These Sample papers are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Paper 1.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Paper 1
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | XII |
| Subject | Biology |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 1 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 12 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme as prescribed by the CBSE is given here. Paper 1 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Biology is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
General Instructions:
- There are total 26 questions and five sections in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A contains question number 1 to 5, Very Short Answer Type Questions of one mark each.
- Section B contains question number 6 to 10, Short Answer Type Questions of two marks each.
- Section C contains question number 11 to 22, Short Answer Type Questions of three marks each.
- Section D contains question number 23, Value Based Question of four mark.
- Section E contains question number 24 to 26, Long Answer Type Questions of five marks each.
- There is no overall choice in the question paper, however, an internal choice is provided in one question of two marks, one question of three marks and all three questions of five marks. An examiner is to attempt any one of the question out of the two given in the question paper with the same question number.
- No. of printed pages are three.
SECTION-A
Question 1.
What is Allen’s Rule?
Question 2.
How does saliva act in body defence?
Question 3.
What are antherozoids?
Question 4.
What is acrosome?
Question 5.
Expand EFB.
SECTION-B
Question 6.
During an excavation assignment, scientists collected pollen grains of a plant preserved in deeper layers of soil. Analyse the properties of pollen grains which help in the fossilization.
Question 7.
Protein synthesis machinery revolves around RNA but in the course of evolution it was replaced by DNA. Justify.
Question 8.
Identify two ways in which Spirulina is helpful to mankind.
OR
Keeping beehives in crop fields has several advantages. List any two.
Question 9.
Suryakant had banana plantation in his field. Quality of the fruit was excellent but the yield suffered due to infection of the plants by a virus. Suggest a fast and efficient method to get healthy and a large number of plants in the next generation without compromising on the existing quality. Justify the section of your method.
Question 10.
Besides acting as ‘conduits’ for energy transfer across tropic levels, predators play other important roles. Justify.
SECTION-C
Question 11.
Explain three out breeding devices.
Question 12.
After implantation, interdigitation of maternal and foetal tissues takes place. Identify the tissues involved and justify their role.
Question 13.
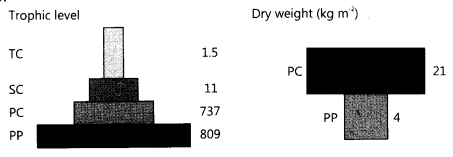
Compare the two ecological pyramids of biomass given below and explain the situation in which this is possible. Also construct an ideal pyramid of energy if 200,000 joules of sunlight is available
Question 14.
With respect to Messelson and Stahl’s Experiment, answer the following questions:
(a) Identify the method used to distinguish between heavy and light isotopes of nitrogen.
(b) With the help of diagrams, compare the results for the DNA isolated after 20 minutes of experiment with the DNA which was isolated after 40 minutes.
Question 15.
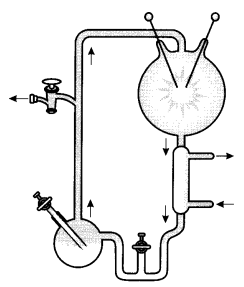
A student was simulating Urey and Millers experiment to prove the origin of life. The set up used by the student is given
(a) Find out the reasons why he could not get desired results
(b) What conclusion was drawn by Urey and Miller through this experiment?
(c) Compare the conclusion drawn with the theory of spontaneous generation.
Question 16.
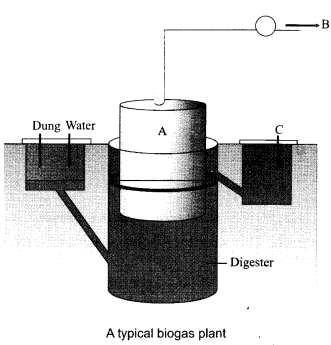
Given below is a figure of a biogas plant.
(a) Identify ‘A’ and justify its floating nature.
(b) Identify the products ‘B’ and ‘C’ and discuss their significance
Question 17.
According to Global Hunger Index 2014 two billion people suffer from hidden hunger. Apply your knowledge of plant breeding techniques to suggest a programme to improve public health. Specify four objectives of the programme. Also mention one example of such a produce
Question 18.
DNA separated from one cell, when introduced into another cell is able to bestow some of the properties of former to the latter. What is this change called in technical terms? Describe the experimental evidences which led to the discovery of the above phenomenon.
Question 19.
When someone buys packets of cigarettes, he can not miss the statutory warming that is present on the packing which warns against smoking and says how it is injurious to health. Yet, smoking is very prevalent in our society, both among young and old. Advise the adolescents about the importance of avoiding smoking. (Mention any six points.)
Question 20.
Biotechnology has helped farmers to get pest resistant cotton crops. Explain the technique adopted along with its mode of action. (Mention six points)
OR
(a) Draw the figure of vector pBR322 and label the following:
- Origin of replication
- Ampicillin resistance site
- Tetracycline resistance site
- Bam HI restriction site
(b) Identify the significance of Origin of replication
Question 21.
(a) Given below is a single stranded DNA molecule. Frame and label its sense and antisense RNA molecule. 5’ATGGGGCTC 3’ sense
(b) How the RNA molecules made from above DNA strand help in silencing of the specific RNA molecules?
Question 22.
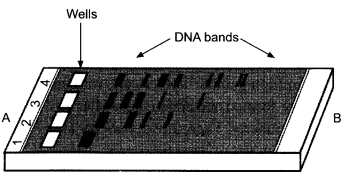
Rajesh was doing gel electrophoresis to purify DNA fragments. Given below is the sketch of the observations of the experiment performed by him.
(a) At which end he would have loaded the samples and where?
(b) Analyse the reason for different positions taken up by the DNA bands.
(c) Elaborate the step he would have followed to visualize DNA bands.
SECTION-D
Question 23.
Mohit and Sumit want to buy a new car for their company. Mohit insisted on buying a CNG car with a better mileage but Sumit insisted on buying a diesel version of a high end car with better music system and AC but relatively low mileage.
(a) Being a responsible citizen of Delhi, how will Mohit convince Sumit about his decision in the wake of rising pollution levels?
(b) What qualities of personality are being exhibited by Mohit in doing so?
(c) Suggest two more measures which can help in reducing vehicular pollution.
SECTION-E
Question 24.
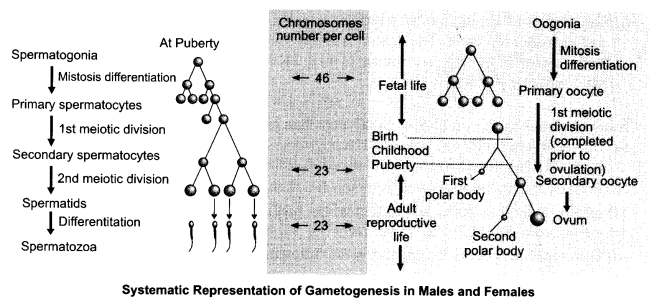
Human female is not fertile after menopause whereas males can produce gametes at any age after puberty. Analyse the statement and schematically represent a comparison between gametogenesis in males and females.
OR
A village health worker was taking a session with women. She tells the women that one has to be very careful while using oral pills as method of birth control. Wrong usage can actually promote conception.
(a) Analyze the statement and compare the merits and demerits of using oral pills and surgical methods of birth control.
(b) Village women were confused as to how a thin metallic Copper loop can provide protection against pregnancy. Justify the use explaining the mode of action of IUDs
Question 25.
Observe the representation of genes involved in the lac operon given below-
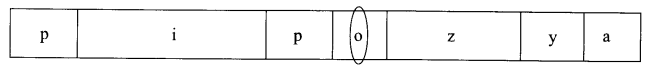
(a) Identify the region where the repressor protein will attach normally.
(b) Under certain conditions repressor is unable to attach at this site. Explain.
(c) If repressor fails to attach to the said side what products will be formed by z, y and a?
(d) Analyze why this kind of regulation is called negative regulation.
OR
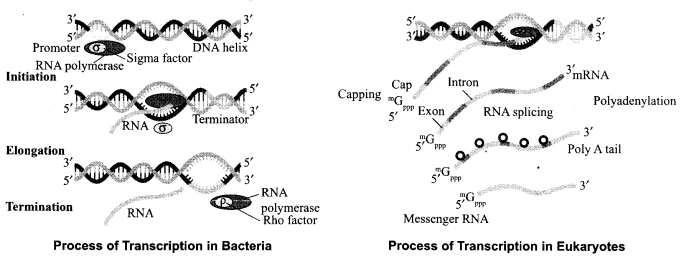
Transcription in eukaryotes is more complex process than in prokaryotes. Justify and compare the initiation, elongation and termination in bacterial cells with eukaryotes.
Question 26.
The graph below shows Species – Area relationship:
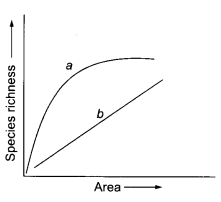
(a) If b denotes the relationship on log scale
- Describe a and b
- How is slope represented? Give the normal range of the slope.
- What kind of slope will be observed for frugivorous birds and mammals in a tropical forest?
(b) Species diversity of plants (22%) is much less than that of animals (72%). Analyze the reasons for greater diversity of animals as compared to plants
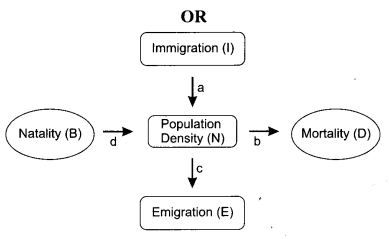
(а) Which of the above represents the increase or decrease of population?
(b) If N is the population density at time t, then what would be its density at time (t+1)? Give the formula.
(c) In a barn there were 30 rats. 5 more rats enter the barn and 6 out of the total rats were eaten by the cats. If 8 rats were born during the time period under consideration and 7 rats left the barn, find out the resultant population at time (t + 1).
(d) If a new habitat is just being colonized, out of the four factors affecting the population growth which factor contributes the most?
Answers
SECTION-A
Answer 1.
According to Allen’s Rule, mammals in colder climate have shorter ears and shorter limbs to minimise heat loss.
Answer 2.
Saliva is chemically composed of lysozume which digests the bacterial cell wall and kills them.
Answer 3.
Ans. The male gamete or male reproductive unit is called antherozoids or spermatozoa.
Answer 4.
A cap-like structure present in the anterior of head of sperm is known as acrosome.
Answer 5.
Ans. European Federation of Biotechnology.
SECTION-B
Answer 6.
Pollen has an outer layer called exine which is made of sporopollenin. Sporopollenin is the most resistant organic material known which can withstand high temperature, strong acids and alkali. No enzyme has been known so far which cap degrade sporopollenin.
Answer 7.
Since RNA was unstable and prone to mutations, DNA evolved from RNA with chemical modifications that make it more stable.
DNA has double stranded nature with complementary strands. These further resist changes by evolving a process of repair.
Answer 8.
Spirulina is a source of food rich in protein, minerals, fats, carbohydrates and vitamins, it can grow on waste water from potato processing plants, straw, molasses, animal manure and even sewage, so it also reduces water pollution.
OR
Pollination management, versatile use of resources, production at no cost. (Any two)
Answer 9.
He can grow thousands of plants through tissue culture of meristem by micropropagation/He can remove the meristem and grow it in-vitro using tissue culture technique./Although the plant is infected with a virus, the meristem (apical and axillary) is free of viruses.
Answer 10.
Besides acting as ‘conduits’ of energy transfer across trophic levels, predators play other important roles like
(1) They keep prey population under control
(2) Predators also help in maintaining species diversity in a community by reducing the intensity of competition among competing prey species
SECTION-C
Answer 11.
(1) Pollen release and stigma receptivity is not synchronized to discourage self-pollination which has resulted in inbreeding depression.
(2) Self incompatibility, a genetic mechanism to prevent self pollen from fertilising the ovules by inhibiting pollen germination or pollen tube growth in the pistil.
(3) Production of unisexual flowers to prevent both autogamy and geitonogamy.
Answer 12.
After implantation interdigitation of maternal and foetal tissues results in formation of structural and functional unit between embryo and maternal body called placenta.
Its role are:
(1) It facilitates supply of oxygen and nutrients to the embryo and removal of carbon dioxide and excretory material.
(2) It also acts as an endocrine tissue and produces hormones like HCG, hPL, estrogen, Progesteron, relaxin, etc.
Answer 13.
The first pyramid of biomass corresponds to a terrestrial ecosystem which shows a sharp decrease in biomass at higher trophic levels. Second pyramid refers to a small standing crop of phytoplankton supporting a large standing crop of zooplankton/aquatic ecosystem. An ideal pyramid of energy of 200,000 joules of sunlight is available which is drawn below:
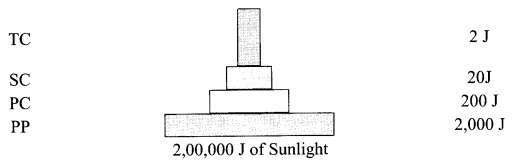
Answer 14.
(a) Centrifugation in a CsCl density gradient.
DNA isolated after 20 min had a hybrid 14N15N and intermediate density.
(b)
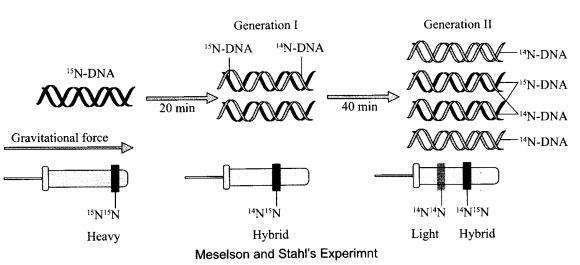
DNA extracted from the culture after 40 min was composed of equal amount of N14N15 DNA and of light DNA.
Answer 15.
(a) He could not get desired results because:
- O2 was used instead of H2
- Temperature maintained was 800° C instead of 8000.
(b) It was concluded that life could have come from pre-existing non living organic molecules and their formation was preceded by chemical evolution.
(c) He observed formation of Amino acids when in a closed flask CH4, H2, NH3 and water vapour were heated at 8000° C in presence of electric discharge. Analysis of meteorite content also reveals similar compounds indicating that similar process are occurring elsewhere in space/ Chemical evolution. Urey and Miller proved that life originated abiogenetically whereas theory of spontaneous generation emphasized that units of life called spores were transferred to different planets including Earth.
Answer 16.
(a) ‘A’ is the floating cover which is placed over the slurry, which keeps on rising as the gas is produced in the tank due to the microbial activity.
(b) ‘B’ is the biogas which is a mixture of gases consisting of methane, hydrogen sulphide and carbon dioxide. It can be used as a source of energy to nearby houses as it is inflammable. ‘C’ is the spent slurry or sludge which is removed through another outlet and may be used
as a fertiliser.
Answer 17.
Biofortification which is breeding of crops with higher levels of vitamins and minerals, or higher protein and healthier fats to improve public health.
The four objectives of Biofortification are:
- Protein content and quality
- Oil content and quality
- Vitamin content and
- Micronutrient and mineral content.
For an example, in 2000, maize hybrids was produced that had twice the amount of the amino acids, lysine and tryptophan as, compared to existing maize hybrids
Answer 18.
In 1928, Frederick Griffith conducted a series of experiments with Streptococcus pneumoniae
and witnessed a miraculous transformation in the bacteria. During the course of his experiment, a change in the physical form of bacteria was observed.
When Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria was grown on a culture plate, some produce shiny colonies (S) while other product rough colonies (R). This happened because the S strain bacteria have a mucous (polysaccharide) coat, while R strain does not. Mice infected with the S strain L (virulent) die from pneumonia infection but mice infected with the R strain did not develop
pneumonia.
S Strain → Inject into mice → Mice die
R Strain → Inject into mice →Mice live
Griffith killed bacteria by heating them. He observed that heat-killed S strain bacteria injected into mice did not kill them. When he injected a mixture of heat-killed S and live R bacteria, 1 the mice died. Moreover, he recovered living S bacteria from the dead mice.
From above experiment he concluded that the R strain bacteria had somehow been transformed by the heat-killed S strain bacteria. Some ‘transforming principle’, transferred from the heat- killed S strain, had enabled the R strain to synthesise a smooth polysaccharide coat and become virulent. This must be due to the transfer of the genetic material.

Answer 19.
Tobacco in cigarettes contains a large number of chemical substances including nicotine, an alkaloid. Avoiding smoking can help to reduce the risk of various health diseases such as:
- Increased blood pressure and heart rate caused by Nicotine stimulation of adrenal gland to release adrenaline and nor-adrenaline into blood.
- Cancers of lung, urinary bladder, throat and oral cavity.
- Reducing the risk of bronchitis and emphysema.
- Avoiding the association with increased risk of coronary heart disease, gastric ulcer, etc.
- Smoking increases carbon monoxide (CO) content in blood and reduces the concentration of haem-bound oxygen which causes oxygen deficiency in the body.
- It may bring on diabetes of Type 2.
Answer 20.
The technique involves the use of a popularly known bio pesticide Bt toxin produced by bacteria, Bacillus thuriengiensis.
Bt toxin protein when ingested by the insect gets converted to its active form due to alkaline pH of the gut.
The activated toxin binds to the surface of midgut epithelial cells.
It creates pores in these cells that cause swelling and lysis and eventually kills the insect.
The genes (cry genes) encoding this protein are isolated from the bacterium and incorporated into crop plants like cotton. The proteins encoded by these cry genes control the pest. Specifically, cry I Ac and cry II Ab control cotton bollworm (Helicoverparmigera), an insect belonging to Lepidoptera which earlier used to destroy the whole crop.
(a)
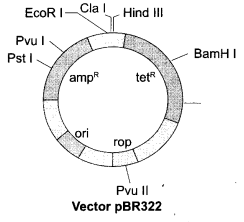
(b) Origin of replication is responsible for controlling number of copy of the DNA sequence inserted.
Answer 21.
(a) 5’ATGGGGCTC 3’ sense
3 ’ TACCCCGAG 5’ antisense
RNA 5’AUGGGGCUC 3’ sense
3’ UACCCCGAG 5’ antisense 2
(b) The two strands of RNA (i.e. sense and antisense) being complementary will bind with each other and form double stranded RNA as a result its translation and protein expression would be inhibited.
Answer 22.
(a) He would have loaded the samples near end A; in the wells.
(b) The DNA fragments separate (resolve) according to their size through sieving effect provided by the agarose gel. Hence, the smaller the fragment size, the farther it moves.
(c) After staining the DNA with ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV radiations the DNA bands appear coloured.
SECTION-C
Answer 23.
(a) Mohit will give following reasons:
- CNG bums most efficiently, unlike petrol or diesel, in the automobiles and very little of it is left unburnt.
- CNG is cheaper than petrol or diesel, cannot be siphoned off by thieves and adulterated like petrol/Diesel.
(b) Mohit shows concern towards environment, awareness towards sustainable development,
(c) Phasing out of old vehicles, use of unleaded petrol, use of low sulphur petrol/diesel, use of catalytic converters in vehicles and application of stringent pollution level norms for vehicles.
SECTION-D
Answer 24.
In human female oogenesis is initiated during embryonic development stage when a couple of million gamete mother cells (oogonia) are formed within each foetal ovary. No more oogonia are formed and added there after birth. A large number of these follicles degenerate from birth to puberty. Therefore at puberty only 60,000 to 80,000 primary follicles are left in each ovary which get utilised till menopause.
After menopause female is no more fertile as she cannot do ovulation whereas in males at puberty, spermatogonia multiply by mitosis and increase in numbers, some of which periodically undergo meiosis throughout the life.
Comparison between gametogenesis in male and female
| Particulars | Male | Female | |
| (1) | Process | Spermatogenesis | Oogenesis |
| (2) | Beginning of process | Begins at puberty | Begins during fetal development |
| (3) | Location | Testis | Ovary |
| (4) | Number of gametes produced | Life long production (millions) | Fixed amount only – 400 mature) |
| (5) | Gametes per germ cell | Four | One |
| (6) | Timing of gamete formation | Continuous (any time) | Once a month (menstrual cycle) |
| (7) | End of process | Fertility is life long but reduces | Fertility stops at menopause |
| (8) | Timing of gamete release | Any time | Monthly cycle |
| (9) | Meiotic divisions | Uninterrupted | Arrested |
| (10) | Germ line epithelium | Involved in gamete, production | Not involved in gamete production |
| Contraceptive pills | Surgical method | |
| Merits |
|
|
| Demerits |
|
|
(b) Mode of action of IUDs:
- IUDs increase phagocytosis of sperms within the uterus.
- Cu++ released suppress sperm motility and fertilising capacity of sperms.
- The hormone releasing IUDs make uterus unsuitable for implantation and the cervix hostile to the sperms.
Answer 25.
(a) Operator region O
(b) In presence of an inducer- Lactose.
y-permease
(c) z-β galactosidase
a-Transacetylase
(d) Regulation of lac operon by repressor is called negative regulation as it is constitutive (all the time) repressor. The operon is always in off position due to presence of repressor and is switched on only in presence of an inducer. Inducer Lactose or allolactose interacts with repressor making it inactive.
OR
Transcription is more complex in eukaryotes than prokaryotes due to the following reasons:
(a) In prokaryotes, only one type of RNA polymerase is involved whereas in eukaryotes three types of RNA polymerases are involved in addition to RNA polymerase.
(b) Primary transcription contain both non-functional exon and introns. Splicing is involved.
(c) nRNA undergo capping and tailing where methyl guanosine triphosphate and adenylate are added at 5′ and 3′ end respectively.
(d) Difference in process is depicted in the following figures
Answer.
(a)
(i) ‘a’ → S = CA2
‘b ’→ log S = log C + Z log A
(ii) Slope-Z (repression coefficient). Normal range of the slope is 0.6 to 1.2.
(iii) Value of Z= 1.15
(b) There is a greater diversity of animals as compared to plants because animals have an adaptive ability to ensure their survival in changing environment as compared to plants. For example, insects and animals have developed complex nervous system to control and co-ordinate their body structure. Other body structures such as repeated body segments with paired appendages and external cuticles have made insects versatile for their survival in different habitats.
OR
(a) ‘a’ and ‘d’ represents increase of population and ‘b’ and ‘c’ represent decrease of population.
(b) Nt+1=N, + [(B + I)-(D + E)]
(c) Nt = 30; I = 5; E = 7 ; D = 6 ; B = 8
Putting the value in the formula Nt +1 = Nt + [(B +1) – (D + E)]
Nt +1 = 30 + [(8 + 5) – (6 + 7)] = 30 + [13 – 13] = 30 + 0 = 30 rats
(d) Immigration contributes the most
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Paper 1 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Paper 1, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
