- Nucleotide and nucleoside
- Starch and glycogen
Question 12.
In the lanthanoid series (Ce → 58 to Lu → 71)
- Which element’s, compound acts as oxidising agent?
- Which element show +2 oxidation state (name any one)?
- Which element has largest atomic radii?
Question 13.
Write down the hybridisation and magnetic character of the following complexes according to VBT:
- [CoF6]3-
- [Ni(NH3)4]2+
Question 14.
Complete the following reactions:
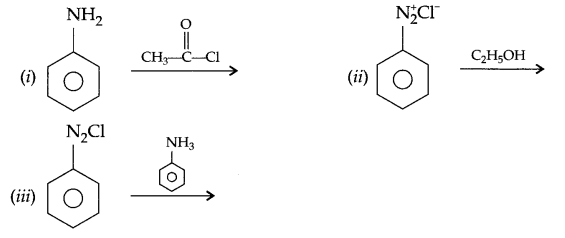
OR
Account for the following:
- Methylamine in water reacts with ferric chloride to precipitate hydrated ferric oxide.
- Diazonium salt of aromatic amines are more stable than those of aliphatic amines.
- Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is preferred for synthesising primary amines.
Question 15.
Differentiate between the following pairs:
- Macromolecular colloids and multimolecular colloids
- Peptisation and coagulation
- Electrophoresis and electrodialysis.
Question 16.
A decimolar solution of K4[Fe(CN)6] (Potassium ferrocyanide) is 50% dissociated at 300 K. Calculate the osmotic pressure of the solution.
Question 17.
How are the following conversions carried out?
(i) Propene to propane-1-ol
(ii) Benzaldehyde to benzyl alcohol.
(iii) Butyl magnesium chloride to pentan-1-ol.
Question 18.
A first order reaction is get 50% completed in 50 minutes, how long will it take [A] to reduced to 60% of its initial concentration?
Question 19.
If NaCl is doped with 10-3 mol % of SrCl2, what is the concentration of cation vacancies?
Question 20.
Describe the following:
- Role of stabilizer in the froth floatation process.
- Role of silica in the metallurgy of copper.
- Role of cryolite in the metallurgy of aluminium.
Question 21.
Write two uses of each of the following polymers.
(i) PVC
(ii) Bakelite
(iii) Nylon-6, 6
Question 22.
In the following pairs of halogen compounds which compound undergoes faster SN1 reaction.
(i) CH2 = CH-CH2Cl and CH3-CH = CH-Cl
(ii) CH3CH2-Br and CH3CH2-I
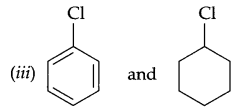
Question 23.
Mr. Naresh an employee in a multinational company due to his hectic schedule and stress started taking sleeping pills. His one of the friend Amit requested him to discontinue taking these pills and asked him to join yoga session and pranayam which improved condition of Mr. Naresh.
After reading the above passage answer the following questions:
- Write the values shown by Amit.
- ‘Nhich class of drugs is used in sleeping pills?
- Why is it not advisable to take sleeping pills without consultation with the doctor?
- Give an example of tension relieving drug.
Question 24.
(a) Write the product formed in the following:
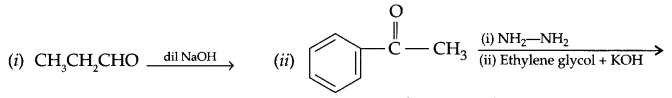
(b) Give simple tests to distinguish the following pairs of compotmds:
- Ethanal and propanal
- Benzoic acid and ethyl benzoate
- Benzaldehyde and acetophenone
OR
(a) Give reasons:
- CH3CHO is more reactive than CH3COCH3 towards HCN.
- 4-Nitrobenzoic acid is more acidic than benzoic acid.
(b) Describe the following:
- Cannizzaro reaction
- Cross aldol condensation
- Rosenmund reaction.
Question 25.
(a)
- State Kohlrausch law.
- Find the number of faraday used for electrolysis of one mole A1203.
(b) Find emf of the following electrochemical cell at 298 K.
Pt | Sn4+ (0.02 M), Sn2+ (0.04 M) || Fe3+ (0.08 M), Fe2+ (0.04 M) | Pt
![]()
OR
(a) Define the following terms:
- Molar conductivity
- Corrosion
(b) The resistance of a conductivity cell containing 0.001 M KCl solution at 298 K is 1500 Ω. What is the cell constant if conductivity of 0.001 M KCl solution at 298 K is 0.146 × 10-3 S cm-1?
Question 26.
(a) Complete the following equations:
- I– + O3 + H2O →
- H3PO2 + NaOH →
(b)
- Name the noble gas, other than Xe which forms true compound.
- HCl reacts with powdered iron to give ferrous chloride and not ferric chloride. Assign suitable reason.
- Which is more reactive SF6 or SF4? Give reason for your answer.
OR
(a) What happens when
- Cl2 reacts with hot concentrated solution of NaOH.
- XeF6 is mixed with SbF5 and heated.
(b) Give appropriate reason for each of the following:
- Sulphur shows more catenation property than oxygen.
- NH3 has more boiling point than PH3.
- Fluorine form only one oxoacid, HOF.
Answers
Answer 1.
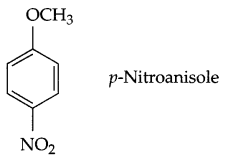
Answer 2.
Unbalanced bombardment of particles of dispersion medium on dispersed phase causes brownian movement.
Answer 3.
Dicyanidodimethanaminedinitrosylchromium (III) chloride.
Answer 4.
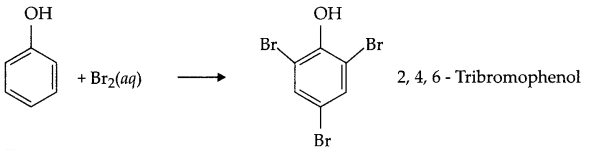
Answer 5.
Zero order reaction.
Answer 6.
Colligative property: Those properties of dilute solution of non volatile solute in volatile solvents which depend on the total number of solute particles in per unit volume are called colligative property e.g.
- Relative lowering of vapour pressure
- Elevation in boiling point.
Answer 7.
Answer 8.
- Since (n-1)d and ns orbitals takes part in bond formation due to their comparable energy, transition elements show variable oxidation states.
- It is due to comparable energy of 5f, 6d and 7s orbital, any member of electron can participate to bond formation so actionoids show variable oxidation state.
Answer 9.
- Anisotropic solid: Solids which have different arrangement of particles in different directions such as crystalline solids are anisotropic solids. In these solids, physical properties like refractive index are different when measured along different directions in a same solid.
- Ferromagnetic solid: Solids which are attracted very strongly by a magnetic field are ferromagnetic solids e.g., iron, cobalt, nickel etc. Here, all domains (group of metal ions) orient in same direction of applied magnetic field to produce strong magnetic effect and this persist even when magnetic field is removed.
Answer 10.
- Enantiomers: The optical isomers which are non superimpossible mirror image of one another are known as enantiomers.
- Chiral compounds: The molecule having atleast a chiral carbon and have non superimposable mirror image are known as chiral compounds. A molecule having a single asymmetric carbon atom is chiral is nature.
OR
The nucleophile having two nucleophilic centre but at a time only one attach with electrophilic centre is known as ambident nucleophile, e.g CN– and NC–, NO–2 and ONO– etc.
Answer 11.
- Hormones are biochemical compound responsible for passing information to a body organ to carry out certain work and it itself does not take part in reaction. On the other hand enzymes are protein which acts as biochemical catalyst for specific organic reaction in all living organism.
- Nucleotide and nucleoside: Nucleoside is a base-sugar unit which contains a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) and a nitrogenous base. On the other hand, nucleotide is ester of nucleoside and phosphoric acid.
In short, nucleotide gives sugar + base + phosphate on hydrolysis but nucleoside gives only sugar and base. - Starch and glycogen: Starch is polymer of α-glucose attached with α-glycoside linkage and stored in plant body.
On the other hand, glycogen is form of carbohydrate stored in the animal body. Its structure is similar to amylopectin of starch.
Answer 12.
- Cerium (Ce)
- Europium (Eu)
- Europium (Eu)
Answer 13.
(i) The arrangement of electrons information of [CoF6]3- according to VBT is
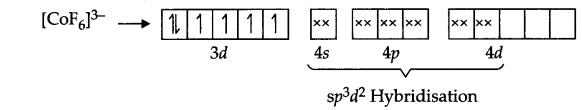
Magnetic character – Paramagnetic
(ii) The arrangement of electrons in the formation of [Ni(NH3)4]2+, (Ni2+ → 3d8)
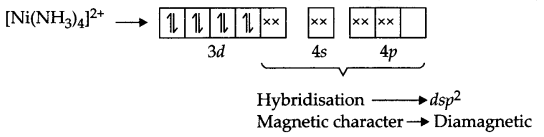
Answer 14.
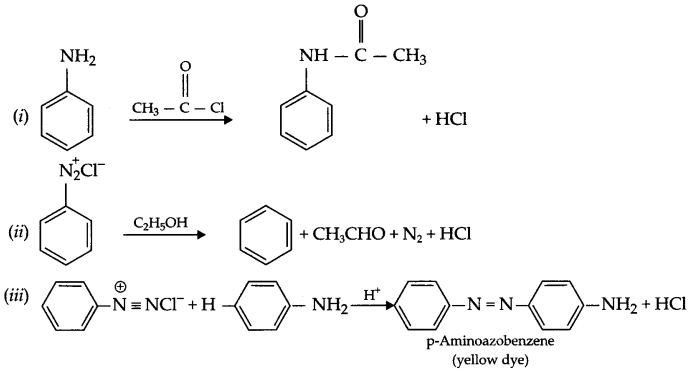
OR
- Methylamine reacts with water to produce OH– ion which combines with FeCl3 to give hydrated ferric oxide.
- CH3NH2 + H2O → CH3NH3 + OH–
- FeCl3 + OH– → Fe(OH)3 + 3Cl–
- Fe(OH)3 → Fe2O3 . xH2O
- The stability of arenediazonium ion is explained on the basis of resonance.
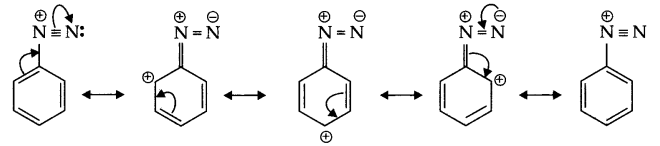
There is partial double bond character between benzene ring and nitrogen atom so these diazonium salts are stable at lower temperature. - Gabriel phthalimide synthesis gives pure primary amine and phthalic acid formed regenerated during reaction and it is solid hence can be easily separated.
Answer 15.
1. In macromolecular collides particles are of large enough size hence can form colloid easily. These are usually polymers.
On the other hand, in multimolecular colloids the smaller particles aggregated together to come in colloidal range e.g. sulphur sol, gold sol etc.
2. Peptisation: The process in which freshly prepared precipitate into colloidal sol by shaking it with suitable electrolyte in dispersion medium.
On the other hand, in coagulation colloidal system get precipitated out and get settled.
3. In electrophoresis particles of dispersed phase on passing electricity move toward electrode of opposite charge and causes coagulation.
When the process of dialysis that is, removing dissolved substance from a colloidal solution is carried out under applied electric field, it is known as electrodialysis.
Answer 16.
The dissociation of K4[FeCN)6] gives following ions

Concentration, C = 0.1 m, T = 300 K
Osmotic pressure, π = i CRT
π = 3 × 0.1 × 0.082 × 300
π = 7.38 atm.
Answer 17.
Conversion:
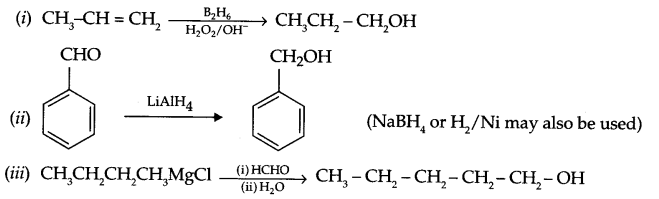
Answer 18.
Given :

Answer 19.
Since for addition of one Sr2+ ion two Na+ ion need to be displaced i.e. one vacancy will be created for each Sr2+ ion.
Concentration of cation vacancies = Concentration of Sr2+ ion = 6.022 × 1023 × \(\frac { { 10 }^{ -3 } }{ 100 } \) ions/mole of NaCl
= 6.022 × 1018 ions/mole of NaCl
Hence concentration of cation vacancies is 6.022 × 1018 vacancies/mole of NaCl
Answer 20.
- Froth stabilizers stabilizes the froth i.e. forms thick scum of froth. Some of the stabilizers used are cresol, aniline etc.
- It acts as flux and removes FeO impurity as slag FeSiO3, which can be easily removed.
FeO + SiO2 → FeSiO3 - Cryolite reduces melting point of Al2O3 and increases electrical conductivity. Molten cryolite acts as solvent for alumina (Al2O3).
Answer 21.
| Polymer | Use |
| (i) PVC | Waterpipes, rain coat manufacturing, hand bags |
| (ii) Bakelite | Electrical Switches, computer discs, handles of utensils |
| (iii) Nylon 6, 6 | Textile fibre, parachute making, heavy duty tyres. |
Answer 22.
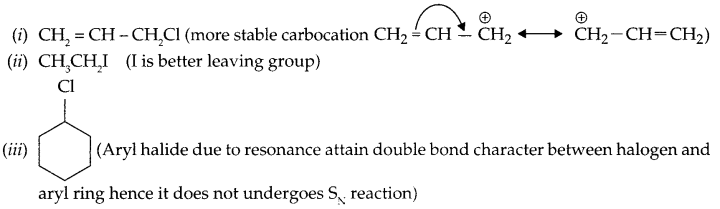
Answer 23.
- Caring nature, helpful
- Tranquilizers
- Most of the drugs taken in higher does may prove fatal and hence a doctor must be consulted before taking drugs.
- Phenelzine or iproniazid
Answer 24.
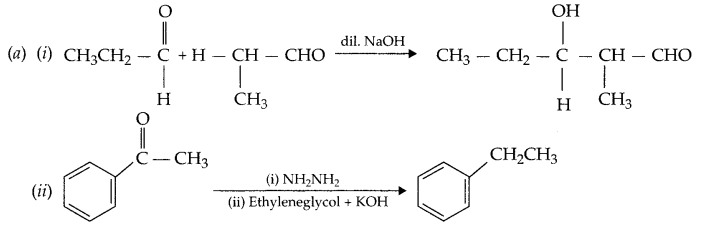
(b) 1.
Reagent | Ethanal | Propanal |
NaOH(aq) + I2 | Yellow ppt. of CHI3 form | No ppt. |
2.
| Reagent | Benzoic acid | Ethyl benzoate |
| NaHCO3(aq) | Brisk-effervescene due to release of CO2 | No reaction |
3.
Reagent | Benzaldehyde | Acetophenone |
Tollens’ reagent Ammoniacal AgNO3 and heat | Silver mirror will form on wall of test tube | No reaction |
OR
(a)
- There is more positive charge on carbonyl carbon in case of CH3CHO but in acetone due to +I-effect of two methyl group carbonyl carbon has less positive charge so less reactive towards HCN.
- Due to -I effect of nitro group, benzoate ion will be more stabilised so 4-nitrobenzoic acid is more acidic than benzoic acid.
(b) 1. Cannizzaro reaction: Aldehyde having no alpha hydrogen oxidised and reduced in presence of concentrated alkali.
![]()
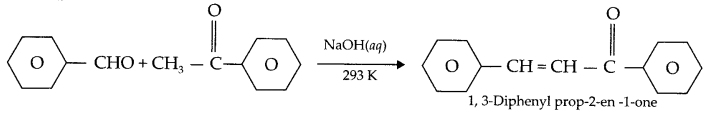
2. Cross aldol different condensation: When aldol condensation is carried out between two different aldehydes or two different ketones or one aldehyde and a ketone, even when one aldehyde does not contain α-hydrogen, such condensation reaction in presence of aqueous alkali is Known as cross aldol condensation. e.g.
3. Rosenmund Reaction: Acyl chloride is hydrogenated selectively to an aldehyde over catalyst, palladium on BaSO4. This reaction is called Rosenmund reduction.
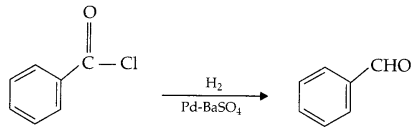
[Note in the named reaction statement does not required]
Answer 25
(a)
- Kohlrausch law: H states that limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte can be represented as the sum of the individual contributions of the cation and anion of the electrolyte.
- 6F
- Al2O → 2Al3+ + 3O2-
- 2Al3+ + 6e– → 2Al
So 6F is required for I mole of Al2O3.
(b) Cell reaction for given cell
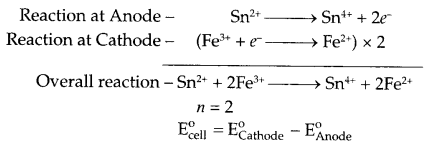
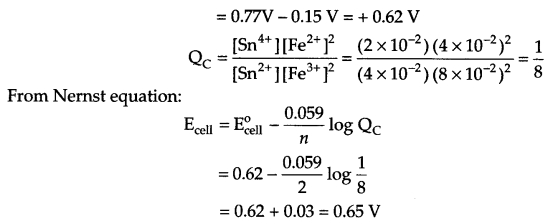
OR
(a)
- Molar conductivity (Δm): Molar conductivity of a solution at a given concentration is the conductance of the volume V of solution containing one mole of electrolyte kept between two electrodes with area of cross section A and distance of unit length i.e.
- Δm = \(k\frac { A }{ l } \) (where l = 1 and A = V volume containing 1 mole of electrolyte)
- Corrosion: It is tarnishing or eating away of any active metal under environmental factors. Usually metal oxides, hydroxides and carbonates are formed due to corrosion.
(b) Concentration = 0.01 Ω R = 1500 Ω
G* (cell constant) = ?
K (conductivity) = 0.416 × 10-3 S cm-1
Since, k = \(\frac { Cellconstant }{ R } \)
Cell constant = k × R
= 0.146 × 10-3 × 1500 = 0.219 cm-1
Answer 26.
(a)
- 2I– (aq) + O3(g) + H2O → I2(s) + O2(g) + 2OH–(aq)
- H3PO2 (aq) + NaOH (aq) → NaH2PO2 (aq) + H2O (l)
(b)
- Kr (Krypton)
- The reaction between iron and HCl produces H2 (gas) which prevents formation of ferric chloride.
Fe + 2HCl → FeCl2 + H2 - SF4 is more reactive than SF6 because in SF6, six F atom sterically protects sulphur atom. In SF4, H2O molecule can easily approach sulphur atom and can attack on it.
SF4 + 2H2O → SO2 + 4HF
OR
(a)
- Disproportionation reaction takes place in which chlorine from its zero oxidation state in Cl2 gets disproportionate into NaC103 (oxidised form) and NaCl (reduced form). The reaction is
3Cl2 + 6 NaOH (Hot and cone.) → NaClO3 + 5 NaCl + 3 H2O - XeF6 + SbF5 → [XeF5]+[SbF6]–
XeF6 loses its F– ion which is taken by SbF5 to form cationic and anionic species. Due to ionic species, this mixture will conduct electricity in molten state.
(b)
- Due to stronger S-S single bond than O-O single bond sulphur shows more catenation property.
- Due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding in NH3 its boiling point is more than PH3.
- Due to lack of d-orbital in F it forms only one oxoacid.
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 6 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 6, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
