Analysing Electromagnetic Waves
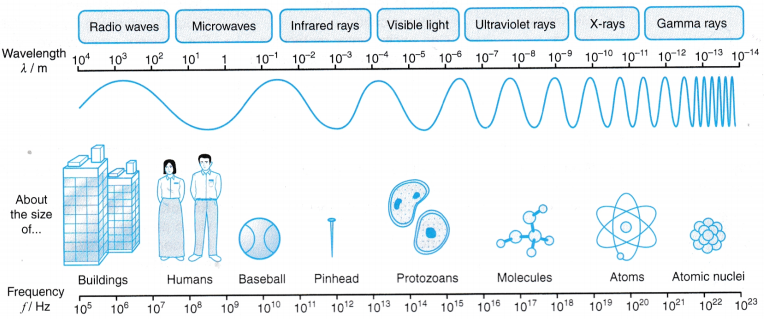
- The electromagnetic spectrum consists of a group of waves of similar nature. The members of the electromagnetic spectrum arranged in increasing frequencies (decreasing wavelengths) are radio waves, microwaves, infrared rays, visible light, ultraviolet rays, X-rays and gamma rays.
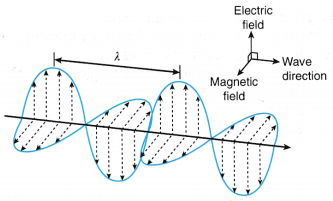
- Electromagnetic waves are joint electric and magnetic fields which can travel through space with no need of a medium to carry them. Figure shows the representation of electromagnetic waves.
- All the members of the electromagnetic spectrum
(a) transfer energy from one place to another
(b) are transverse waves
(c) can travel through a vacuum
(d) travel with a speed of 3 x 108 m s-1 in a vacuum
People also ask
- Analysing Reflection of Waves
- Analysing Refraction of Waves
- Analysing Interference of Waves
- Analysing Diffraction of Waves
- Analysing Sound Waves
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
Table lists out the sources, characteristics and applications of the electromagnetic spectrum.
| Type and wavelengths | Sources | Characteristics | Applications |
| Radio waves λ : 103 — 10-1 m  |
|
|
|
| Microwaves λ : 10-1 – 10-3 m  |
|
|
|
| Infrared rays λ : 10-3 – 10-6 m  |
|
|
|
| Visible light λ : 8 x 10-7 – 4 x 10-7 m  |
|
|
|
| Ultraviolet rays λ : 10-7– 10-9 m  |
|
|
|
| X-rays λ : 10-9 – 10-11 m 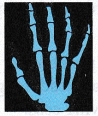 |
|
|
|
| Gamma rays λ : 10-11 m or less  |
|
|
|
Detrimental Effects of Electromagnetic Waves
- The human eye cannot detect ultraviolet rays but an overexposure to these rays can cause blindness. Overexposure to ultraviolet rays can also cause sunburn and skin cancer.
- Due to the high energy associated with short wavelength radiations, ultraviolet radiations, X-rays and gamma rays can damage living tissues. These radiations ionise atoms and molecules in living cells. These cells may die or become cancerous.
- X-rays have very high penetrating power. These rays have adverse effects on living cells. Cancer and genetic defects can be induced by exposure to X-rays.
- Gamma rays have very high penetrating power. Exposure to gamma rays can lead to genetic defects and the harming of living cells.
