CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 1 are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 1.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 1
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | XII |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 1 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 12 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme as prescribed by the CBSE is given here. Paper 1 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Chemistry is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time Allowed : 3 Hours
Max. Marks : 70
General Instructions
- All questions are compulsory.
- Question number 1 to 5 are very short answer questions and carry 1 mark each.
- Question number 6 to 10 are short answer questions and carry 2 marks each.
- Question number 11 to 22 are also short answer questions and carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 23 is a value based question and carry 4 marks.
- Question number 24 to 26 are long answer questions and carry 5 marks each.
- Use log table, if necessary. Use of calculators is not allowed.
Questions
Question 1.
Name the transition element which does not exhibit variable oxidation state.
Question 2.
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
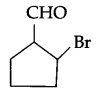
Question 3.
For a reaction R → P, half life is observed to be directly proportional to initial concentration of reactants. What is the order of the reaction?
Question 4.
Write structure of 2, 4-dinitrophenyl hydrazone of benzaldehyde.
Question 5.
In the given graph of Freundlich isotherm, which parameter is represented by the slope of the line?
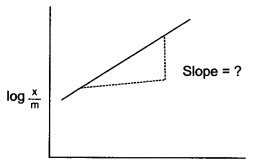
Question 6.
Complete the following reactions:
- FeCl3 + NH4OH →
- XeF4 + H2O →
OR
- Ba(N3)2 Heat→
- NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2 →
Question 7.
Define the following terms:
- Osmotic pressure
- Hypertonic solution
Question 8.
Draw the structures of the following
(a) BrF3
(b) H2SO5
Question 9.
- How much electricity in terms of Faraday is required for reduction of 1 mol of MnO–4 to MnO2?
- Predict the product of electrolysis of AgNO3 using platinum electrode.
Question 10.
Write the equation involved in the following reactions:
- Carbylamine reaction
- Diazotisation reaction
Question 11.
Calculate (a) molality, (b) molarity and (c) mole fraction of KI if the density of 20% by mass aqueous KI solution is 1.2 g/ml.
Question 12.
Resistance of a conductivity cell filled with 0.1 mol L-1 KCl solution is 100 Ω. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.02 mol L-1 KCl solution is 520 Ω, calculate the conductivity and molar conductivity of 0.02 mol L-1 KCl solution. The conductivity of 0.1 mol L-1 KCl solution is 1.29 S/m.
Question 13.
Explain how the two complexes of nickel, [Ni(CN)4]2- and [Ni(CO)4] have different structures but have the same magnetic behaviour.
Question 14.
Write one difference in each of the following:
- Chemisorption and physisorption
- Reversible and irreversible sols
- Multimolecular and macromolecular colloids
Question 15.
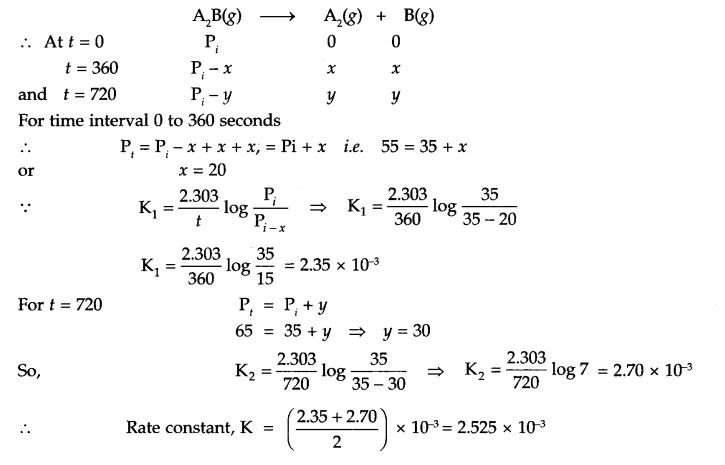
For the following decomposition reaction at 500 K, following data are obtained:
A2B(g) → A2(g) + B(g)
| t(sec) | P(mm Hg) |
| 0 | 35 |
| 360 | 55 |
| 720 | 65 |
Calculate the rate constant.
Question 16.
Identify X,Y and Z in the following reaction:
![]()
Question 17.
- What is the significance of addition of NaCN in froth flotation process?
- Write the principle of method used for purification of zinc.
- Name the method used for purification of titanium.
Question 18.
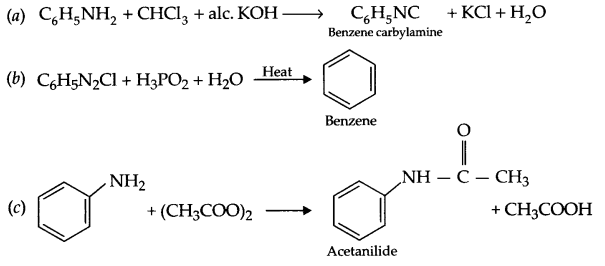
Complete the following reactions:
(a) C6H5NH2 + CHCl3 + alc. KOH →
(b) C6H5N2Cl + H3PO2 + H2O →
(c) C6H5NH2 + (CH3COO)2O →
Question 19.
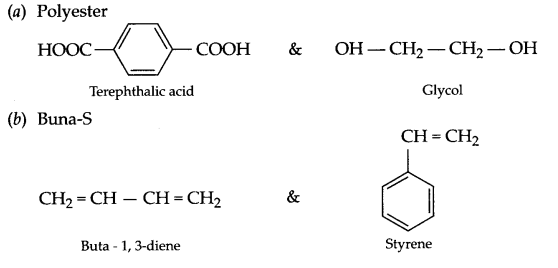
Write the structures of monomers used for getting the following polymers:
(a) Polyester
(b) Buna-S
(c) Bakelite
Question 20.
Mention one use of each of the following drugs:
- Ranitidine
- Iproniazid
- Tincture iodine
Question 21.
Assign suitable reason for the following:
- BiH3 is the strongest reducing agent among all the hydrides of group 15 elements.
- H2O is a liquid but H2S is a gas.
- O3 acts as a powerful oxidising agent.
Question 22.
Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compound .
(a) Phenol and benzoic acid
(b) Propanol and propanone
(c) Benzoic acid and ethyl benzoate
Question 23.
Piyush’s mother used to take aspirin, an analgesic quite often to get relief from body pain. She is becoming habitual of it. Piyush is a science student and he asked his mother not to take overdoses of aspirin, though it is very popular as it may result into stomach problems.
- Why did Piyush stop his mother to avoid overdose of aspirin?
- What values are associated with Piyush’s suggestion?
Question 24.
- Account for the following:
- Transition metals from interstitial compounds.
- Transition metals and their compounds acts as good catalyst.
- Mn (II) ions shows maximum paramagnetic behaviour amongst the bivalent ions of 3d-series.
- Describe the oxidising action of K2Cr2O7, and write the ionic equations for its reaction with
- H2S
- SO2
OR
(a) Describe the preparation of potassium dichromate from iron chromite ore. What is the effect of increasing pH on a solution of potassium dichromate?
(b) What is lanthanoid contraction? What are the consequences of lanthanoid contraction?
Question 25.
(a) Analysis show that Nickel oxide has formula Ni0.94O1.00. What fraction of Ni exists as Ni2+ ions and as Ni3+ ions?
(b) Explain the following with suitable examples:
- Ferromagnetism
- Paramagnetism
- Antiferromagnetism
OR
(a) Ag crystallises in a fee lattice with all the atoms at the lattice points. The length of the edge is found to be 4.077 × 10-8 cm. The density of silver is 10.5 g/cm3. Calculate the atomic mass of silver.
(b) Write two differences between schottky and frenkel defects.
Question 26.
(a) Carry out the following conversions
(i) Ethyl magnesium chloride to propan-l-ol.
(ii) Phenyl magnesium bromide to 1-phenyl-ethan-l-ol.
(iii) Benzyl chloride to benzaldehyde
(b) Account for the following :
- Alcohols can form hydrogen bond with water, hence they are more soluble than hydrocarbons.
- Tertiary alcohol gives stable 3° carbocation which can lose p-hydrogen to give alkene instead of giving haloalkane.
OR
(a) Name the reagent for the following reactions:
- Oxidation of 1° alcohol to carboxylic acid
- Butan-2-one to butan-2-ol
- Phenol to 2,4, 6-tribromophenol
(b) Write the mechanism of hydration of ethene to yield ethanol.
Answers
Answer 1.
Sc, Zn, Cd (Any one)
Answer 2.
2-bromo cyclopentane carbaldehyde
Answer 3.
Second order
Answer 4.
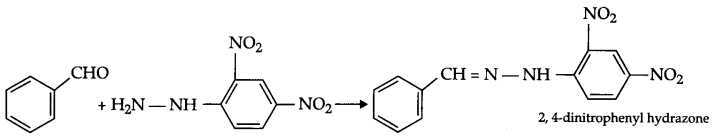
Answer 5.
Slope of line represents 1n value, i.e reverse of number of a layers of a adsorption.
Answer 6.
- 2FeCl3 + 3NH4OH(aq) → Fe2O3 . xH2O(s) + 3NH4Cl
- 6XeF4 + 12H2O → 4Xe + 2XeO3 + 24HF + 3O2
OR
- Ba(N3)2 Heat→ Ba + 3N2
- 2NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2 → 2NH3 ↑ + CaCl2 + H2O
Answer 7.
- Osmotic pressure : It is the pressure applied on higher concentration side of a semipermeable membrane so that there is no net flow of solvent molecules in either side of the membrane.
- Hypertonic solution : The solution having an osmotic pressure more than the reference solution is known as Hypertonic solution.
Answer 8.
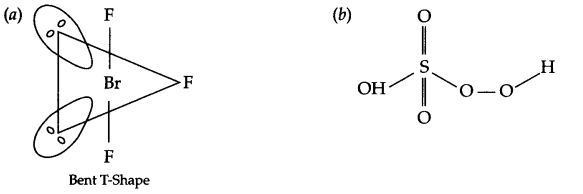
Answer 9.
- MnO–4 + 3e → MnO2
3 Faraday electricity is required - At cathode : Ag+ + e → Ag
An anode: 2H2O + 4e → O2 + 4H+
So products of electrolysis are Ag and 02.
Answer 10.
- Carbylamine reaction
RNH2 + CHCl3 + 3KOH heat→ RNC +3KCl + 3H2O - Diazotisation : Aniline on reaction with NaNO2 and cone. HCl at 8°C forms benzene diazonium chloride.
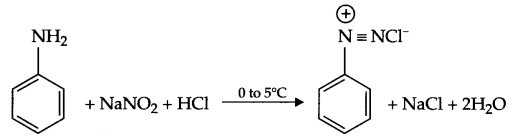
Answer 11.
Mass % of KI solution → 20%, d = 1.2 g/mL.
(a) Molality, m :
wA = 100 – 20 = 80 g

Answer 12.
From question, conductivity (K) = 1.29 S/m = 1.29 x 10-2 S cm-1
Cell constant (G*) = conductivity (K) × Resistance
= 1.29 × 10-2 × 100 = 1.29 cm-1
Conductivity for 0.02 M solution
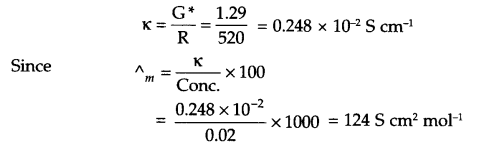
Answer 13.
In [Ni (CN)4]2- Ni exist in Ni2+ state, i.e.
Ni2+ → [Ar] 3d and CN– is a strong field ligand, so it causes pairing
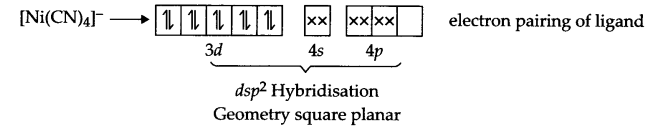
In [Ni(CO)4], Ni exist in Ni(o) state and electrons of 4s gets paired up in 3d orbital due to strong field ligand-CO.
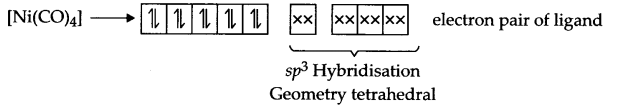
As discussed above, geometry is different in both the cases but none of these have impaired electrons, hence both are diamagnetic.
Answer 14.
1
| Chemisorption | Physisortion |
| Single layer adsorption | Multiple layer adsorption |
| Irreversible | Reversible |
| ΔHads = -80 to + 240 kJ/mol | ΔHads = -40 kJ mole |
2. Reversible sols : The solution which can be changed from sol to suspension and suspension to sol by simply addition or elimination of dispersion medium.
Irreversible sols: Sols which cannot be changed from suspension to sol or vice versa by simply adding or eliminating the dispersion medium.
3. Multimolecular colloids : In such colloids particles of dispersed phase are of small size and large number of such particles needs to come together to form colloid. On the other hand particles of macromolecular colloids, are of large enough size to come in colloidal range and forms colloids simply on mixing with dispersion medium.
Answer 15.
Since at t = 0, intial pressure (pi) is for A2B only
Answer 16.
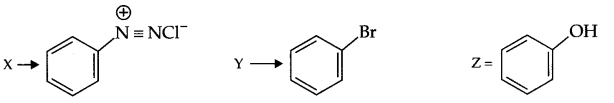
Answer 17.
- NaCN acts as a depressant in froth flotation process and hence prevents the formation of undesirable froth.
- Liquation method is used for the purification of zinc. Its principle signifies that metal should have less melting point than the impurity.
- Van Arkel process
Answer 18.
Answer 19.
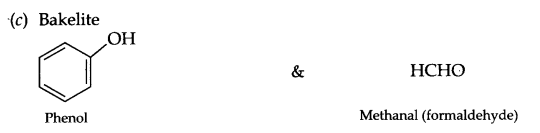
Answer 20.
- Ranitidine → Acts as antacid
- Iproniazid → Antidepressant drug (or Tramquilizer)
- Tincture iodine → Antiseptic
Answer 21.
- Among 15th group elements, Bi is of the largest size and hence Bi-H bond is the longest.
As a result BiH3 acts as the strongest reducing agent because of easy formation of H2. - Due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding, H2O is a liquid whereas H2S which does not have such bonds exist as a gas.
- O3 gets dissociated to give nascent oxygen which is responsible for its strong oxidising action
O → O + ‘O’
Answer 22.
(a)
| Reagent | Phenol | Benzoic acid |
| Neutral FeCl3 | Dark-green, grey violet complex | No colour change |
| NaHCO3 (sol.) | No gas evolves | CO2 evolves |
(b)
| Reagent | Propanol | Propanone |
| NaOH + I2 heat | No reaction | Yellow ppt of CHI3 forms |
(c)
Reagent | Benzoic acid | Ethyl benzoate |
| NaHCO3 (aq) | CO2 gas evolves (Effervesence of CO2) | No gas evolves |
Answer 23.
- Overdoses of any medicine is harmful and it has its own side effects. Overdose of Aspirin may damage the wall of stomach and may cause ulcer.
- Concern for mother, scientific attitude and knowledge of chemistry.
Answer 24.
- Due to suitable size of interstitial spaces they accomodate smaller atoms and form strong metal-metal bond and that is why transition metals form interstitial compounds.
- Transition metal shows variable oxidation state and have high charge density on metal ions, hence transition metals and their compounds acts as good catalyst.
- Mn (atomic no → 25) → [Ar] 3d4 4s2
In Mn2+ ions, Mn has the electronic configuration → [Ar]3d5
It means there are five impaired electrons, hence it shows maximum paramagnetism.
- In K2Cr2O7, oxidation number of Cr is +6 but its +3 state is more stable, as a result K2Cr2O7 acts as a good oxidising agent, particularly in acidic medium.
- Cr2O2-7 + 3S2- + 14H+ → 2Cr3+ + 3S + 7H2O
- Cr2O2-7 + 3SO2 + 2H+ → 2Cr3+ + 3SO2-4 + H2O
OR
(a) Preparation of Potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7):
Step I : Iron chromite to sodium chromate:
FeCr2O4 + Na2CO3 + O2 → Na2CrO4 + Fe2O3 + CO2
Step II : Sodium dichromate to potassium dichromate:
![]()
Step III : Sodium chromate to potassium dichromate :
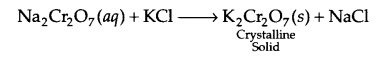
Effect of pH:
With increase in pH, potassium dichromate converts in potassium chromate:

(b) Contraction in size from Lanthanum to Lutetium due to filling of electrons in 4f orbitals which has poor shielding effect, is known as lanthanoid contraction.
Consequences of lanthanoid contraction:
- 5d series elements have nearly same radii as that of 4d series.
- Comparable size of all Ln3+ ions, so separation becomes difficult.
- Due to slight gradation in size these can be separated by ion exchange method.
Answer 25.
(a) Considering 100 such molecules, there will be 94 nickel ions and 100 O2- ions.
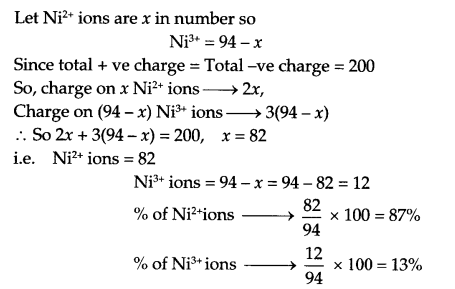
(b)
- Ferromagnetism : The molecular domains of ferromagnetic substances get aligned in the same direction under the influence of electric or magnetic field permanently. The property exhibited by such substances is known as ferromagnetism. Such substances can be made into permanent magnet, e.g. Fe, Ni, Co, CrO2 etc.
- Paramagnetism : Paramagnetic substances are weakly attracted towards the magnetic field and the properties of paramagnetism is due to the presence of unpaired electrons. It behaves as magnet only in magnetic field, e.g. O2, Cu2+, Fe3+ etc.
- Antiferromagnetism : The molecular domains of such substances get aligned in parallel are antiparallel direction in equal number, hence such substances cannot be magnetised and are neutral towards the magnet, e.g. MnO, Fe2O3, FeO etc.
OR
(a) From the given information for silver crystal
Z = 4, a = 4.077 × 10-8 cm, d = 10.5 g cm-3, m = ?
d = ZMa3NA
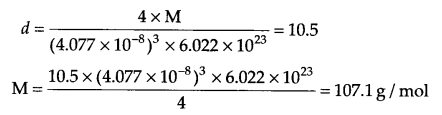
Molar mass of silver = 107.1 g/mol
(b)
| Schottky defect | Frenkel defect |
| Density decreases | No change in density |
| Comparable size of cation and anion | Uncomparable size of cation and anion |
Answer 26.
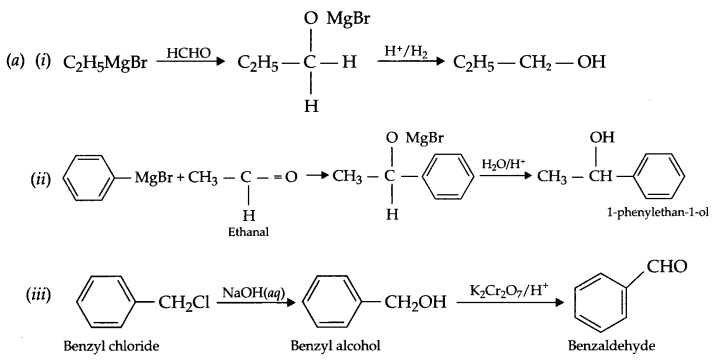
(b)
- Alcohols can form hydrogen bond with water, hence they are more soluble than hydrocarbons.
- Tertiary alcohol gives stable 3° carbocation which can lose p-hydrogen to give alkene instead of giving haloalkane.
OR
(a)
- KMnO4 (alc.) followed by acidic hydrolysis
- LiAlH4
- Br2(aq)
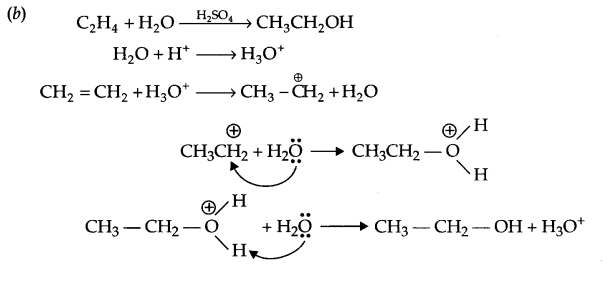
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 1 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 1, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
