CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 4 are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 4.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 4
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | XII |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 4 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 12 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme as prescribed by the CBSE is given here. Paper 4 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Chemistry is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time Allowed : 3 Hours
Max. Marks : 70
General Instructions
- All questions are compulsory.
- Question number 1 to 5 are very short answer questions and carry 1 mark each.
- Question number 6 to 10 are short answer questions and carry 2 marks each.
- Question number 11 to 22 are also short answer questions and carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 23 is a value based question and carry 4 marks.
- Question number 24 to 26 are long answer questions and carry 5 marks each.
- Use log table, if necessary. Use of calculators is not allowed.
Questions
Question 1.
1. Define F-centre.
Question 2.
According to Hardy Schulze rule arrange the following in increasing order of coagulating power.
PO3-4, Cl–, [Fe(CN)6]4-
Question 3.
Write harmful effects of tetrachloromethane.
Question 4.
Write down the IUPAC name of
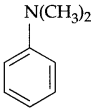
Question 5.
Which class of drugs is used in sleeping pills?
Question 6.
- How will you classify brass and steel?
- What are the factors that affect the solubility of a gas in a liquid?
Question 7.
How much Faraday’s of electricity is required for electrolysis of following
- 1 mol Al2O3 to Al
- 1 mol Cr2Cu2 to Cu
Question 8.
(a) Write two differences between order and molecularity of reaction.
(b) Define specific rate constant.
Question 9.
COCl3 . 4NH3 is the formula for an octahedral coordination compound. It does not liberate NH3 but forms a precipitate of AgCl on treatment with aqueous AgNO3 solution. Write the structure and IUPAC name of the complex.
OR
For the complex [NiCl4]– write
- Its IUPAC name
- Its hybridisation type
- The shape of the complex
Question 10.
Complete each synthesis by giving missing starting material reagents or products.
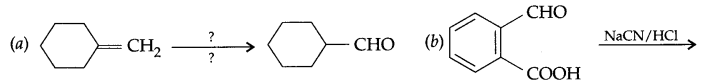
Question 11.
- Why do we require artificial sweetening agents?
- Which type of detergents are biodegradable?
- What are broad spectrum antibiotics?
Question 12.
(a) Why sulphur is added during vulcanisation of rubber?
(b) Name a thermosetting polymer.
(c) What is the significance of 6,6 in Nylon 6,6?
Question 13.
Write the Nernst equation and find emf of the following cell at 25°C.
Pt | Sn4+ (0.04 M), Sn2+ (0.03 M) || Fe3+ (0.08 M), Fe2+ (0.06 M) | Pt
Emf of half electrodes is
![]()
Question 14.
0.6 mL of acetic acid (CH3COOH) having density 1.06 g/mL is dissolved in 1 litre of water. The depression in freezing point observed for this is 0.0205°C. Calculate van’t Hoff factor and the dissociation constant for the acid.
OR
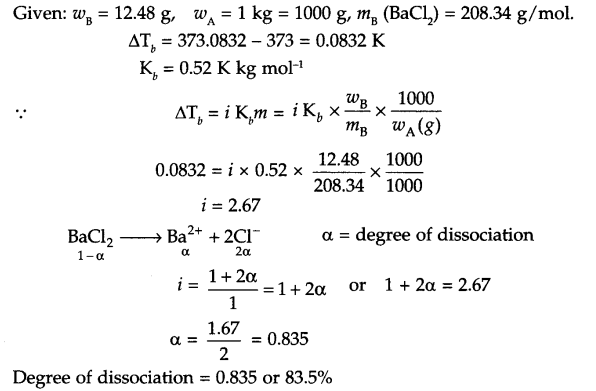
An aqueous solution containing 12.48 g of BaCl2 in 1.0 kg of water boils at 373.0832 K. Calculate the degree of dissociation of BaCl2 (Given, Kb for the water = 0.52 K kg mol-1, molar mass of BaCl2 = 208.34 g/mol).
Question 15.
(a) Carboxylic acids are acidic in nature. Give reason.
(b) Explain following name reactions with suitable example:
(i) Aldol condensation
(ii) Cannizzaro’s reaction
Question 16.
Account for the following:
(a) NH2 group of aniline is acylated before carrying out nitration.
(b) pKb of aniline is more than that of methylamine.
(c) Ethylamine is soluble in water whereas aniline is not.
Question 17.
Rate constant A: of a reaction varies with temperature ‘T’ according to the equation
log k = log A – \(\frac { { E }_{ a } }{ 2.303R } (\frac { 1 }{ T } )\)
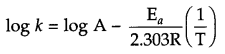
Where Ea is the activation energy. When a graph is plotted for log k is \(\frac { 1 }{ T }\) a straight line with slope of -4250 K is obtained. Calculated Ea for this reaction (R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1)
Question 18.
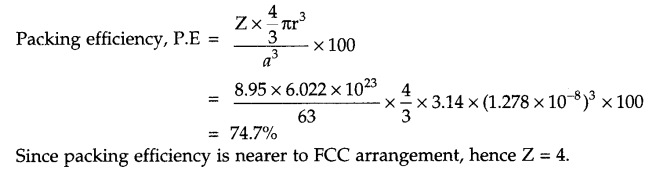
The density of copper metal is 8.95 g/cm3 and radius of its atom is 127.8 pm. Which type of unit cell occur in copper metal according to the above information?
Question 19.
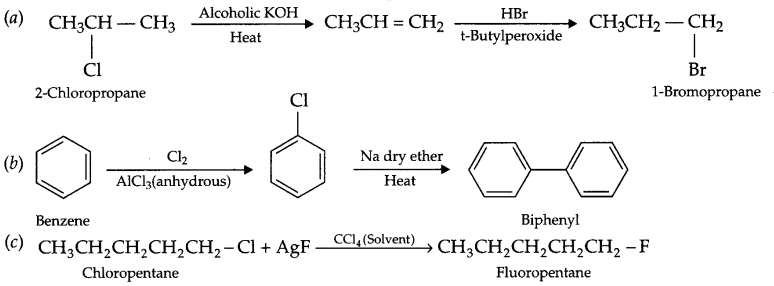
How will you convert the following:
(a) 2-Chloropropane to 1-Bromopropane
(b) Benzene to biphenyl
(c) Chloropentane to fluoropentane
Question 20.
- What will be the observed change when concentration of soap increases in its aqueous solution?
- Define zeta potential.
- What leads to hardening of lather on tanning?
Question 21.
Arrange the following in increasing order of property indicated for each set:
- H2O, H2S, H2Te, H2Se (acidic strength)
- NH3, SbH3, BiH3, AsH3 (basic strength)
- F2, Cl2, Br2, I2 (Bond dissociation enthalpy)
Question 22.
(a) Name the deficiency diseases caused due to lack of vitamin A and E in the diet.
(b) Name the component of starch which is water soluble.
Question 23.
Malti a housewife used to get his gold jewellary cleaned by a goldsmith at no cost. Her daughter Rekha, a chemistry student once accompanied her mother to the jeweller’s shop where she observed that goldsmith used to keep all jewellery in a solution and then return it after washing, so she asked her mother to avoid such cleaning.
Answer following questions as per above passage.
- What chemical did you think in which jewelleries were dipped?
- Which substance goldsmith used to recover gold from solution?
- What is the IUPAC names of complex formed with added substance and content of the solution?
- What are the values associated with Rekha’s advice?
Question 24.
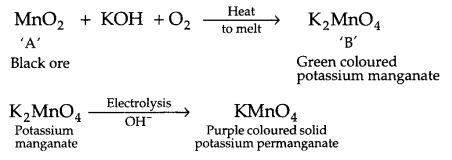
(a) A black coloured ore -A on fusion with alkali metal hydroxide in presence of air, produce a green coloured compound -B, which on electrolytic oxidation in alkaline medium gives a dark purple coloured compound ‘C’. Identify compound A, B and C and write the reactions involved.
(b)
- Hf and Zr have nearly same size. Give reason.
- Name an alloy of lanthanoids.
OR
- CuCl is colourless in solid state but turns blue in aqueous solution, give reason.
- Calculate the spin only magnetic moment for Ti in TiCl3.
- Name two transition metal ions of first series which always form colourless compound.
- Give two uses of mischmetal.
- What are different oxidation states exhibited by lanthanoids?
Question 25.
Give suitable reason for the following:
- PCl5 conducts electricity in molten state.
- Sulphur exhibits greater tendency for catenation as compared to oxygen.
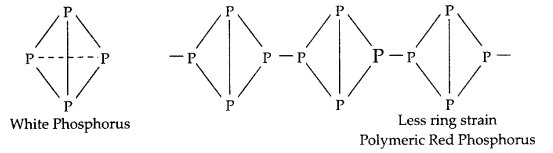
- White phosphorus is more reactive than red phosphorus.
- Bi5+ acts as oxidising agent.
- SF4 is more reactive than SF6.
OR
Assign reason for the following:
(a)
- SF6 is known but SH6 is not.
- R3P = O exists but R3N = O is not.
(b) Draw shape of ICl–2 ion.
(c) Complete the following chemical reactions:
- C6H12O6 \(\underrightarrow { { H }_{ 2 }{ SO }_{ 4 } } \)
- ClO–3 + Cl– \(\underrightarrow { { H }^{ + } }\)
Question 26.
(a) Distinguish between the following pairs with a suitable chemical test:
(i) Benzyl alcohol and phenol
(ii) Methanol and propan-2-ol
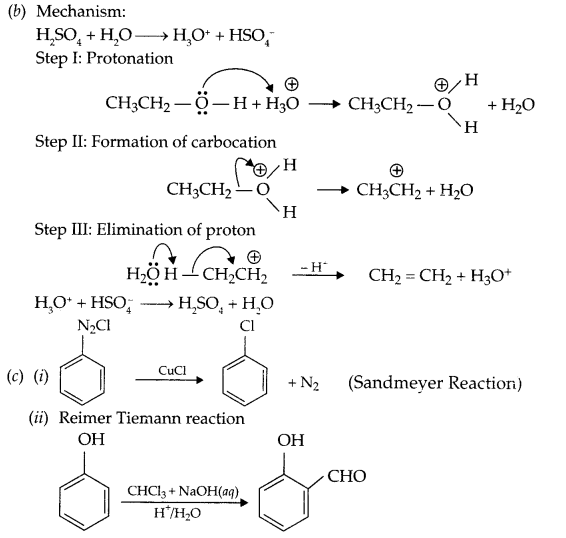
(b) Write mechanism for the following reaction:
C2H5OH \(\xrightarrow [ heat ]{ { ConcH }_{ 2 }{ SO }_{ 4 } }\) CH2 = CH2
(c) Write chemical reaction to illustrate the following named reactions:
(i) Sandmeyer’s reaction
(ii) Reimer Tiemann reaction.
OR
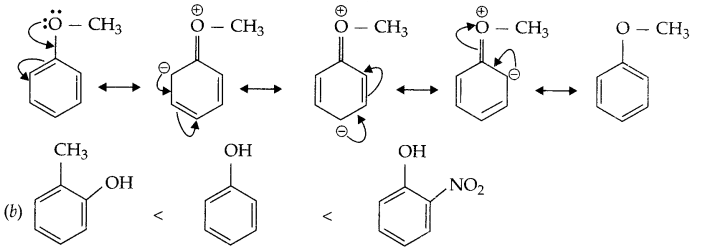
(a) Explain the fact that methoxy group present on benzene ring in anisole activates it towards electrophilic substitution reaction.
(b) Arrange according to increasing order of acidic nature.
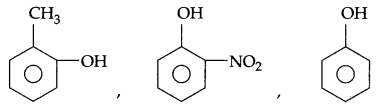
(c) Alcohols have higher boiling point than corresponding ethers. Give reason.
(d) Out of ortho and para nitrophenol which one is steam volatile and why?
Answers
Answer 1.
The lattice site where instead of a negative ion, an electron is accommodated for electrical neutrality is known as F-centre (such centres are responsible for generation of colour in crystal).
Answer 2.
Increasing order of coagulating power is based on the fact that higher the charge on the ion, higher will be its coagulating power.
Cl– < PO3-4 < [Fe(CN)6]4-
Answer 3.
Tetrachloromethane causes liver cancer in human, dizziness, coma, irregular heart beat, eye irritation and it also depletes the ozone layer, (any one of two effects only).
Answer 4.
N, N-Dimethylaniline
Answer 5.
Tranquilizer
Answer 6.
- Brass is a substitutional solid solution whereas steel is interstitial solid solution.
- Factors affecting solubility in a liquid are temperature, pressure of gas, nature of gas and nature of solvent.
Answer 7.
- Al2O3 → 2Al3+
2Al3+ + 6e– → 2Al
Thus, 6F of electricity is required. - Cu2Cl2 → 2Cu+
2Cu+ + 2e– → 2Cu
Thus, 2F of electricity is required.
Answer 8.
(a)
Order | Molecularity |
It is determined from rate law equation which is set on the basis of experiment. | It is determined from law of mass action equation based on balanced chemical reaction. |
| It may be positive, negative, zero or fractional. | It will be positive integer only it cannot be negative, zero or a fractional number. |
(b) It will be equal to rate of reaction when concentration of all reactants is unity.
Answer 9.
Structure of complex is [Co(NH3)4Cl2] Cl
Name: Tetraamminedichloridocobalt(III) chloride.
OR
- Tetrachloridonickelate(H) ion
- sp3
- Tetrahedral
Answer 10.
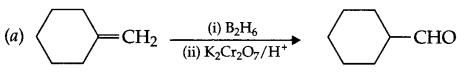
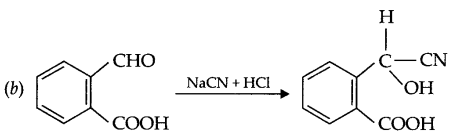
Answer 11.
- For diabetic patients, artificial sweetners are required because they provide sweetness in food like sugar but no calories are added to our body by such agents.
- The detergents having unbranched alkyl chain are biodegradable.
- The antibiotic which acts on both gram positive and gram negative bacteria and so used to cure wide range of diseases are known as broad spectrum antibiotics.
Answer 12.
(a) Sulphur added during vulcanisation forms cross link at the reactive sites of double bonds and thus the rubber gets stiffened. 5% sulphur is added for manufacturing of tyre.
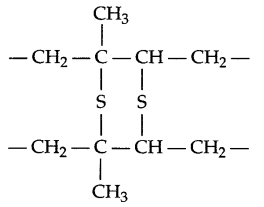
(b) Bakelite, melamine. (Any one)
(c) 6, 6 represent two monomers having 6 carbon in each. These monomers are as follows:
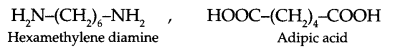
Answer 13.
For the given cell, half reactions at cathode and anode are as follows:

Ecell = 0.62 – \(\frac { 0.059 }{ 2 } \) (-0.1250)
Ecell = 0.62 + 0.004 = 0.624 V
Answer 14.

Answer 15.
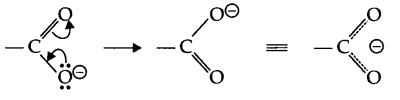
(a) Carboxylate ion formed after releasing H+ ion from carboxylic acid is resonance stabilised, hence carboxylic acids are acidic in nature.
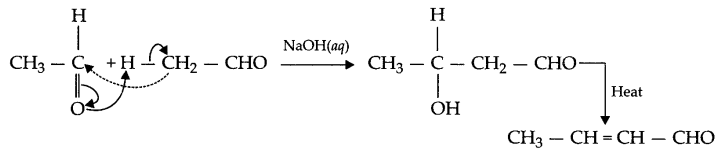
(b) (i) Aldol condensation : Aldehydes and ketones having “α-hydrogen” get condensed in the presence of aq. alkali to give β-hydroxy aldehydes or β-hydroxy ketones.
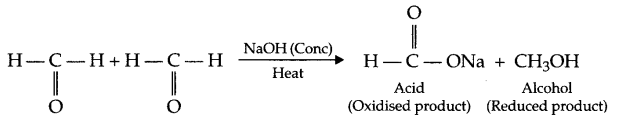
(ii) Cannizzaro reaction : The aldehyde having no alpha (a) hydrogen get oxidised and reduced in the presence of concentrated (50% NaOH solution) alkali. This disproportionation reaction is known as Cannizzaro reaction.
Answer 16.
(a) NH2 group of aniline is acetylated so that controlled nitration can be carried out at para position only, otherwise a mixture of ortho, meta and para products will form.
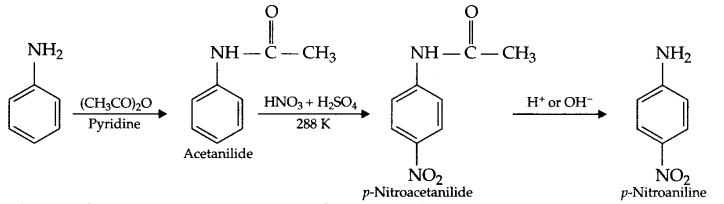
(No need to write reaction to answer this question).
(b) Aniline is a weaker base than methylamine due to its lone pair is involved in resonance and develops a positive charge on nitrogen of aniline. Also, aryl group is electron withdrawing through-R effect. So pKb of aniline is more than methylamine.
(c) Ethylamine is soluble in water because it can form H-bonding with water whereas aniline posses hydrophobic aryl group. Also electron pair of nitrogen is involved in resonance, hence it cannot form hydrogen bonding with water. So aniline is insoluble in water.
Answer 17.
log k vs 1/T graph for given equation will be
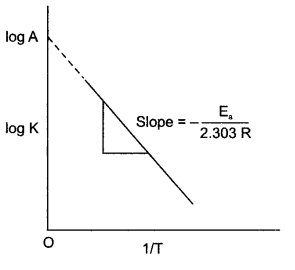
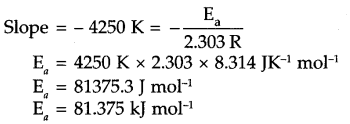
Answer 18.
Radius of atom = 127.8 pm
= 127.8 × 10-10 cm
Density = 8.95 g/cm3
Molar mass = 63 g/mol
Z = ?
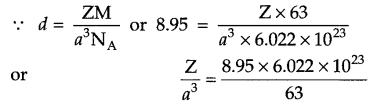
Answer 19.
Answer 20.
- At lower concentration soap dissolved in water acts as true electrolyte but on increasing the concentration it will form a colloidal solution known as micelle.
- The potential difference between the fixed layer of dispersed phase and the diffused layer of opposite charges in called zeta potential.
- Animal hide, which has positively charged particles is soaked in tannin, which contains negatively charged colloidal particles, mutual coagulation takes place. This results in the hardening of leather.
Answer 21.
- H2O < H2S < H2Se < H2Te
- BiH3 < SbH3 < AsH3 < NH3
- I2 < F2 < Br2 < Cl2
Answer 22.
(a)
Vitamin | Deficiency disease | Sources |
A | Xerophthalmia/Night blindness | Fish, cod-liver oil, carrot |
| E | Muscular weakness | Sunflower oil |
(b) Amylose is water soluble component of starch.
Answer 23.
- NaCN or KCN solution
- Zinc dust
- Au + NaCN → Na [Au(CN)2]
IUPAC name is Sodium dicyanidoaurate (I). - Concern for family, knowledge of chemistry, keen observation.
Answer 24.
(a) The dark black coloured ore is pyrolusite which on processing gives purple coloured compound ‘C’ which is potassium permanganate. The reaction involved is
(b)
- Due to lanthanoid contraction.
- Mischmetal (95% lanthanoids + 5% iron)
OR
- CuCl3 get disproportionate in aqueous solution due to high hydration energy for Cu2+ and so turns blue in colour.
Cu+ \(\underrightarrow { { H }_{ 2 }O } \) Cu2+ + Cu - Spin only magnetic moment = \(\sqrt { n(n+2) } \) BM, where n is number of unpaired electrons
TiCl3 → Ti3+ → 3d1 configuration i.e. 1 unpaired electron
Magnetic moment = \(\sqrt { 1(1+2) } \) = √3 = 1.732 BM - Zn2+
- Used to produce bullets, shells, lighter flint.
- General oxidation state of lanthanoids is +3. +2 oxidation state is observed in Eu and Yb, some elements also show +4 oxidation state like Ce.
Answer 25.
- In solid state PCl5 exists as [PCl4]+ and [PCl6]– ions, hence conducts electricity in molten state.
- S-S single bond is stronger than O-O single bond. In
 there is lone pair-lone pair repulsion which weakens this bond so least chances of catenation.
there is lone pair-lone pair repulsion which weakens this bond so least chances of catenation.
- In P4 tetrahedral unit of white phosphorus there is high ring strain, hence it is more reactive as compared to polymeric red phosphorus.
- Bi3+ is more stable than Bi5+ due to inert pair effect, hence Bi5+ acts as an oxidising agent.
In SF6, Sulphur is sterically surrounded by six fluorine atoms so cannot be approached by lone pair of water so it cannot be hydrolysed, whereas SF4 can be easily approached and thus get hydrolysed.- SF4 + 2H2O → SO2 + 4HF
OR
(a)
- Sulphur is more electropositive than fluorine but less electropositive than H, hence only possible compound with hydrogen is H2S and not SH6.
- There is vacant d-orbital is available in P so dπ-pπ bond is possible between phosphorus and oxygen, whereas it is not possible between N and O. So R3N = O is not likely to form.
(b)
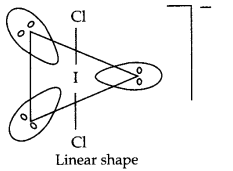
(c)
- C6H12O6 \(\underrightarrow { { ConcH }_{ 2 }{ SO }_{ 4 } } \) 6C + 6H2O
- ClO–3 + Cl– \(\underrightarrow { { H }^{ + } }\) Cl2 + ClO2
Answer 26.
(a) (i)
Reagent | Benzyl alcohol | Phenol |
Na metal | Bubble of H2 evolves | No H2 bubbles |
| Neutral FeCl3 | No reaction | Dark coloured(green,grey-violet) complex forms. |
(ii)
Reagent | Methanol | Propan-2-ol |
| I2 + NaOH(aq) + Heat | No yellow Precipitation | Yellow precipitation of CHI3 will form. |
OR
(a) In resonance structure of anisole there is negative charge on ortho and para position, so -OCH3 activates benzene ring for electrophilic substitution reaction.
(c) Due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding between alcohol molecules as compared to weaker dipole-dipole interactions in other molecules, alcohols have higher boiling point.
(d) Ortho nitrophenol will be steam volatile due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding as compared to intermolecular hydrogen bonding in para nitrophenol.
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 4 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 4, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
