CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 3 are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 3.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 3
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | XII |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 3 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 12 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme as prescribed by the CBSE is given here. Paper 3 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Chemistry is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time Allowed : 3 Hours
Max. Marks : 70
General Instructions
- All questions are compulsory.
- Question number 1 to 5 are very short answer questions and carry 1 mark each.
- Question number 6 to 10 are short answer questions and carry 2 marks each.
- Question number 11 to 22 are also short answer questions and carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 23 is a value based question and carry 4 marks.
- Question number 24 to 26 are long answer questions and carry 5 marks each.
- Use log table, if necessary. Use of calculators is not allowed.
Questions
Question 1.
What is the role of desorption in the process of catalyst?
Question 2.
Write IUPAC name of the following ether pO2N-C6H4-OCH3.
Question 3.
How many ions are produced from the complex [CO(NH3)5(NO2)]Cl in aqueous solution?
Question 4.
What is the role of Zn in the extraction of silver?
Question 5.
What is the type of charge on Agl colloidal sol so formed when KI solution is added to AgNO3 solution?
Question 6.
- What is the formula of a compound in which element Y forms hep lattice and atoms of X occupy 1/3 rd of the octahedral voids?
- Why is frenkel defect not found in pure alkali metal halides?
Question 7.
Calculate E°Cell and ΔrG° for the following reaction at 25°C
A2+ + B+ → A3+ + B, if Kc = 1010 and 1F = 96500 C mol-1
OR
A copper-silver cell is set up. The copper ion concentration is 0.10 M. The Ecell = 0.422 V.
Determine the concentration of [Ag+] in the cell if
![]()
Question 8.
Aluminium crystallises in a cubic close packed structure. Its metallic radius is 125 pm.
(a) What is the length of the side of the unit cell?
(b) How many unit cells are there in 1 cm3 of aluminium?
Question 9.
Draw the structure of following molecules.
(a) PCl+4
(b) XeF+5
Question 10.
A solution is prepared by dissolving 5 g of a non volatile solute in 95 g of H2O, gives a vapour pressure of 23.375 mm Hg at 25°C. Calculate the molar mass of the solute. (P0H2O = 23.75 mm Hg at 25°C).
Question 11.
- What is copper matte?
- Give the principle of electrolytic refining of metal.
- Name the method used to get silicon of high purity.
Question 12.
Complete the following reaction:
- Zn + HNO3 (dilute) →
- Br2 + F2 →
- I–(aq) + O3 (g) →
Question 13.
Give reason for the following:
- Haloalkanes easily dissolve in organic solvents.
- n-Butyl bromide has higher B. pt than f-butyl bromide.
- Vinyl chloride is unreactive in substitution nucleophilic reactions.
Question 14.
Complete the following reactions:
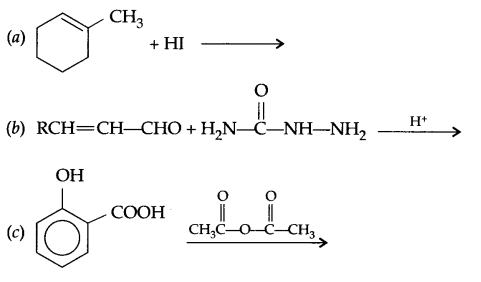
Question 15.
Explain how the phenomenon of adsorption finds application in each of the following processes :
- Production of vacuum
- Heterogeneous catalysis
- Froth floatation process
Question 16.
Define conductivity and molar conductivity for the solution of an electrolyte. Discuss their variation with concentration.
Question 17.
- Two liquids A and B on mixing produce a warm solution. Which type of deviation from
Raoult’s law does it show? - Define vapour pressure.
- Which will give more elevation in boiling point: 1 m Na2SO4 or 1 M NaCl?
Question 18.
Give reason for
- Actinoids show variable oxidation state.
- Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction.
- Compounds of Mn2+ ions are only faintly coloured.
OR
Give explanation for:
- Zn, Cd and Hg are of low melting point.
- Transition metals form alloys.
- Chromium shows maximum melting point.
Question 19.
(a) Draw optical isomer of [Cr (NH3)2 Cl2(en)]+.
(b) [Cr(NH3)6]3+ is paramagnetic while [Co(CN)6]3- is diamagnetic, give reason.
Question 20.
Give reason for the following:
- Most of the known noble gas compounds are those of Xe.
- Write formula of any oxoacid of sulphur.
- Sulphur has higher tendency for catenation than O or Se.
Question 21.
- Write the names and structure of the monomers of the following polymers:
- Neoprene
- Novolac
- Define copolymerisation
Question 22.
- How do antiseptics differ from disinfectants?
- Name two major classes of antibiotics.
- What are biodegradable and non biodegradable detergents?
Question 23.
Anita’s mother was suffering from diabeties and thyroid. She suggested her mother to take protein rich diet as well as green vegetables and in the mean time she suggested her to minimise the intake of carbohydrates. It showed improvement in her mother’s condition. Answer the following questions in the light of above passage:
- Name the hormones whose deficiency causes diabeties and thyroid.
- How do green vegetables help in thyroid problem?
- What values are possessed by Anita?
Question 24.
(a) The rate constant for the decomposition of a hydrocarbon is 2.418 × 10-5 s-1 at 546 K. If the energy of activation is 179.9 kJ mol-1 what will be the value of pre-exponential factor?
(b) Write two factors which affects the rate of a chemical reaction.
OR
(a) A first order reaction take 100 minutes for the completion of 60% of the reaction. Find the time in which 90% of the reaction will be completed.
(b)
- Define specific rate constant.
- What is the half life period for a reaction?
Question 25.
Explain the following name reactions with suitable chemical reaction(s):
(a) (i) Clemmensen’s reduction
(ii) HVZ reaction
(b) Carry out the following conversions (in not more than two steps).
(i) Ethanal to propan-2-ol
(ii) Phenol to salicylic acid
(iii) Methanal to 3-hydroxy propanal
OR
(a) Distinguish between the following pairs with a suitable example:
(i) Ethanol and ethanal
(ii) Phenol and benzoic acid
(iii) Benzophenone and acetophenone
(b) (i) Write the mechanism for addition of HCN in ethanal.
(ii) Write the mechanism of acid hydrolysis of ethene to give ethanol.
Question 26.
Arrange the following in increasing order as property indicated against each set:
(a)
- C2H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH, (C2H5)3 N and NH3 (Basic strength in gaseous phase)
- C2H5OH, (CH3)2 NH, C2H5NH2 (Boiling point)
- C6H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH, C2H5NH2 (Solubility in water)
(b) Write reaction of HNO2 with
(i) C6H5NH2
(ii) C2H5NH2
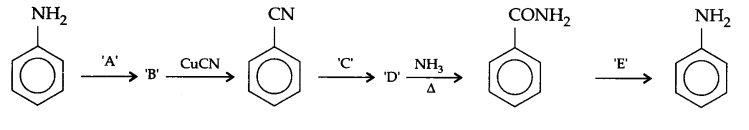
OR
Complete the following reaction sequence :
Answers
Answer 1.
In catalysis reactants get absorbed on the surface of the catalyst and after product formation, these needs to be released from the surface so that new reactant can take its place. So desorption is as necessary as adsorption in the process of catalysis.
Answer 2.
4-Nitro anisole or 4-Nitromethoxy benzene.
Answer 3.
Two ions
[CO(NH3)5 NO2] Cl → [CO(NH3)5 NO2]+ + Cl–
Answer 4.
Zinc displaces silver from its complex with NaCN.
![]()
Answer 5.
Positive charge will appear on the dispersed phase due to adsorption of Ag+ ions on AgI.
Answer 6.
- X3Y
- Due to comparable size of cation and anion no ion can be displaced in the interstitial space, hence frenkel defect is not possible in alkali metal halides (Alkali metal ions are of larger size).
Answer 7.
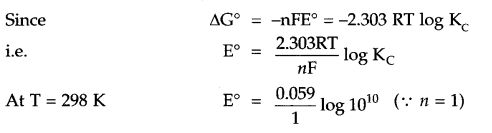
E0 = 0.59V
ΔG0 = -nFE0
= -1 × 96500 × 0.59 = 56935 J = 56.935 KJ
OR
Copper will get oxidised due to less positive reduction potential, so
Reaction at anode – Cu(s) → Cu2+ (aq) + 2e
Reaction at cathode – Ag (aq) + e → Ag (s) × 2
Net cell reaction – 2Ag+(aq) + Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
At T = 298 K, Nemst equation is:
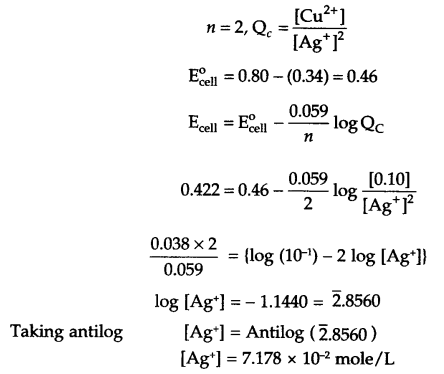
Answer 8.
Aluminium exist in ccp arrangement, i.e. fee unit cell, so
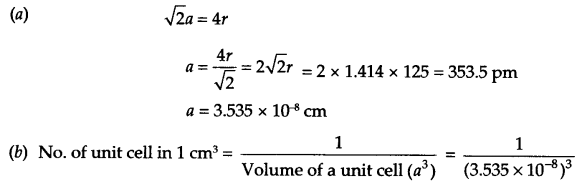
Answer 9.
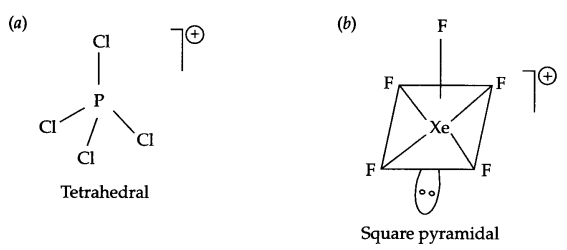
Answer 10.
Mass of solute (wB) = 5 g
Mass of solvent (wA) = 95 g
Vapour pressure of solution = 23.375 mm Hg
Vapour pressure of solvent = 23.75 mm Hg
Molar mass of solute (mB) = ?
From relative lowering in vapour pressure
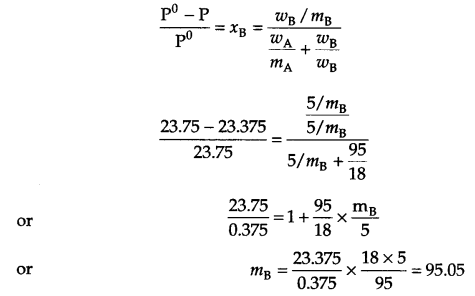
Answer 11.
- Copper matte contains Cu2S (cuprous sulphide and little quantity of FeS (iron sulphide).
- More basic metal (metal having more negative or less positive reduction potential) will come into the solution ind get reduced at cathode, it is the principle of electrolytic refining.
- Zone refining
Answer 12.
- 4Zn + 10HNO3 (dil) → 4Zn(NO3)2 + N2O + 5H2O
- Br2 + F2 → BrF5
- 2I–(aq) + O3(g) → I2 + O2
Answer 13.
- The intermolecular forces exists between haloalkane is of comparable strength as that of organic solvents and haloalkanes, hence haloalkanes easily get dissolved in organic solvents.
- n-Butyl bromide has larger surface area as compared to t-butyl bromide, hence there is stronger van der walls attraction among molecules of n-butyl bromide, so it has more boiling point.
- Due to resonance there is partial double bond character in the bond between C and chlorine, hence substitution nucleophilic reaction is not posible.
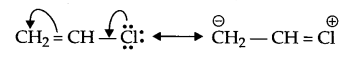
Answer 14.
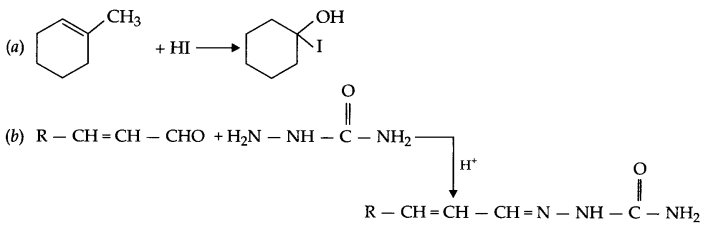
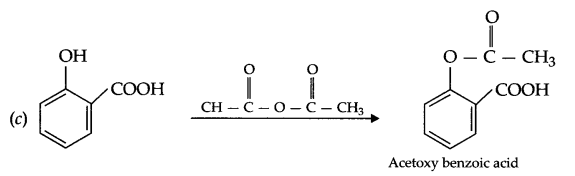
Answer 15.
- Production of vacuum : Remaining gas present in a vessel after creation of vacuum can be absorbed on the surface of charcoal, so that more efficient vacuum can be produced.
- Heterogeneous catalysis : In such catalysis, reactants get adsorbed on the surface of catalyst so that collision among the reactant molecules increases as well as the enthalpy of adsorption is utilised in providing the activation energy to reactants to undergo the reaction.
- Froth floatation process : Ore particles get adsorbed on the surface of pine oil, hence they can be separated as froth by blowing air through it.
Answer 16.
Conductivity : The reciprocal of resistivity is conductivity. Conductivity is the conductance of the electrolytic solution (due to the movement of ions and electrons) of one metre length
and unit area of cross section. Mathematically, conductivity, K = \(\frac { 1 }{ p } \).
Conductivity varies with concentration. As the number of ions per cm3 of solution decreases, conductivity decreases.
Molar conductivity : The conductivity of one molar electrolytic solution is termed as molar conductivity. Mathematically,
Molar conductivity (Δm) = \(\frac { k }{ c } \),
where c = concemtration (in mol m-3)
K = conductivity (in S m-1)
It should be noted that for strong electrolytes there is only a small increase in Δm value with dilution. However for weak electrolytes, there is a large increase in Δm value with dilution.
Answer 17.
- Negative deviations : This is because the vapour pressure, on mixing A and B is lower than the vapour pressure of component liquids A and B of solution.
- Vapour pressure : At a particular temperature, pressure exerted by vapours of a liquid on its surface when vapour is in equilibrium with its liquid is known as vapour pressure.
- 1 m Na2SO4 (Due to more number of ions colligative property will be more).
Answer 18.
- Due to comparable energy of 5f, 6d and 7s orbitals actinoids show variable oxidation state.
- 5f orbitals has poorer shielding effect than 4f orbitals, hence actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction.
- In Mn2+ ions there are five unpaired electrons. On d-d transition (from t2g to eg) pairing of electrons takes place, hence compounds of Mn2+ ions are faintly coloured.
OR
- Zn, Cd and Hg do not have any impaired electron as well as their metallic radii is larger, hence metal-metal bonds are weaker and as a result these elements have low melting point.
- The atomic radii of transition metals as well as the property of filling up of interestial spaces by non-metallic elements (e.g. H,B,C) in the attice sites of transition elements favours them for alloy formation.
- Chromium and other elements of this group have maximum number of impaired electrons so metal-metal bond is quite stronger, as a result these elements have high melting point.
Answer 19.
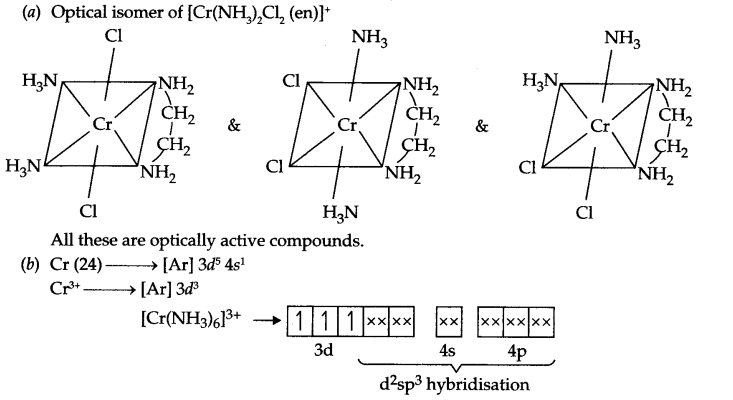
Through NH3 is a strong field ligand but there are three unpaired electrons present, so it will be paramagnetic. In [Co(CN)6]3-, CN– is also a strong field ligand but due to 3d6 configuration in Co3+, pairing takes place and the arrangement of electron pairs for [Co(CN)6]3- is:
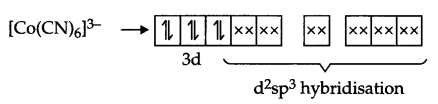
Answer 20.
- Xenon is largest in size among all the noble gas atoms and hence it has lowest ionisation energy, as a result of which most of the compounds are of xenon only.
- In oxygen there is lone pair-lone pair repulsion, so weaker O-O bond. Also, the single bond between Se-Se is weaker due to larger size of Se-atom. Sulphur of being suitable size makes stronger S-S bond and hence shows maximum catention property.
- H2SO4
Answer 21.
- Neoprene
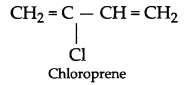
- Novolac → Phenol + HCHO
- Neoprene
- The polymerisation process in which there are two or more different monomers combined together to form a polymer is known as copolymerisation.
Answer 22.
- Both antiseptics and disinfectants are used to kill the microorganisms. Antiseptics are applied on living tissues whereas disinfectants are used on non-living objects.
- Broad spectrum and narrow spectrum antibiotics.
- Biodegradable detergent are decomposed by the microorganisms whereas non biodegradable detergents do not get decomposed by the microorganisms. Biodegradable detergents posses straight allyl chain, but non biodegradable detergents possess branched allyl chain on allyl benzene sulphonate.
Answer 23.
- Diabetes → Insulin
Thyroid → Thyroxin - Green vegetables posses iodine and other diserable minerals.
- Concern for the health of her mother, love for mother, knowledge of chemistry, caring attitude.
Answer 24.
(a) Since
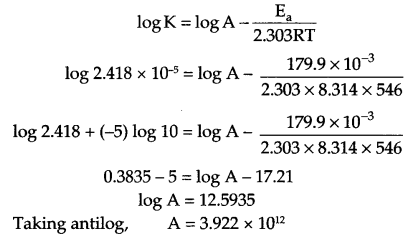
(b) Factors affecting the rate of reaction:
- Temperature
- Concentration
- Pressure
- Catalyst
OR

(b)
- Specific rate constant : It is the rate of reaction when concentration of all the reactants present in the rate law equation is unity.
- Half life period : It is the time required in which half of the reactant gets converted into product.
Answer 25.
(a) (i) Clemmensen’s Reduction : The carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones get reduced to CH2 group on treatment with zinc/sodium amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid.
![]()
(ii) HVZ reaction : Carboxylic acid having an α-hydrogen is halogenated at the α-position on treatment with chlorine or bromine in the presence of small amount of red phosphorous to give “α-halocarboxylic acid”.
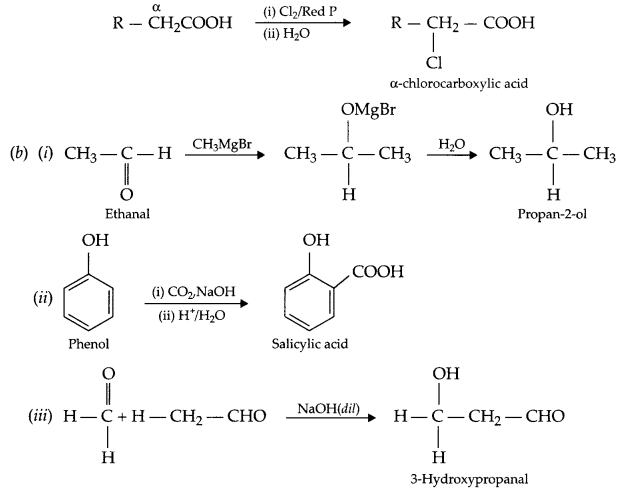
OR
(a) (i)
Reagent | Ethanol | Ethanal |
Na metal | H2 gas evolved | No evolution of H2 gas |
(ii)
Reagent | Phenol | Benzoic acid |
| NaHCO3 (aq) | No evolution of CO2 gas | CO2 gas evolves |
(iii)
| Reagent | Benzophenone | Benzoic acid |
| I2 + NaOH (aq) heat | No precipitate | Yellow precipitate of CHI3 forms |
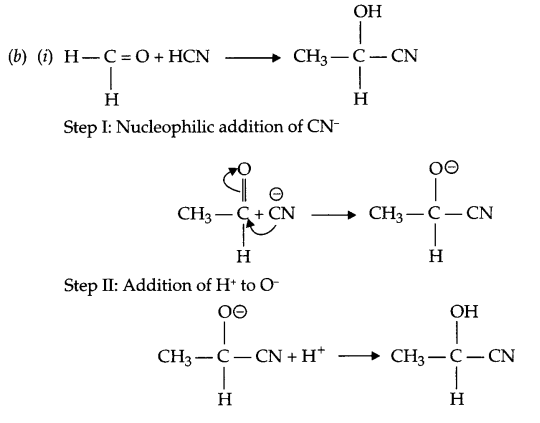
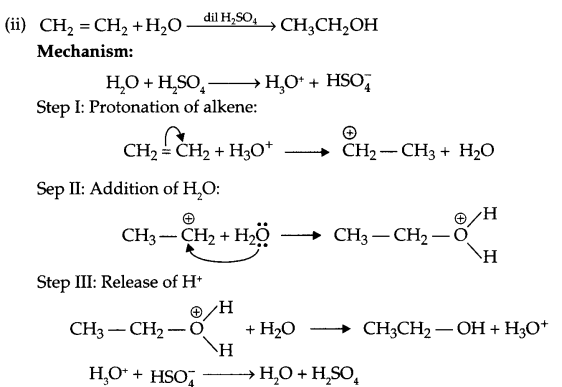
Answer 26.
(a)
- NH3 < CH3CH2NH2 < (CH3CH2)2 NH < (CH3CH2)3N
- (CH3)2NH < C2H5NH2 < CH3CH2OH
- C6H5NH2 < (C2H5)2NH < C2H5NH2
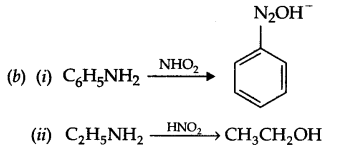
OR
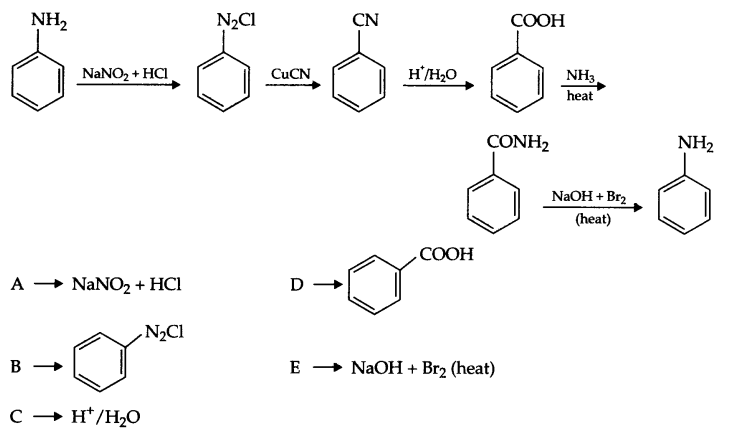
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 3 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 3, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
