How can energy be changed in a chemical reaction?
Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions:
- All chemical substances contain energy in the form of chemical energy.
- During chemical reactions, the chemical energy in the reactants can be changed into other forms, more often into heat energy.
- The unit used in measuring energy is Joule (J).
1 kJ (kilojoules) = 1000 J. - Thermochemistry is the study of changes in heat energy during chemical reactions.
- Based on the energy changes in chemical reactions, chemical reactions can be divided into two types:
(a) Exothermic reaction
(b) Endothermic reaction - The changes of energy in some chemical reactions are shown in Table.
Table: Energy changes involved in chemical reactionsChemical reaction Energy change Combustion of fossil fuels Chemical energy → Heat energy Electrolysis Electrical energy → Chemical energy Chemical cells Chemical energy → Electrical energy Photosynthesis Light energy → Chemical energy Burning of fire crackers Chemical energy → Heat energy, light energy, sound energy
People also ask
- How does the energy level diagram show this reaction is exothermic?
- What is enthalpy of reaction?
- What is heat of precipitation?
- What is heat of displacement?
- What is the enthalpy of neutralization?
- What is the heat of combustion?
- Why is energy released when a bond is formed?
- Applications of exothermic and endothermic reactions in everyday life
- What is meant by the calorific value of a fuel?
What is the definition of exothermic reaction in chemistry?
Exothermic reaction:
- An exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that gives out heat to the surroundings.
- In an exothermic reaction,
(a) chemical energy in the reactants is changed into heat energy,
(b) the heat energy is transferred to the surroundings,
(c) temperature of the surroundings increases,
(d) the reacting mixture and the container become hot. - Surroundings do not involve in the reactions. Surroundings include
(a) container which holds the reactants and the products,
(b) solvent in which the reactions are taking place,
(c) air, and
(d) thermometer. - When a piece of magnesium ribbon is added to some dilute hydrochloric acid in a test tube, a reaction occurs and the test tube becomes hot. This shows that heat has been given out. Thus, the reaction is exothermic.
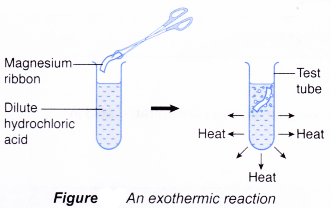
Initial temperature of hydrochloric acid =29.0°C
Highest temperature of the mixture = 31.0°C
Increase in temperature= 2.0°C
There is an increase in temperature
⇒ exothermic
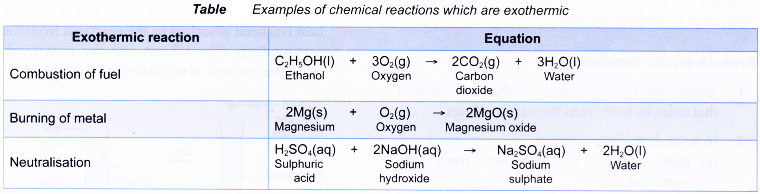
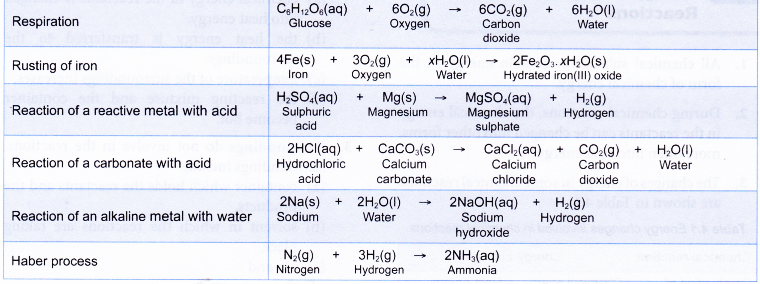
Some examples of chemical reactions which are exothermic are shown below:
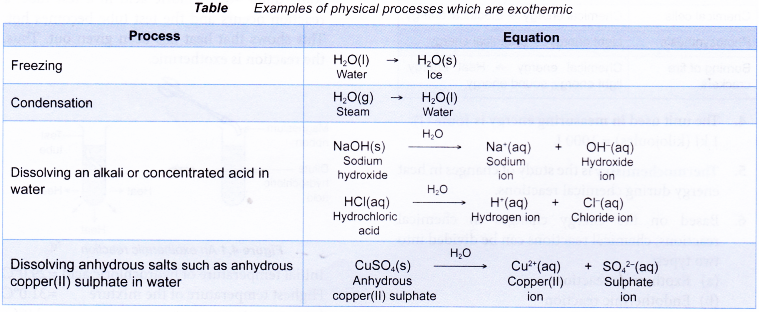
Below Table shows some physical processes which are exothermic.
What is an endothermic reaction?
Endothermic reaction:
- An endothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that absorbs heat from the surroundings.
- In an endothermic reaction,
(a) heat energy is absorbed from the surroundings,
(b) the heat energy is changed into chemical energy,
(c) temperature of the surroundings decreases,
(d) the reacting mixture and the container become cold. - When sodium hydrogen carbonate is added to hydrochloric acid in a test tube, a reaction occurs and the test tube becomes cold. This is because heat has been absorbed by the reactants from the surroundings (the solvent and the container). Thus, the reaction is endothermic.
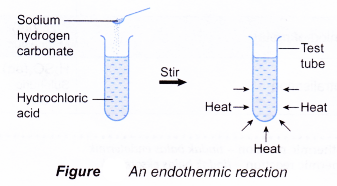
Initial temperature of hydrochloric acid = 29.0°C
Lowest temperature of the mixture = 28.0°C
Decrease in temperature = 1.0°C
There is a decrease in temperature
⇒ endothermic
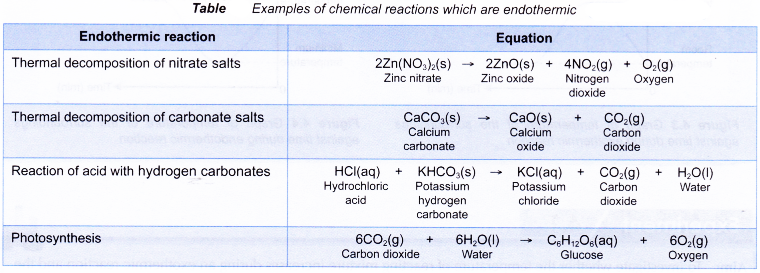
Some examples of chemical reactions which are endothermic are shown in Table.
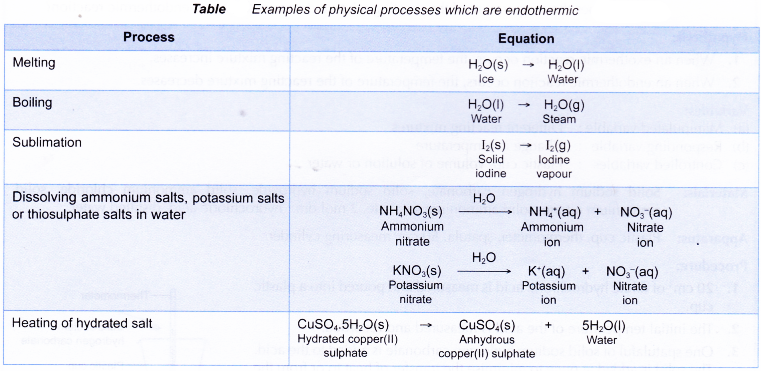
Some physical processes which are endothermic are as shown below.
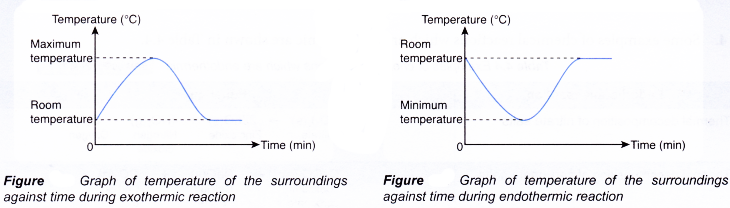
The graphs below show the change in temperature of the surroundings against time during exothermic and endothermic reactions.
Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions Experiment
Aim: To investigate whether the temperature of reacting mixture increases during an exothermic reaction and the temperature of reacting mixture decreases during an endothermic reaction.
Problem statement: Does the temperature of the reacting mixture increase during an exothermic reaction?
Does the temperature of the reacting mixture decrease during an endothermic reaction?
Hypothesis:
- When an exothermic reaction occurs, the temperature of the reacting mixture increases.
- When an endothermic reaction occurs, the temperature of the reacting mixture decreases.
Variables:
(a) Manipulated variable : Different reacting mixtures
(b) Responding variable : Change in temperature
(c) Controlled variables : Plastic cup, volume of solution or water
Materials: Solid sodium hydrogen carbonate, solid sodium hydroxide, solid ammonium chloride, solid ammonium nitrate, solid ammonium sulphate, 2 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid, distilled water.
Apparatus: Plastic cup, thermometer, spatula, 50 cm3 measuring cylinder.
Procedure:
- 20 cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid is measured and poured into a plastic cup.
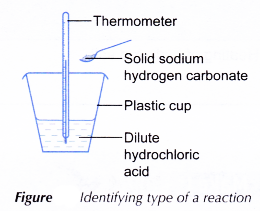
- The initial temperature of the acid is measured and recorded.
- One spatulaful of solid sodium hydrogen carbonate is added to the acid. The solid is added at once to minimise the transfer of heat to or from the surroundings.
- The mixture is stirred with the thermometer.
- The highest or lowest temperature of the reacting mixture is recorded.
- Steps 1 to 5 are repeated using the following mixtures.
- Solid sodium hydroxide + hydrochloric acid
- Solid sodium hydroxide + water
- Solid ammonium chloride + water
- Solid ammonium nitrate + water
- Solid ammonium sulphate + water
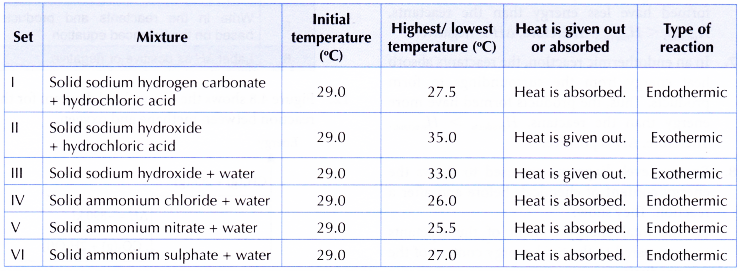
Results:
Discussion:
- From the experiment,
(a) sets I, IV, V and VI are endothermic reactions,
(b) sets II and III are exothermic reactions.
Conclusion:
- An exothermic reaction occurs if there is an increase in temperature of the reacting mixture.
- An endothermic reaction occurs if there is a decrease in temperature of the reacting mixture.
- The hypothesis is accepted.
