What did Bohr Contribute to the Theory of an Atom
Bohr’s model of an atom
In 1912, Niels Bohr put forward a model to explain the structure of an atom. The main postulates of the model are:
- An atom is made up of three particles : electons, protons and neutrons. Electrons have negative charge, protons have positive charge whereas neutrons have no charge, they are neutral. Due to the presence of equal number negative electrons and positive protons, the atom on the whole is electrically neutral.
- The protons and neutrons are located in a small nucleus at the centre of the atom. Due to the presence of protons, nucleus is positively charged.
- The electrons revolve rapidly around the nucleus in fixed circular paths called energy levels or shells. The energy levels or shells are represented in two ways: either by the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 or by the letters K, L, M, N, O and P. The energy levels are counted from the centre outwards.
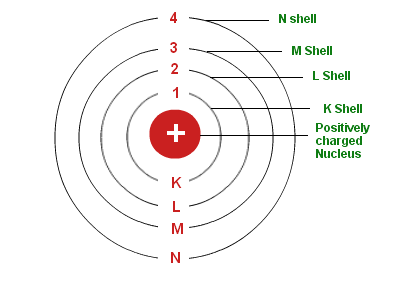
- There is a limit to the number of electrons which each energy level can hold. For example, the first energy level (or K shell) can hold a maximum of 2 electrons; second energy level (or L shell) can hold a maximum of 8 electrons; third energy level (or M shell) can hold a maximum of 18 electrons and fourth energy level (or N shell) can hold a maximum of 32 electrons.
- Each energy level (or shell) is associated with a fixed amount of energy, the shell nearest to the nucleus having minimum energy and the shell farthest from the nucleus having the maximum energy.
- There is no change in the energy of electrons as long as they keep revolving in the same energy level, and the atom remains stable. The change in the energy of an electron takes place only when it jumps from a lower energy level to a higher energy level or when it comes down from a higher energy level to a lower energy level. When an electron gains energy, it jumps from a lower energy level to a higher energy level, and when an electron comes down from a higher energy level to a lower energy level, it loses energy.
The distribution of electrons in different orbits or shells is governed by a scheme known as Bohr bury scheme.
People also ask
- How would you describe the Structure of an Atom
- What was Rutherford’s Original Hypothesis
- What are the Characteristics of Electron, Proton and Neutron
- Explain Bohr Bury rules for Distribution of Electrons into Different Shells
- What are the Isotopes, Isobars and Isotones of an Element
- What did Dalton Contribute to the Understanding of the Atom
- What is the Definition of Atom and Molecule
- What is Atomic Mass
- How has the Model of the Atom Changed Over the Years?
