These Sample papers are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Paper 3.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Paper 3
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | XII |
| Subject | Biology |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 3 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 12 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme as prescribed by the CBSE is given here. Paper 3 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Biology is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
General Instructions:
- There are total 26 questions and five sections in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A contains question number 1 to 5, Very Short Answer Type Questions of one mark each.
- Section B contains question number 6 to 10, Short Answer Type Questions of two marks each.
- Section C contains question number 11 to 22, Short Answer Type Questions of three marks each.
- Section D contains question number 23, Value Based Question of four mark.
- Section E contains question number 24 to 26, Long Answer Type Questions of five marks each.
- There is no overall choice in the question paper, however, an internal choice is provided in one question of two marks, one question of three marks and all three questions of five marks. An examiner is to attempt any one of the question out of the two given in the question paper with the same question number.
- No. of printed pages are three.
SECTION-A
Question 1.
Cross hybridization among the selected parents during any plant breeding programme is meant to be a tedious and a time consuming process. Why?
Question 2.
In which phenomenon, a phenotype of the Fj hybrid offspring does not resemble any of the parent and is intermediate between the expression of two alleles?
Question 3.
It is often seen that replication of DNAdoes not initiate randomly anywhere in DNA, it instead begins at definite regions. Why is it so? Give reason.
Question 4.
List two advantages of inbreeding in animals.
Question 5.
Production of antibiotics has been widespread by the pioneering efforts of which two scientists?
SECTION-B
Question 6.
How is diapause different from hibernation?
Question 7.
What are the two major aims and objectives behind the reproductive child healthcare programmes?
OR
Human Placenta acts as a structural and functional unit between a foetus and maternal body. Justify the statement giving any two basic functions it performs.
Question 8.
In what way does the cell mediated system works in a body when it gets infected?
Question 9.
Both linear DNA and plasmid DNA of same length having one site for a restriction endonuclease are cut and separated on agarose gel electrophoresis. The plasmid DNA shows one DNA band, while a linear DNA shows two fragments. State the reason behind the fact.
Question 10.
Mention two functions of DNA polymerase.
SECTION-C
Question 11.
Co-dominance acts as the phenomenon of resemblance of off springs to both the parents. Justify the statement with the support of a well known example.
Question 12.
Students while performing the experiment were given two different vectors in two different bacterial colonies being cultured in a chromogenic substrate. They observed that the bacterial colonies with cloning vector A were colourless while those with coloning vector B were blue in colour. Explain the phenomenon and the procedure behind the fact that the students were trying to figure out.
Question 13.
Gametogenesis is the phenomenon known for the formation of haploid gametes taking place in both males and females. Observe the flowchart given below highlighting the influence of process of gametogenesis and answer the questions that follows.
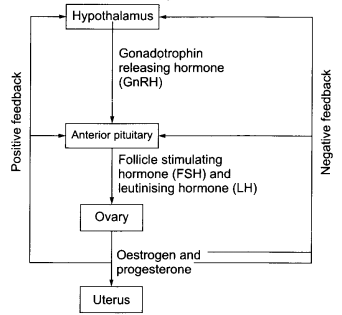
(1) Identify the type of gametogenesis shown and in whom does it take place?
(2) Explain the role of different hormones involved in the complete process
Question 14.
If during the formation of male gametes, each pollen grain produces two male gametes. Then, deduce the number of pollen grains which would be required to fertilise five ovules present in a particular carpel. Give reasons to support your answer.
Question 15.
Mechanism of sex determination differentiates from one another in every living beings. Describe in detail about such mechanism in case of humans, birds and grasshoppers respectively
Question 16.
It is known that Global carbon in the biosphere is fixed through the process of photosynthesis.Explain how is it done and also mention the ways by which carbon is eventually returned to the atmosphere?
Question 17.
In what ways the biocontrol microbes controls their target species through a web of biological interactions? Explain giving some important examples.
Question 18.
It has been recorded that the temperature of the earth’s atmosphere has increased 0.6°C.
(1) What has caused this increase?
(2) Explain its consequences.
OR
Due to uncontrolled excessive hunting, the population of tigers in a forest has become zero. Discuss the long-term effects of this situation on the population of deer in that forest.
Question 19.
(1) What happens when Meloidegyne incognitia consumes cells with RNAi gene?
(2) How agrobacterium vectors are also proved useful in genetic engineering?
Question 20.
Ajay went with his father to see this friend in the hospital. They saw that doctor there was advising Ajay’s friend about the personal hygiene. What according to you is the importance of personal hygiene? List any six measures every person or a society should follow to prevent diseases from spreading by contaminated food and water.
Question 21.
Give reasons for the following:
(1) Competition between intraspecific species tend to be more intense than the interspecific species.
(2) Lichens show obligate mutualism.
(3) Population of different species are not capable of breeding with each other.
Question 22.
With the help of a flowchart, show the process by which the genetic information from one strand of DNA is copied in to RNA in case of prokaryotes.
SECTION-D
Question 23.
While having lunch in canteen, Prateek was discussing with his friends about the movie in which the hero used to donate his sperms to help the couples undergoing infertility. Listening this one of Prateek’s friend argued against such thing and said that this type of activity and movies are just to earn money and they should be banned.Discuss four points with appropriate23.explanation how Prateek will make him understand that helping out couples in such a way is not incorrect.
SECTION-E
Question 24.
What do you understand by the term ‘antibodies’ in our body? Explain in detail about the different types and roles of antibodies.
OR
Drugs like LSD, barbiturates, amphetamines, etc. are used as medicines to help patients with mental illness. However, excessive doses and abusive usage are harmful. Enumerate the major adverse effects of such drugs in humans.
Question 25.
(1) Define the term antibody. Highlight the structural importance of antibody molecule.
(2) Name different types of antibodies found in the blood, mentioning the functions of each.
Question 26.
(1) It has been seen since a long time that different organisms and their population are connected to each other through a special connection. Identify that connection and write about its different types.
(2) Length of a food chain within an ecosystem generally limited to 3-4 trophic levels. Justify.
Answers
SECTION-A
Answer 1.
This is because cross hybridization as a step in a plant breeding programme involves a collection of pollen grains from the desired plants and other pollination techniques to incorporate the desired traits.
Answer 2.
Incomplete Dominance.
Answer 3.
Replication of DNA molecule begins at a definite region called Ori or (origin of replication) because it is this site which binds the pre-replication complex or a protein complex that recognizes, unwinds and begins to copy DNA.
Answer 4.
Advantages of inbreeding in animals are
(1) Necessary in evolving a pure line in any animal breed.
(2) Increases homozygosity
Answer 5.
Ernest Chain and Howard Florey have made the production of antibiotics widespread by pioneering efforts.
SECTION-B
Answer 6.
Hibernation is the phenomenon commonly depicted by cold-blooded animals, which escape cold by hiding themselves in shelters such as burrows muds, etc revealing minimum , physiological activity. It is performed by large animals while, on the other hand, diapause is a stage of suspended development which takes place during unfavourable conditions like stress, etc. The growth and development gets resumed on the return of favourable conditions. This is usually performed by microscopic or very small organisms like zooplanktons etc.
Answer 7.
What are the two major aims and objectives behind the reproductive child healthcare programmes?
OR
Human Placenta acts as a structural and functional unit between a foetus and maternal body.Justify the statement giving any two basic functions it performs.
Answer 8.
In what way does the cell mediated system works in a body when it gets infected?
Answer 9.
Both linear DNA and plasmid DNA of same length having one site for a restriction endonuclease are cut and separated on agarose gel electrophoresis. The plasmid DNA shows one DNA band, while a linear DNA shows two fragments. State the reason behind the fact
Answer 10.
Two functions of DNA polymerase are
(1) It adds nucleotides to the DNA and removes RNA primer from DNA.
(2) It also proofreads the created portion of DNA
SECTION-C
Answer 11.
Co-dominance is the phenomenon in which two alleles expressed themselves independently when present in a single organism, i.e. they neither show dominant recessive relationship nor they show an intermediate condition. Thus, it is true to say that co-dominance acts as the phenomenon of resemblance of offspring to both the parents.
For example, ABO blood grouping in humans beings.
The four phenotypes to blood groups in humans, ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘AB’, ‘O’ are produced by the three different alleles i.e. IA, IB and i of the immunogene.
The alleles IA and IB are completely dominant over ‘i’ an allele, which means that when IA and i are present in an individual only IA expresses and on the other hand when IB and i are present only IB will express, as an allele i does not produce any sugar.
But eventually in the case, where an individual possesses both IA and IB, both the alleles expresses their own types of antigens and the person is said to be having any of the blood group as mentioned below. This is because alleles IA and IB are co-dominant with each other.
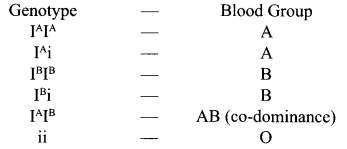
Answer 12.
Students were working to differentiate recombinants and non-recombinants DNA on the basis of production of colour in the presence of a chromogenic substrate.
During this phenomenon, a recombinant DNA is inserted within the coding sequence of an enzyme 1-galactosidase that results in an inaction of the enzyme. Due to which, the bacterial colonies having plasmid inserted within it shows no colouration at all and those without plasmid tends to show blue colour.
Answer 13.
(1) The process shown in the figure above is oogenesis. It is a type of gametogenesis which occurs in females.
(2) The hormones involved in the process of oogenesis in females similar to those involved in the process of spermatogenesis in males with a only difference, that is, oogenesis hormones acts on ovaries to stimulate the complete process.
The process of gametogenesis (oogenesis) in females begins from the part of the brain, (called hypothalamus) which releases a hormone called gonadotropin releasing hormone or GnRH that further stimulates the release of hormones to act on gonads.In female, Follicle stimulating hormone acts on anterior pituitary which stimulates the folliciles present in the ovary containing the developing eggs. It also stimulates the ovary to produce the hormone, called oestrogen. This leads to the development of secondary sexual characteristics including the development of breasts and deposition of fat in some places. It also signals a drop in FSH and the production of LH (Leutinising hormone). This LH further causes the process of ovulation (i.e. the release of the egg in the females).
Answer 14.
Each pollen grain generates to produce two male gametes that are carried through a pollen tube to the embryo sac. This pollen tube enters the embryo sac through the filliform apparatus of one of the synergids present at the micropylar end and releases two male gametes.Out of these two male gametes, one fuses with the egg cell while, the other fuses with the secondary nucleus. Therefore, one pollen grain can fertilise only one ovule. Therefore, in order to process fertilisation of five ovules, five pollen grains will be required.
Answer 15.
Sex determination mechanism in humans, birds and grasshopper are as follows:
(1) Humans: In case of human beings, females have homogametic (XX) and males have heterogametic (XY) sex chromosome. Hence, in this case, the sperm is responsible for the determination of sex of the offspring.
(2) Birds: In case of birds, females have heterogametic (ZW) and males have homogametic
(ZZ) sex chromosomes. Hence, egg is responsible for the sex determination of the offspring,
(3) Grasshopper: These show XO type of sex determination. Some species of grasshoppers bears X-chromosome while, others do not have sex chromosome. The female have homogametic (XX) and the male have heterogametic (XO) sex chromosome.
Answer 16.
The CO2 is added to the atmosphere mainly by burning of the fossil fuels, volcanic activities and by the process of respiration. Decomposers also contribute substantially to CO2 pool by their processing of waste materials and dead organic matter of land and oceans.
About 4 x 1013 kg of carbon is fixed annually in the biosphere through photosynthesis.
Answer 17.
Biological control refers to the use of biological methods for controlling plant diseases, pests and weeds etc.
Some examples of biological controls are:
(1) Ladybird and dragonfly are used to get rid of aphids and mosquitoes respectively.
(2) Bacillus thuringiensis is used for the control of butterfly caterpillar.
(3) Fungus species Trichoderma are used in controlling infection in roots.
(4) Baculoviruses are used as narrow spectrum insecticidal applications
Answer 18.
(1) Increase in atmospheric concentration of greenhouse gases (CO2) has resulted in the rise of atmospheric temperature by 0.6°C (global warming).
(2) Consequences for the increase in temperature are
(а) Weather and climate change by rising temperature and melting of ice caps, glaciers worldwide
(b) Rise in water levels of seas and oceans.
(c) Affects food production.
(d) Sudden changes in rainfall pattern and occurrence of frequent floods, droughts, hurricanes.
OR
If the number of predators (tigers) get reduced, the number of prey (deer) population will increase which will increase the pressure on the vegetation. As a result, plant population will decrease due to overgrazing. Little vegetation puts pressure on deer population and as a result deer population will decrease due to starvation, death or migration. Thus, ultimately the tigers (predators) will be affected.
Answer 19.
(1) If Meloidegyne incognitia consume cells with RNAi gene, silencing of specific mRNA occurs due to a complimentary dsRNA molecule formation which binds and prevents translation of mRNA (silencing) thus, causing death of the nematode.
(2) Agrobacterium vectors are used for the introduction of nematode-specific genes into the host plant by producing both sense and antisense RNA into host cells. As these two RNA’s are complementary to each other, they form dsRNA and initiates silencing the specific mRNA of the nematode.
Answer 20.
Preventive measures for diseases spread by contaminated food and water are
(1) Proper disposal of water and excreta.
(2) Cleaning and disinfection of pools, water tanks and other water reservoirs.
(3) Storing raw and the cooked food separately.
(4) Cooking food in clean water and keeping it at safe temperature.
(5) Body should be clean, nails and hairs should be cut regularly
(6) Hygienic practice should be adopted at hotels and restaurants
Answer 21.
(1) Intraspecific competition is more intense because the requirements of individuals of same species are very similar.
(2) Lichens set a good example of obligate mutualism because of the naturalistic relationship between the fungi and algae or cyanobacteria in which an algae prepares food, while the fungus helps in the absorption of nutrients and provide protection.
(3) Different species in a population are unable to breed with each other because of various types of biological and physical barriers.
Answer 22.
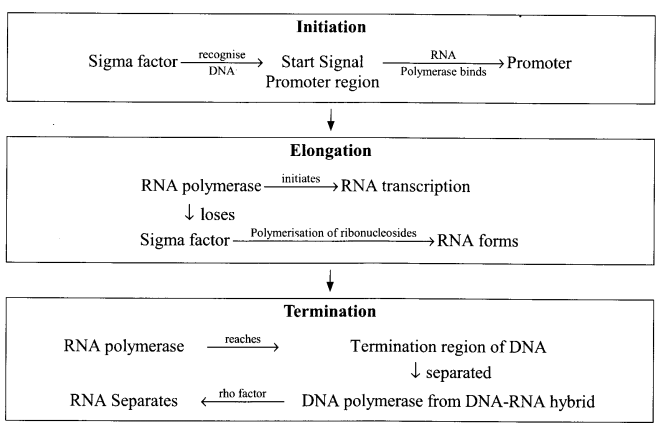
SECTION-D
Answer 23.
Prateek will share following points with his friend in the support of the discussion.
- Infertility is the condition in which man is unable to ejaculate enough semen containing sperm to fertilize the female’s egg.
- Sperm donation can also help the couples if the man has certain genetic defect such as haemophilia or couple is suffering from Rhesus incompatability.
- By doing this a person can help a family to have a child.
- Thus, donation of sperm, if done in a legalized way, is not a bad thing to do.
Answer 24.
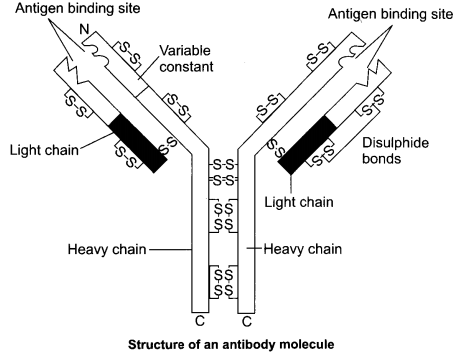
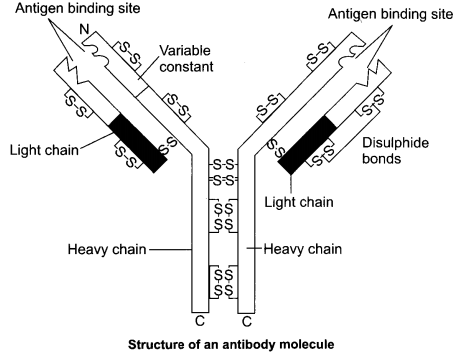
(1) Antibody is a type of a protein molecule produced by B-Lymphocytes in response to pathogens present in our blood to fight with them. T-Cells do not secrete antibodies directly however, they help B-Cells to produce them. Each antibody molecule has four peptide chains. Out of the four chains two small chains are called light (landa) chains and two large chains are called heavy (H) chains.
An antibody is represented as H2I2 molecule. In our body, different type of antibodies are produced such as IgA, IgM, IgE, IgG. All these antibodies are found in blood.
| Types of Antibodies | Functions |
| IgG | Most prevalent class of antibody 75-80% of total antibody. Protects against fungi, bacteria, toxins, etc. It can cross placenta from mother to child and provides immune protection to newborns. Responsible for Rh factor in blood. |
| IgM | Third most common antibody. If constitutes 5-10% total antibodies. They are first to be produced in response to encounter with a pathogen. Responsible for blood transfusion reactions in ABO blood system. |
| IgA | Second most prevalent antibody. It is about 15% of the total antibodies. Secreted through parts lined by mucous system. Found in secretions from nose, eyes, lungs and digestive tract, saliva, tears, etc. Also found in colostrum, i.e., breast milk for newborns for immune protection. |
OR
Harmful effects of drugs like LSD, barbiturates, amphetamines etc are:
- Anxiety, shakiness, nausea, sweating and loss of mind control.
- Reckless behavior, vandalism and violence.
- Lack of interest in personal hygiene, fluctuations in weight and appetite.
- Depression, fatigue and aggressive behaviour.
- Social adjustment problems.
- Withdrawal symptoms can be severe and life threatening.
- Excessive dose of drugs may lead to coma and death due to respiratory, heart failure or cerebral haemorrhage.
Answer 25.
(1) Antibody is a type of a protein molecule produced by B-Lymphocytes in response to pathogens present in our blood to fight with them. T-Cells do not secrete antibodies directly. However, they help
B-Cells to produce them. Each antibody molecule has four peptide chains. Out of the four chains, two small chains are called light (landa) chains and two large chains are called heavy (H) chains.
An antibody is represented as H2I2 molecule. In our body, different type of antibodies are produced such as IgA, IgM, IgE, IgG. All these antibodies are found in blood.
| Types of Antibodies | Functions |
| IgG | Most prevalent class of antibody 75-.80% of total antibody. Protects against fungi, bacteria, toxins, etc. It can cross placenta from mother to child and provides immune protection to newborns. Responsible for Rh factor in blood. |
| IgM | Third most common antibody. If constitutes 5-10% total antibodies. They are first to be produced in response to encounter with a pathogen. Responsible for blood transfusion reactions in ABO blood system. |
| IgA | Second most prevalent antibody. It is about 15% of the total antibodies. Secreted through parts lined by mucous system. Found in secretions from nose, eyes, lungs and digestive tract, saliva, tears, etc. Also found in colostrum, i.e., breast milk for newborns for immune protection. |
Answer 26.
(1) Different organisms or population of an ecosystem are connected to each through a sequence or a series of connection called food chain. Through this chain the food and its contained energy is passed as a food of a later member of a sequence. It is actually known as a feeding chain of organisms in an ecosystem.
There are mainly two types of food chains in the ecosystem:
- Grazing food chain
- Deteritus food chain
(2) The amount of energy flow in an ecosystem decreases with successive tropic levels as only 10% of energy gets transferred from one trophic level to next successive level. The energy lasts in the form of respiration and other important activities for maintaining life. If more trophic levels are present, the residual energy will be limited and decreases to such an extend that it cannot further support any trophic level by the energy flow. Thus, it is rightly said that the food chain is generally limited to the 3-4 trophic levels only.
For example,
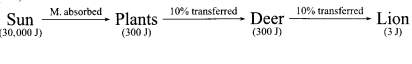
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Paper 3 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Paper 3, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
