These Sample papers are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Paper 1
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Paper 1
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | X |
| Subject | Science |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 1 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 10 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme as prescribed by the CBSE is given here. Paper 1 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 10 Science is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time : 3 hr
Maximum Marks : 80
General Instructions
- The question paper comprises two sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections.
- All questions are compulsory.
- All questions of Section A and B are to be attempted separately.
- There is an internal choice in two questions of three marks each and one question of five marks.
- Question numbers 1 and 2 in Section A are one mark questions. They are to be answered in one word or in one sentence.
- Question numbers 3 to 5 in Section A are two marks questions. These are to be answered in 30 words each.
- Question numbers 6 to 15 in Section A are three marks questions. These are to be answered in about 50 words each.
- Question numbers 16 to 21 in Section A are 5 marks questions. These are to be answered in 70 words each.
- Question numbers 22 to 27 in Section B are based on practical skills. Each question is a two marks question. These are to be answered in brief.
SECTION A
Question 1.
“Reuse is better than recycling of materials”. Give reason to justify this statement. (1)
Question 2.
Complete and balance the following equation: (1)
Fe(s) + H2O (g) → (1)
Question 3.
An element is placed in 2nd group and 3rd period of the periodic table. It burns in oxygen to form basic oxide. (2)
(a) Identify the element.
(b) Write its electronic configuration.
(c) Write the chemical formula of the compound formed when it reacts with chlorine.
Question 4.
If an object is kept at 20 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm, where would the image be formed? (2)
Question 5.
Give reasons for the following: (2)
(i) Silver bromide is stored in a dark brown coloured bottle.
(ii) Oil and fats containing food items are flushed with nitrogen.
Question 6.
The Railways first used glass tumblers to serve tea in trains which were replaced by Kulhads and disposable plastic cups. Now they are using paper cups. (3)
(a) Tumbler of which material is the best to serve tea keeping the environment and hygiene in mind?
(b) What are the disadvantages of using Kulhads?
(c) What are the disadvantages of using disposable plastic cups?
Question 7.
(i) Two students ‘A’ and ‘B’ want to prepare dil H2SO4. Student ‘A’ added cone. H2SO4 to water slowly with constant stirring while student ‘B’ added water to cone. H2SO4. Name the student who was correct and why? What will happen in case of the other student? (3)
(ii) What is the colour change when a stain of curry on a white cloth comes in contact with soap and why?
Question 8.
(a) Mention the part of the brain which (3)
- enables us to ride a bicycle
- regulates peristalsis
(b) Deficiency of hormone ‘X’ results in swelling of a gland present in the neck region. This results in swollen neck. Identify the hormone ‘X’ and name the mineral needed for production of this hormone in our body.
(c) What is chemotropism ? Give an example
Question 9.
(a) State the laws of refraction.
(b) What is the refractive index of a medium? (2+1)
Question 10.
(a) What is the role of split rings in an electric motor?
(b) A positively charged particle projected towards west is deflected towards north by a magnetic field what is the direction of the magnetic field?
(c) In what respect motors are different from generators? (1+1+1)
OR
(a) Compare the strength of the induced current when the conductor moves
- parallel to magnetic field lines
- perpendicular to magnetic field lines
(b) How can magnetic field around a solenoid be changed without having any relative motion between the solenoid and the source of magnetism?
(c) How will the induced current be affected if the direction of the magnetic field
is reversed?
Question 11.
(a) Why can’t two magnetic field lines intersect?
(b) Why does a current carrying loop of wire, always point in the N-S direction, when freely suspended?
(c) In what direction will a magnetic compass deflect if it is placed on the west side of a wire which is carrying current in a vertically upward direction? (1+1+1)
Question 12.
(a) List the events taking place in plants during photosynthesis. (3)
(b) What is the significance of transpiration in a plant body?
Question 13.
Table given below shows the mass number and the number of neutrons in four elements P, Q, R , S (3)
| Element | P | Q | R | S |
| Mass Number | 12 | 20 | 23 | 35 |
| No. of Neutrons | 6 | 10 | 12 | 18 |
(i) Write the atomic number and electronic configuration of these elements.
(ii) Which of these is chemically inert?
Question 14.
(a) Compare the structure and functioning of nephrons in kidneys and alveoli in lungs.
(b) How is separation of oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood useful in birds and mammals? (3)
Question 15.
Mohan installed rooftop solar panels in his new house. He has calculated that the initial cost of the solar panels would be recovered in 5 years time due to a decrease in his electricity bill. He was happy that he has done his bit towards conserving the environment.
(a) What is the energy conversion in a solar cell?
(b) What material is used to connect solar cells to form a solar panel?
(c) What values are exhibited by Mohan ? (1+1+1)
Question 16.
(i) A metal ‘M’ is found in nature as MCO3. It is used in galvanising iron articles. Name the metal.
(ii) How can the metal be obtained from its carbonate ore? Write chemical equations involved. (5)
Question 17.
An organic compound ‘A’ with molecular formula C2H6O on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 gives a compound ‘B’ which is used as a preservative. Compound ‘A’ is often used for sterilisation of skin by doctors. Compound ‘A’ reacts with ‘B’ to form a sweet smelling substance ‘C’
(i) Name the compounds A and B.
(ii) Write the structural formula of ‘C.
(iii) Write the chemical equations involved. (5)
Question 18.
(a) Draw a neat diagram of the human female reproductive system and label the following parts:
- Part responsible for producing ova.
- Site for fertilization.
- Structure which accomodates the growing embryo.
- Birth canal.
(b) Why prenatal sex determination has been prohibited by law? (5)
OR
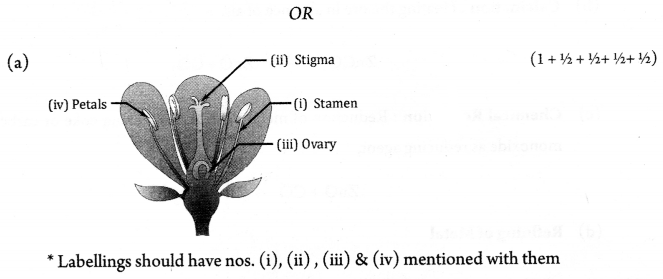
(a) Draw a neat diagram of longitudinal section of a flower and label the following parts:
- male reproductive part
- female reproductive part which traps pollen grains
- female reproductive part which produces ova
- part which attracts insects for pollination
(b) How is pollination different from fertilization? (5)
Question 19.
(a) In a Mendelian cross, tail plants with purple flowers (dominant) were crossed with dwarf plants with white flowers (recessive). How would you denote:
- The genotype of two parents
- The genotype and phenotype of F1 progeny
- The results obtained by selfing F1 progeny to get F2 progeny. Give the ratio obtained in F2 progeny
(b) Can the wings of butterfly and wings of bat be considered homologous? Why or why not? (5)
Question 20.
(a) What would be the image distance in a myopic human eye, if an object is kept at
- 25 cm from the eye;
- infinity?
(b) Draw diagrams showing the defect Hypermetropia and its correction.
(c) A child wears corrective lenses of focal length -50 cm. What defect is he suffering from? What is the power of his lenses ? (1+2+2)
Question 21.
(a) How much current will a device of power 100 W draw from a source of (1+2+2)
(b) Two devices of resistance R1 and R2 are put across 220 V. Which of the two will consume energy at a greater rate if R1 is more than R2 ?
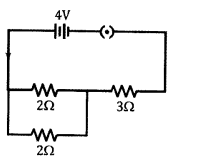
(c) In the circuit diagram shown, Calculate
- total resistance in the circuit
- total current in the circuit
- find the voltage across 3Ω resistor
SECTION B
Question 22.
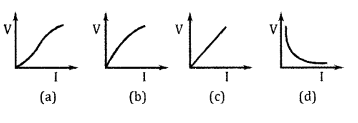
(a) Which of the following graphs represent ohmic resistance?
(b) Judge the resultant resistance of parallel combination of 1Ω and 103 Ω. (1+1)
Question 23.
Draw a ray diagram showing image formation by a convex lens for magnification -1. (2)
Question 24.
In an experiment to study the properties of acetic acid, answer the following questions. (2)
(a) Name the substance which on addition to acetic acid produces Carbon dioxide gas.
(b) How is CO2 gas tested in the lab? Write equation.
Question 25.
Rahul adds aqueous solution of Barium Chloride to an aqueous solution of sodium sulphate. What would he observe? Write equation.(2)
Question 26.
When we open a dicot seed, then its embryo shows two parts. Name these two parts and write their functions. (2)
Question 27.
Out of potato, sweet potato, radish and carrot: make pairs of homologous organs and analogous organs. Also give reasons for the pairing. (2)
ANSWERS
SECTION A
Answer 1.
In reuse we use things again and again, no energy is used / but in recycling some energy is used (1)
Answer 2.
3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2 ↑ Iron (II) (III) oxide. (1)
Answer 3.
(a) Mg (Magnesium) (1/2)
(b) 2,8,2 (1/2)
(c) Mgcl2 (1)
Answer 4.

Image would form 60 cm in front of the mirror (1/2)
Answer 5.
(i) Silver bromide is photosensitive in nature and decomposes in presence of light. So it is stored in dark coloured bottle. (1/2)
2Ag Br(s) light→ 2Ag+Br2 (1/2)
(ii) Nitrogen is chertiically inert so it provides a non-reactive atmosphere and prevents rancidity. (1)
Answer 6.
(a) Paper cups are the best as paper cups are disposable and biodegradable and can also be recycled. (1)
(b) Rulhads are made up ofclay and result in the loss of the fertile top soil (1)
(c) Disposable plastic cups are non biodegradable they pollute the environment. (1)
Answer 7.
(i) Student ‘A’ is correct because the mixing of acid with water is highly exothermic and the heat evolved will be absorbed by water as water has high specific heat. (1)
If the mixing is done the other way, then the heat evolved, might result in splashing of acid, formation of corrosive mist of acid or breaking of glass beaker in which mixing is done. (1)
(ii) The colour of the stain changes to reddish brown as turmeric powder in presence of soap (basic) changes to reddish brown. (1)
Answer 8.
(a)
- Cerebellum (1/2)
- Medulla (1/2)
(b) Hormone X = Thyroxine mineral needed for the production of Thyroxine = Iodine (1/2 + 1/2)
(c) Chemotropism – Response of plant parts towards chemicals e.g. Growth of pollen tube towards ovule in ovary. (1/2 + 1/2)
Answer 9.
(a)
- The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the interface of the transparent media at the point ofincidence, all lie in the same plane. (1)
- The ratio of sine of angle ofincidence to the sine of angle of refraction is a constant, for the fight of a given colour and for the given pair of media. (1)
(b) Refractive index of a medium is the ratio of the speed offight in air or vacuum to the speed of fight in that medium. (1)
Answer 10.
(a) Split rings reverse the direction of current in the motor coil, every half rotation. (1)
(b) Vertically up. (1)
(c) Motors convert electrical energy to mechanical energy but generators convert mechanical energy to electrical energy. (1)
OR
(a) (i) No current is induced. (1/2)
(ii) Maximum current is induced. (1/2)
(b) By changing the current in the primary coil. (1)
(c) The direction of induced current would reverse. (1)
Answer 11.
(a) Two magnetic field fines cannot intersect as at the point of intersection, the compass would have two directions to point, which is not possible. (1)
(b) Current carrying loop behaves as a dipole and alligns itself in the N-S direction. (1)
(c) Towards South. (1)
Answer 12.
(a) Events in Photosynthesis
- Absorption of light energy by Chlorophyll (1/2)
- Conversion of light energy into chemical energy (1/2)
- Photolysis of water / Splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen in presence of light (1/2)
- Reduction of CO2 into carbohydrate (1/2)
(b) Significance of Transpiration
- helps in absorption and upward movement of water and minerals from roots to leaves helps in ascent of sap. (1/2)
- helps in temperature regulation (1/2)
Answer 13.
Configuration

(ii) Q is chemically inert as its octet is complete (1)
Answer 14.
(a) Similarities in structure (1/2)
- both are microscopic
- richly supplied by blood vessels
- have thin membranes for easy diffusion
Difference in structure (1/2)
Alveoli are Sac like, nephron are tubular
Similarity in functioning (1/2)
Both help to get rid of wastes from the body
Difference in functioning (1/2)
Alveoli helps in exchange of gases i.e. O2 & CO2 between blood and lungs.
Nephron helps to filter the blood from Urea & other harmful chemicals.
(b) Separation of oxygenated blood & deoxygenated blood in animals and birds allow a highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body. (1/2)
This helps them to produce more energy for maintaining their body temperature (1/2)
Answer 15.
(a) Solar energy to electrical energy (1)
(b) Silver (1)
(c) Intelligent, responsible (1)
Answer 16.
(i) Metal ‘M’ is Zn, ore- ZnCO3 (1+4)
(ii) ZnCO3
(a) Conc. of ore is done by Hydraulic washing which is based on the difference in density of ore and the gangue.
(b) Calcination : Heating the ore in absence of air.
ZnCO3 △→ ZnO+CO2
(c) Chemical Reduction : Reduction of metal oxide is done using coke or carbon monoxide as reducing agent
ZnO + CO → Zn + CO2↑
(d) Refining of Metal
Answer 17.
(i) Compound A → C2H5OH (1)
B → CH3COOH (1)
(ii) Compound C → CH3COOC2H5 (1)
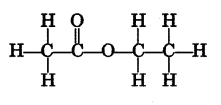
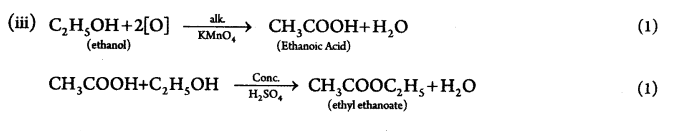
Answer 18.
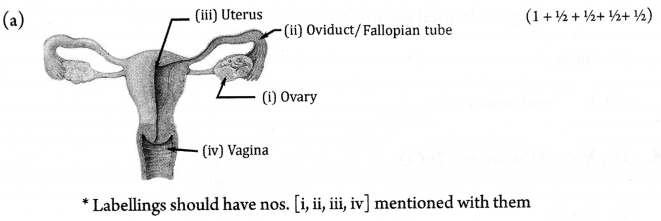
(b)
• To prevent female foeticide/sex selective abortion of female foetuses. (1)
• To maintain a healthy child sex ratio. (1)
| Pollination | Fertilization |
| (i) Transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma | Fusion of male & female gamete to from a zygote |
| (ii) Seen only in plants | Seen in plants as well as animals |
| (iii) Pollination leads to fertilization. | Fertilization leads to formation of embryo |
| (iv) Pollination is of two types-self & cross pollination | Fertilization is of two types internal and external fertilization |
Answer 19.
(a)
(i) Genotype of parents – Tall plants with purple flowers = TTWW dwarf plants with white flowers = ttww
(1/2 + 1/2)
(ii) Genotype of F1 progeny – TtWw. (1/2)
Phenotype of F1 progeny – All are tall with purple flowers (1/2)
(iii) Result
Tall and purple = 9
Tall and white = 3 ratio = 9:3:3:1 (1/2 + 1/2)
Dwarf and purple = 3
Dwarf and white = 1
(b) No wings of butterfly & birds are considered analogous and not homologous. (1)
This is because they have different origin & structure but have same function of flying. (1/2 + 1/2)
Answer 20.
(a) (i) 2 cm
(ii) Less than 2 cm
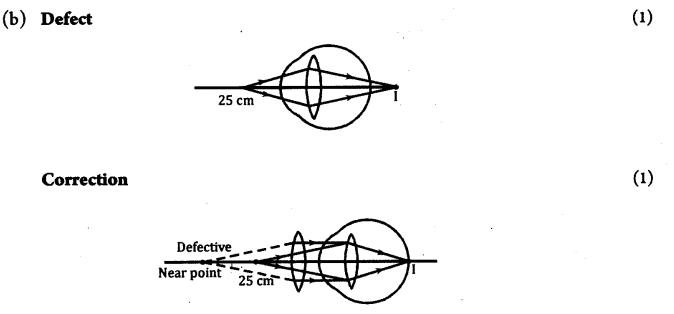
(c) f = – 50 cm
Child is suffering from myopia as the lens is concave.
f= – 0.5 m, p = 1f=−10.5 = -2 D
Answer 21.
(a) P = 100 W
V = 220V
I = ?
P = 100 S ,
P = VI ⇒ I = PV=100220=511
(b) R2 will consume energy at a greater rate as P ∝ 1R when V is constant [P = V2R ] (1)
(c) (i) Rp = ?
1Rp=12+12=22 ⇒ R = 1 Ω
Total R = 1 + 3 = 4 Ω
(ii) I = VR=44 = 1A
(iii) V = IR=1 x 3 = 3V
SECTION B
Answer 22.
(a) (c) part (1)
(b) Less than 1 Ω (1)
Answer 23.
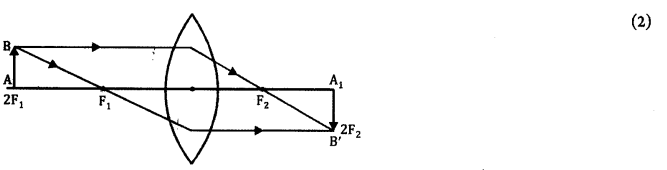
Answer 24.
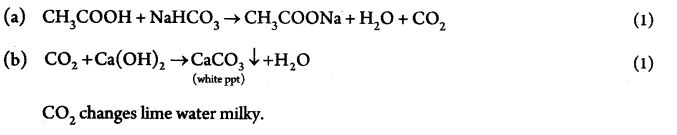
Answer 25.
White ppt. of BaS04 is formed.
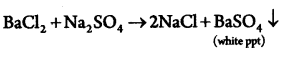
Answer 26.
Two parts of embryo
• Plumule – grows into shoot (1/2 + 1/2)
• Radicle – grows into root (1/2 + 1/2)
Answer 27.
Radish & carrot – Homologous – both are roots ie have same origin (1/2 + 1/2)
Potato & carrot – Analogous – Potato is a stem whereas carrot is a root so origin is different but both have same function of storing food. (1/2 + 1/2)
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Paper 1 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Paper 1, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
