These Sample papers are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Paper 5.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Paper 5
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | XII |
| Subject | Biology |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 5 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 12 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme as prescribed by the CBSE is given here. Paper 5 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Biology is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
General Instructions:
- There are total 26 questions and five sections in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A contains question number 1 to 5, Very Short Answer Type Questions of one mark each.
- Section B contains question number 6 to 10, Short Answer Type Questions of two marks each.
- Section C contains question number 11 to 22, Short Answer Type Questions of three marks each.
- Section D contains question number 23, Value Based Question of four mark.
- Section E contains question number 24 to 26, Long Answer Type Questions of five marks each.
- There is no overall choice in the question paper, however, an internal choice is provided in one question of two marks, one question of three marks and all three questions of five marks. An examiner is to attempt any one of the question out of the two given in the question paper with the same question number.
- No. of printed pages are three.
SECTION-A
Question 1.
Enzyme cellulase can be used for the isolation of genetic material from plant cells only and not for animal cells. State a reason.
Question 2.
Owners of motor vehicles equipped with catalytic converters, are advised to use unleaded petrol. Why?
Question 3.
In what way, the Cry gene has brought beneficial changes in the genetically modified crops?
Question 4.
Mention any two major harms that may occur in future to the environment by the use of CFCs.
Question 5.
Give any one similarity between the hydrarch and Xerarch successions of plants.
SECTION-B
Question 6.
Differentiate between the following.
(1) Zoospore and zygote
(2) Homothallic and heterothallic
Question 7.
It is imperative for the physical and psychological well being that HIV/AIDS person should not be isolated from family and society. Provide a reason.
Question 8.
State a reason why genetic variability acts as the root of any breeding programme.
OR
Biofortified maize and wheat are considered to be nutritionally much improved than the original crops. State any two reasons.
Question 9.
After observing an amazing diversity of creatures in Galpagos islands, Darwin made a conclusion that all varieties of finches had evolved from an original seed-eating finches. Give reason.
Question 10.
It is often said that human female ovary produces only one egg in a month. Then how many eggs do you think would have been released by the mother to give birth to the identical twins?
SECTION-C
Question 11.
Draw a labelled diagram of sectional view of a human ovary showing various stages of follicles growing in it.
OR
How are assisted reproductive technologies helpful to humans? How are ZIFT & GIFT different from intra uterine transfers? Explain.
Question 12.
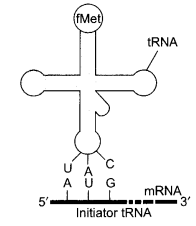
One of the codons on mRNA is AUG. Draw the structure of tRNA adapter molecule for this codon. Explain uniqueness of this tRNA.
Question 13.
(a) Draw a schematic representation of the structure of a transcription unit and show the following in it:
- Direction in which transcription occurs.
- Polarity of the two strands involved.
- Template strand.
- Terminator gene.
(b) Mention the function of promotor gene in transcription.
Question 14.
Who proposed chromosomal theory of inheritance? Point out any two similarities in the behaviour of chromosomes and genes.
Question 15.
How is innate immunity different from the immunity that you acquire through vaccine?Describe any two ways by which innate immunity can be accomplished?
Question 16.
Explain the efforts which must be put in to improve health, hygiene and milk yield of cattle in a dairy farm.
Question 17.
(a) Name the virus that causes AIDS in humans.
(b) Explain the sequence of events that follows when this virus attacks to cause immune deficiency in humans.
Question 18.
How and why is the bacterium Thermus acquaticus employed in recombinant DNA technology?Explain.
Question 19.
Why should biological control of pests and pathogens be preferred to the conventional use of chemical pesticides? Explain how the following microbes act as biocontrol agents:
(a) Bacterium thuringiensis
(b) Nucleopolyhedrovirus
Question 20.
Why is Agrobacterium tumefaciens a good cloning vector? Explain.
Question 21.
Particulate and gaseous pollutants along with harmless gases are released from the thermal power plant.
(1) Name any two harmless gases released.
(2) Name the most widely used device of removing particular pollutants from the air. Explain how the device is used.
Question 22.
Fertilisation is essential for production of seed, but in some angiosperms, seeds develop without fertilisation.
(1) Given an example of an angiosperm that produces seed without fertilisation. Name the process.
(2) Explain the two ways by which seeds develop without fertilisation.
SECTION-D
Question 23.
While planning and organising any celebration or function a large quantity of paper is used in the form of writing pads, file covers, elaborate invitation cards, decorative posters, gift wrappings, paper plates, etc. After the function is over, the bulk of the used paper gets dumped into the dustbins. (a) Write your comments on such a paper usage.
(b) Give your suggestions.
- How would you reuse the paper effectively that got dumped into the dustbins?
- In which two alternative ways would you have liked to use the paper for such functions and celebrations?
(c) Explain the long term effects of such practices on the environment.
SECTION-E
Question 24.
(a) Draw a diagrammatic sketch of the sectional view of a typical anatrapous ovule.
(b) List the components of the embryo sac and mention their fate on fertilisation.
OR
(a) Give a schematic representation of spermatogenesis in humans.
(b) At which stage of life does gametogenesis begin in human male and female respectively?
(c) Name the organs where gametogenesis gets completed in human male and female respectively.
Question 25.
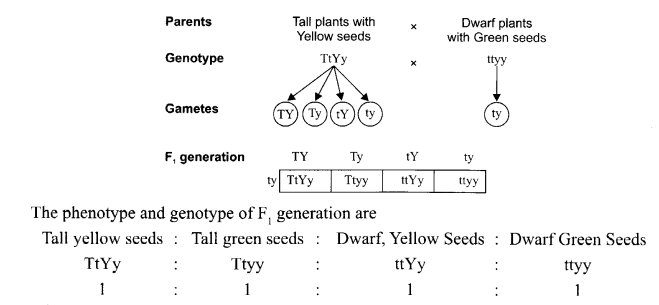
A tall tea plant with yellow seeds (heterozygous for both the traits) is crossed with a dwarf pea plant with green seeds. Using a Punnett square, work out the cross to show phenotypes and the genotypes of F generation.
OR
(a) Why is DNA molecule a more stable genetic material than RNA? Explain.
(b) “Unambiguous”, “degenerate” and “universal” are some of the salient features of genetic code. Explain.
Question 26.
(a) Why are herbivores considered similar to predators in the ecological context? Explain.
(b) Differentiate between the following interspecific interactions in a population.
- Mutualism and competition.
- Commensalism and Amensalism
OR
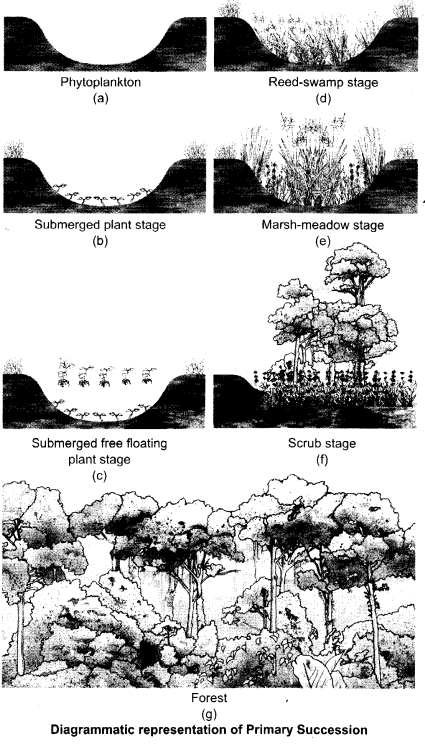
(a) Trace the succession of plants on a dry bare rock.
(b) How does phosphorous cycle differ from carbon cycle?
Answers
SECTION-A
Answer 1.
Cellulose is a substance that makes up the cell walls of most of the plants. Thus, enzyme cellulase is used for the isolation of genetic material for plant cells only because animal cells do not have a cellulosic cell wall.
Answer 2.
Unleaded petrol i.e. petrol not treated with lead is eventually advised to use over leaded petrol or any other fuel because it does not emit harmful gases in the atmosphere and eventually does not cause any harm to it.
Answer 3.
Cry gene being isolated from protein crystals of bacterium bacillus thuringiensis is been expressed in different crop plants in order to provide the resistance to the insects without the need for insecticides.
e g. Bt potato, Bt tomato, Bt soybean etc.
Answer 4.
Continuous use of CFC’s may harm the environment in future in the following two ways:
- May cause change in temperature of climate
- May cause failure of rainfall on earth.
Answer 5.
Both hydrarch and Xerarch successions leads to medium water conditions (mesic) i.e neither too dry (xeric) nor too wet (hydric) conditions.
SECTION- B
Answer 6.
(1) Differences between zoospore and zygote are
| Zoospore | Zygote |
| (1) It is a haploid cell and is motile in nature. | It is a diploid cell and is non-motile in nature. |
| (2) It is usually formed during asexual reproduction in lower plants and fungi | It is usually formed due to fusion of male and female gametes in sexual redproduction. |
(2) Differences between homothallic and heterothallic are
| Homothallic | Heterothallic |
| A condition is which male and female reproductive structures are present in the same individual. | A condition is which male and female reproductive structures are present in the different individual. |
| These are self fertile, e.g. Chara. | These are not self fertile, e.g. Marchantia |
Answer 7.
The reason behind this fact is that HIV/AIDS is not transmitted by a mere touch or any physical contact, rather it spreads though body fluids or by sharing infected needles and by the transfusion of contaminated blood and blood products.
Answer 8.
Genetic variability is known as the ability or capability of a biological system i.e. an individual and population that changes over time. The variability of a trait eventually describes how much that trait tends to vary response to environment and genetic influences.
OR
Biofortified maize and wheat are nutritionally improved because of following two main reasons
- Hybrid maize is much rich in the amount of amino acids, lysine and tryptophan.
- And hybrid wheat is much rich in the quantity of protein in it.
Answer 9.
Darwin concluded that after originating from a common ancestral seed-eating stock, the finches must have radiated to different geographical areas and had undergone adaptive changes, especially in the type of beaks.
Answer 10.
The identical twins are monozygotic in nature and are produced from the two parts of the same zygote. Thus, only one egg has to be released from the female ovary in order to give rise to the identical twins.
SECTION- C
Answer 11.
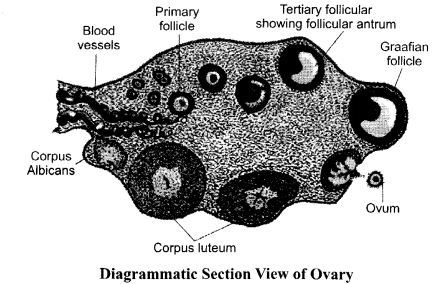
The infertile couples could be assisted to have children through certain special techniques known as assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
ZIFT: The zygote or early embryo with upto 8 blastomeres is transferred into the fallopian tube called zygote intra fallopian transfer (ZIFT).
GIFT: It is the transfer of an ovum collected from a donor into the fallopian tube of another female who cannot produce one but can provide suitable environment for fertilisation and further development of the embryo.
Intra uterine transfer refers to the introduction of embryo with more than 8 blastomeres into the uterus of a female to complete its further development.
Answer 12.
This tRNA is specific for amino acid Methionine and it also acts as initiator codon.
Answer 13(a)
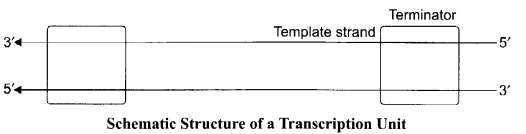
(1) Transcription occurs in 5’→ 3′.
(b) Promotor gene has DNA sequence that provide binding site for RNA polymerase.
Answer 14.
It was proposed by Sutton and Boveri.
Similarities:
- Both genes and chromosomes occur in pairs in a diploid cell (2n).
- Both of them separate out during gametogenesis to enter into different gametes.
Answer 15.
| Innate Immunity | Acquired Immunity |
| 1. Its a non-specific type of defence present from the birth in an individual and is inherited from parents. | 1. It is a pathogen specific which is not present from the birth and develop through vaccination. |
| 2. It does not cause side effects. | 2. It cause certain reaction against vaccination. |
Innate immunity can be accomplished by the following barriers:
(1) Physiological barriers: Tears in eyes, acid in stomach and saliva in mouth, etc. prevent microbial growth.
(2) Cytokine barriers: Interferons produced by virus-infected cells protect non-infected cells from further viral infection.
Answer 16.
The following efforts need to be put in for improvement in health, hygiene and milk yield of cattle in a dairy farm.
- The cattle in the dairy farm must be housed and fed properly.
- Cleanliness should be maintained in the milking area.
- The health of dairy cattle should be of utmost importance and veterinary doctor must be invited regularly.
- Regular inspections of farm, maintaining records, identification and rectification of problems should be done along with maintaining precautionary measures.
- Milking should be done in a dirt-free area and all the sanitary conditions should be maintained.
- High-yielding and disease-resistant breeds can be selected to maximise benefits.
Answer 17.
(a) Human Immunodeficiency Virus.
(b) After the entry of the virus into the body of a person, the virus enters into the macrophages, where RNA genome of the virus replicates and forms viral DNA by the help of the enzyme reverse transcriptase.
The viral DNA gets incorporated into the host cell’s DNA and directs the infected cells to produce viruses. The macrophages continue to produce virus that enters the helper T-lymphocytes. Thus, the number of helper T-lymphocytes progressively decrease in the body of infected person.
Answer 18.
DNA Polymerase (Taq polymerase) in recombinant technology is obtained from bacterium Thermus aquaticus.
- DNA polymerase (thermostable) remain active during the high temperature induced during denaturation of double stranded DNA.
- This enzyme extends the primers using the nucleotides provided in the reaction and the genomic DNA as template.
- The repeated amplification is achieved by this enzyme and the amplified fragment if desired can be used to ligate with a vector for further cloning.
Answer 19.
The chemical pesticides cause pollution of water bodies as well as ground water, besides getting stored in plants. These chemicals are toxic and thus extremely harmful to human beings and other animals.
(a) Baccilus Thuringiensis: This toxin genes are introduced into plants to make them resistant to attack by insects and pests. They are available in sachets as dried spores, which are mixed with water and sprayed onto vulnerable plants. When they are eaten by the insect larvae, the toxin is released in the gut and becomes active and kills the larvae. Specific Bt toxin genes are obtained from Baccilus thuringiensis.
(b) Nucleopolyhedrovirus: These viruses are excellent candidates for species-specific, narrow spectrum insecticidal applications. This is especially desirable when beneficial insects are being conserved to aid in an overall Integrated Pest Management (IPM) programme.
Answer 20.
Agrobacterium tumifaciens is a soil bacterium which causes disease in many dicot plants. It is able to deliver a piece of DNA known as T-DNA, to transform the normal cells into tumour cells and direct these tumour cells to produce the chemical required by the pathogen. The tumour inducing (Ti) plasmid of Agrobacterium tumifaciens has been modified into a cloning vector which is no more pathogenic to the plants but still delivers genes of interest into a variety of plants.
Answer 21.
(1) Nitrogen and oxygen.
(2) Electrostatic precipitator.
Electrostatic precipitator has electrode wires that are maintained at an electric current of several thousand volts, which produces corona that releases electrons. These electrons attach to dust particles and give them a negative charge. Collecting plates are earthed that attract charged dust particles.
Answer 22.
(1) In the members of family Asteraceae, seed develop without fertilisation. This process is palled apomixis.
(2) Two ways by which seeds develop without fertilisation:
(a) In some species, the diploid (2n) egg cell is formed without reduction division and develops into embryo without fertilisation.
(b) In many varieties of citrus and mango fruits, some of the nuclear cells surrounding the embryo sac starts dividing, protrudes into the embryo sac and develops into embryos.
SECTION-D
Answer 23
(a) Such use of paper is harmful to the environment and is a waste of resources.
(b)
(1) Waste papers can be used for gift wrapping or making paper bags. File covers can be reused in other functions or be distributed to volunteers for reuse.
(2) Gift wrapping could be done by old newspapers, or used papers, thermocol plates can be used instead of paper plates.
(c) Such wasteful use of paper will lead to increase in deforestation which can lead to desertification of land.
SECTION-E
Answer 24.
(a)
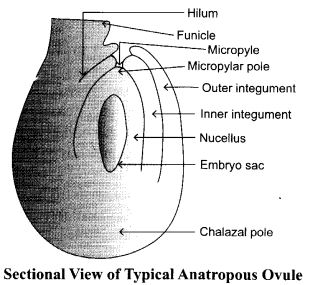
(b) The embryo sac contains 3 antipodals, 3 synergids, 1 egg and 2 polar nuclei.
- After positive pollen-pistil interaction, the pollen tube develops and enters the ovule through synergids guided by filiform apparatus.
- One of the male garnets fertilises the female gamete to form diploid zygote.
- The another male gamete fuses with secondary nucleus to form a triploid Primary Endosperm Nucleus (PEN) that develops into endosperm.
- The three antipodals at chalazal end and synergids at micropylar end start degenerating.
OR
(a)
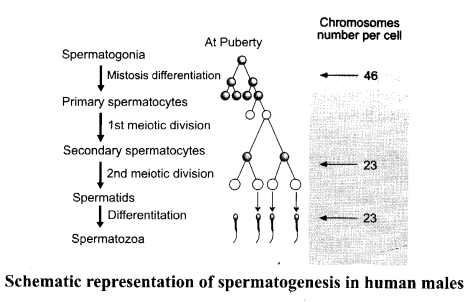
(b) Gametogenesis, i.e., spermatogenesis in males and oogenesis in females starts at puberty.
(c) In human males the process is completed in the testes (seminiferous tubules) while in the female it is completed in the fallopian tube (oviduct).
Answer 25.
OR
(a) In DNA, presence of thymine at the place of uracil confers more stability to DNA. In the nucleotide of RNA the 2′ OH group is a reactive group and this makes RNA labile and degradable, while DNA is chemically less reactive and structurally more stable.
(b)
Unambiguous: One codon specifies only one particular amino acid and not any other hence known as unambiguous.
Degenerate: Some amino acids specifies more than one codon hence the codon is said to be degenerate.
Universal: A particular codon coding for an amino acid is same for all organisms (except in mitochondria and some protozoa).
Answer 26.
(a) Herbivores are animals feeding on plants. Although they are classed differently they are considered predators. Like predators transfer energy across trophic levels, herbivores also do the same. Besides this, they also keep the population of their prey under control, for example, when the prickly pear cactus was introduced in Australia in early 1920s, they spread rapidly causing havoc. Their population was controlled by introducing cactusfeeding predator.
(b)(1)
| Mutualism | Competition |
1. This interaction benefits both the interacting species. 2. The two individuals may be physically or physiologically associated. 3. E.g., lichens present mutualism between fungus and algae where fungus absorbs nutrition and provides protection and algae provides food. | 1. In this interaction, both the interacting species suffer negatively. 2. There is no physical association between the competitors. 3. E.g., in some American lakes, visiting flamingoes and resident species compete for their common food. |
when the prickly pear cactus was introduced in Australia in early 1920s, they spread rapidly causinghavoc. Their population was controlled by introducing cactusfeeding predator.
a mango tree benefits by getting shelter and nutrition but the mango tree is not affected. Ammensalism is the interaction between two different species, in which one species is harmed and other is neither benefited nor harmed, e.g., penicillum produces toxin killing other microorganisms but is not affected itself.
OR
(a) The species that invade a bare area are called pioneer species, e.g., lichens. The lichen secretes some acids to dissolve rock and help in weathering and soil formation. Later, some small bryophytes invade and hold the small amount of soil. The bryophytes are succeeded by herbs, shrubs, and ultimately big trees. At last a stable climax forest is formed. The xerophytic habitat get converted into mesophytic one.
| Phosphorus Cycle | Carbon Cycle |
1. Phosphorus returns to the soil. 2. The atmospheric input of phosphorus through rainfall is much smaller. 3. There is no gaseous exchange of phosphorus between organism and environment. | 1. Carbon is released into the atmosphere. 2. The atmospheric input of caarbon from rainfall is greater. 3. Carbon gas is exchanged between organism and atmosphere during respiration. |
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Paper 5 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Paper 5, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
