Applications of Reflection of Light in Daily Life
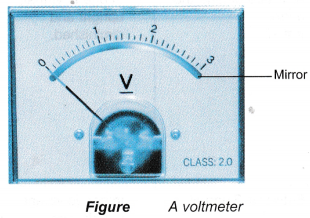
- Meters like ammeters and voltmeters use a mirror to avoid parallax error. The reading is taken from a position such that the image of the pointer is directly under the pointer.
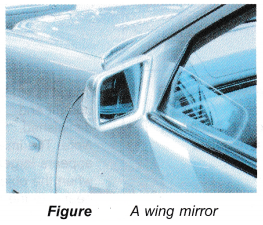
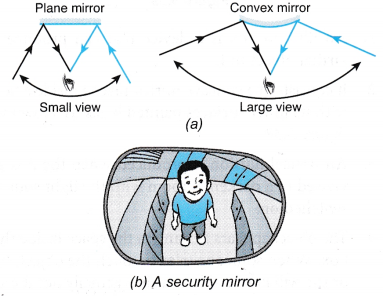
- The wing and rear-view mirrors of a car are made of a convex and a plane mirror respectively. The two wing mirrors enable the driver to see objects on both sides of the car. The rear-view mirror enables the driver to see things behind the car.
- A microscope uses a mirror to reflect light to the specimen under the microscope.
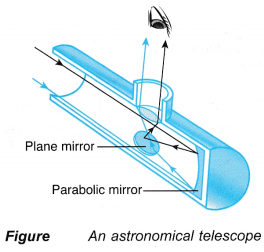
- An astronomical reflecting telescope uses a large parabolic mirror to gather dim light from distant stars. A plane mirror is used to reflect the image to the eyepiece.
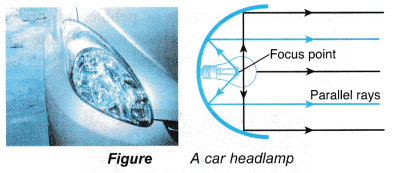
- Parabolic mirrors are used in torches and car headlamps as reflectors. A small lamp is placed at the focus point of the mirror to produce parallel rays.
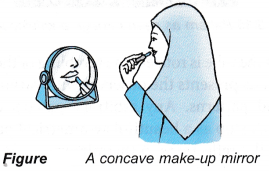
- Concave mirrors with long focal length can be used as shaving mirrors or make-up mirrors as they form magnified and upright images.
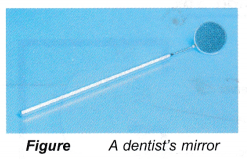
- Concave mirrors are also used by dentists to examine the teeth of a patient. The concave mirror forms a magnified image of the teeth.
- A convex mirror has a wider view than a plane mirror. Therefore, convex mirrors are used as driving mirrors and as shop security mirrors.
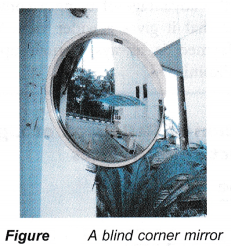
- Convex mirrors are also used as blind corner mirrors on the road to help drivers view traffic around sharp corners.
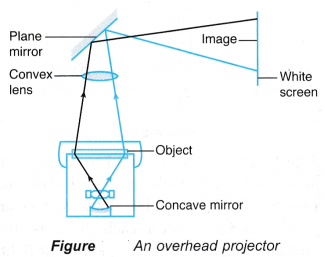
- An overhead projector as in figure uses a concave mirror to reflect light from the object to the screen.
People also ask
- What is Reflection of Light?
- What is the Law of Reflection of Light?
- What do you mean by Total Internal Reflection?
- Applications of Total Internal Reflection
- Image Reflection by a Plane Mirror
- Which Type of Image is Formed by a Plane Mirror?
- Is an Image formed by Reflection Real or Virtual
- Reflection of Light from Spherical Mirror
- What are Concave and Convex Mirrors?
- How is Focal Length related to Radius of Curvature?
- How is the Image Formed by a Spherical Mirror?
Application of Reflection of Light in the Construction of Devices
Periscope
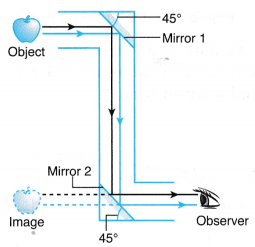
- A periscope is a device used to see objects over an obstacle. It is made up of two plane mirrors mounted in a long tube. Both mirrors are set parallel to each other at each corner of the tube and at an angle of 45° to the path of the light rays.
- Light from the object is reflected through 90° by each mirror before entering the eye of an observer.
- Periscopes are often used in double-decker buses to let the driver see the situation in the upper deck.
- Periscopes are also used in submarines to observe the surrounding areas above the water surface.
Kaleidoscope
- A kaleidoscope is an optical device that produces colourful patterns and designs.
- It consists of a tube of plane mirrors with one end closed. The tube can be in the form of a triangle, square, rectangle or hexagon as shown in Figure.
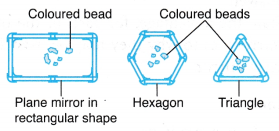
- Pieces of coloured beads or pebbles are placed inside the tube. The observer looks in one end and light enters the other end, reflecting off the mirrors.

- As the tube is rotated, the tumbling of the coloured beads presents the observer with varying colours and patterns. Any arbitrary pattern of objects shows up as a beautiful symmetrical pattern due to the reflections in the mirrors.
- The kaleidoscope is used by designers to yield carpet and wallpaper patterns.
An Illusion Box
- An illusion box is a device that can produce a virtual object in it.
- It consists of a concave mirror placed inside a box with its inner surfaces painted black as shown in Figure.
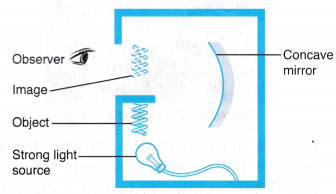
- An optical illusion is produced when the box is viewed in a darkened room with the light source switched on.
- The object appears to hang in the space inside the box. When someone tries to touch the object, he or she will not be able to as it is actually not there.
