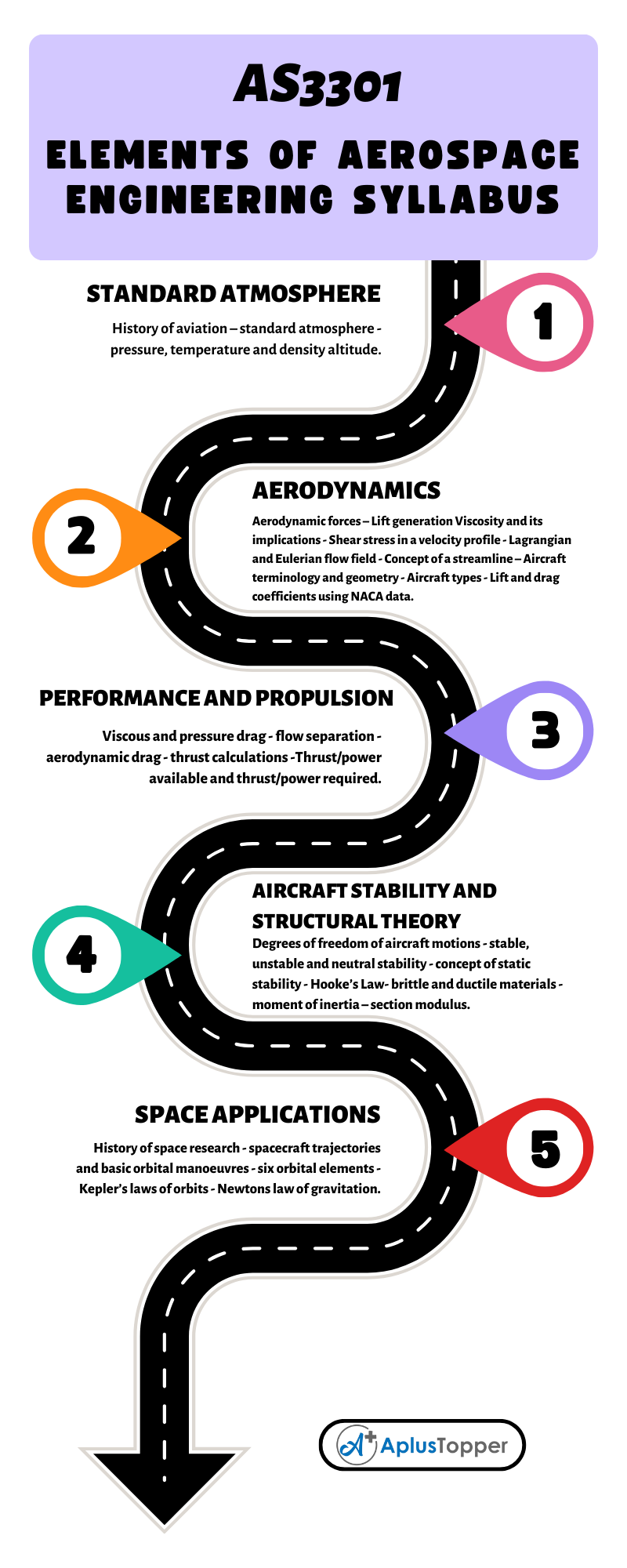
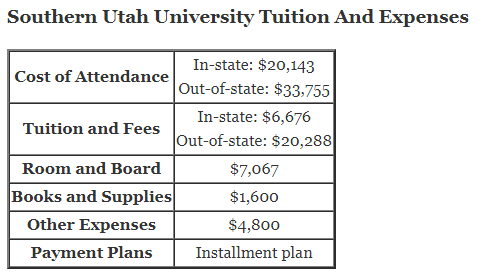
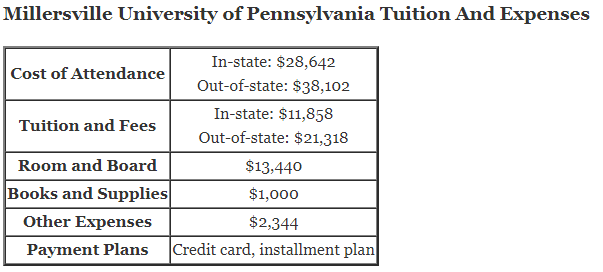
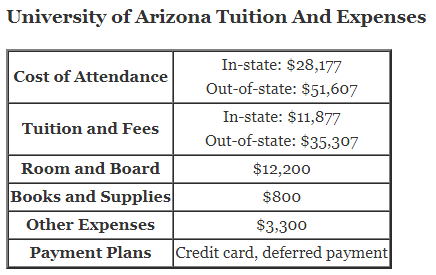
What are the Laws of Indices?
What are the Laws of Indices?Definition of indicesIf a is any non zero real or imaginary number and m is the positive integer, then am = a. a. a. a……. a (m times). Here a is called the base and m is the index, power or exponent. Laws of indices (7) If x…
What is Arithmetico–Geometric Sequence?
What is Arithmetico–Geometric Sequence?https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5L0HvXfmNsAArithmetico-geometric Progression (A.G.P.)Definition: The combination of arithmetic and geometric progression is called arithmetico-geometric progression. nth term of A.G.…
Quadratic Equations
Quadratic EquationsAn equation in which the highest power of the unknown quantity is two is called quadratic equation. Types of quadratic equationQuadratic equations are of two types:Purely quadraticAdfected quadraticax2 + c = 0 where a, c ∈ C and b = 0…
Geometric Mean
Geometric MeanIf a, G, b are in G.P., then G is called Geometric Mean (G.M.) between a and b. If a, G1, G2, G3, …. Gn, b are in G.P. then G1, G2, G3, …. Gn are called n G.M.’s between a and b.Insertion of geometric means:Single G.M. between a and b: If a…
Complex Numbers
Complex Numbers“Complex number is the combination of real and imaginary numbers” Basic concepts of complex numberDefinition: A number of the form x + iy where x, y ϵ R and i = √-1 is called a complex number and ‘i’ is called iota. A complex number is us…
Injective, Surjective and Bijective
Injective, Surjective and Bijective One-one function (Injection)A function f : A ⟶ B is said to be a one-one function or an injection, if different elements of A have different images in B. Thus, f : A ⟶ B is one-one. a ≠ b ⇒ f(a) ≠ f(b) for all a, b ∈ A…
The Binomial Distribution
The Binomial DistributionGeometrical method for probabilityWhen the number of points in the sample space is infinite, it becomes difficult to apply classical definition of probability. For instance, if we are interested to find the probability that a po…
Partial Fractions
Partial Fractions An expression of the form \(\frac { f(x) }{ g(x) }\), where f(x) and g(x) are polynomial in x, is called a rational fraction.Proper rational functions: Functions of the form \(\frac { f(x) }{ g(x) }\), where f(x) and g(x) are polynomia…
Polar and Cartesian Coordinates
Polar and Cartesian CoordinatesCartesian co-ordinates of a pointThis is the most popular co-ordinate system. Axis of x: The line XOX’ is called axis of x. Axis of y: The line YOY’ is called axis of y.Co-ordinate axes: x axis and y axis together are calle…
Equation of Circles
Equation of CirclesLet’s review what we already know about circles. Definition: A circle is a locus (set) of points in a plane equidistant from a fixed point. Now, if we “multiply out” the above example (x-2)2 + (y+5)2 = 9 we will get: (x-2)2 + (y+5)2 …