Advantages And Disadvantages Of Self Pollination: The exchange of dust grains from the anther of bloom to the shame of something similar or another blossom is called Pollination. In angiosperms and the greater part of the gymnosperms, Pollination is a fundamental cycle for sexual proliferation. Pollination might be of the accompanying two sorts:
- Self Pollination
- Cross-Pollination
The exchange of dust grains from anthers to the disgrace of a similar blossom is known as self-pollination. Self – Pollination happens just in the event of sexually open blossoms, where the anthers and disgrace mature at the same time.
In such a case, the shame gets the dust grains from a similar blossom or different bloom of a similar plant. Whenever a blossom is pollinated by its own dust, it is called autogamy as in wheat, pea, rice, and so on At the point when dust grains from one bloom are moved on the disgrace of another blossom borne on a similar plant, it is called geitonogamy.
Students can also find more Advantages and Disadvantages articles on events, persons, sports, technology, and many more.
What is Self Pollination? Advantages And Disadvantages Of Self Pollination 2022
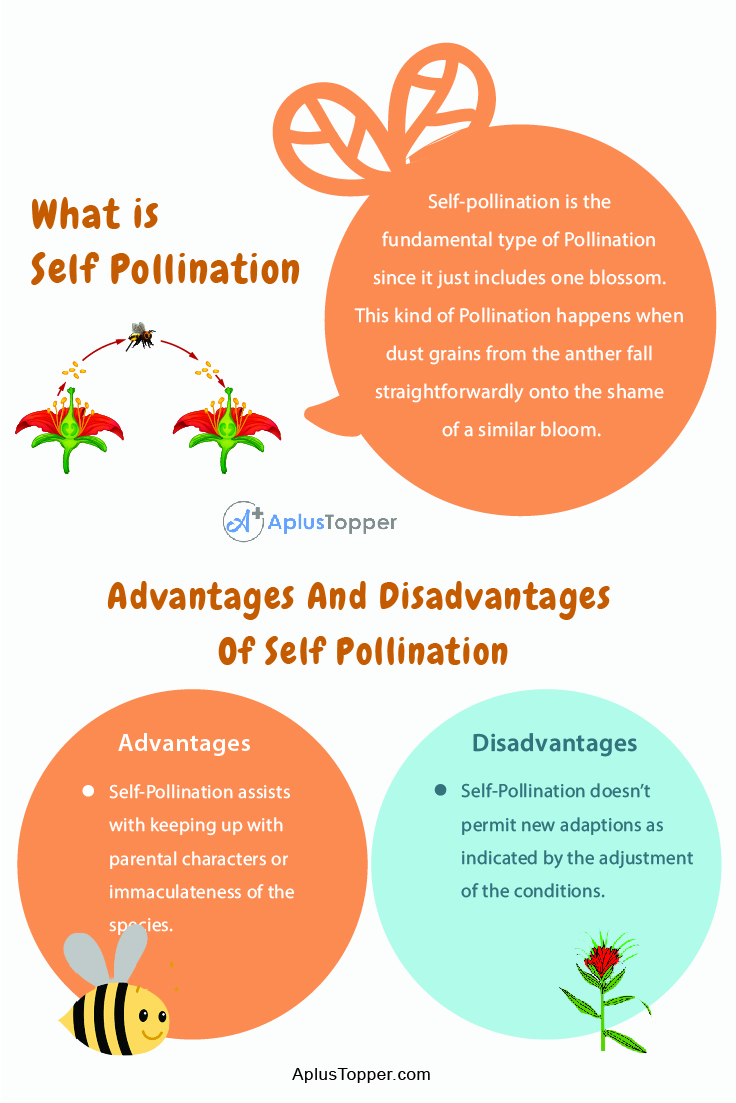
Self-pollination is the fundamental type of Pollination since it just includes one blossom. This kind of Pollination happens when dust grains from the anther fall straightforwardly onto the shame of a similar bloom. Albeit this sort of Pollination is basic and speedy, it brings about a decrease in hereditary variety on the grounds that the sperm and egg cells of a similar blossom share hereditary data.
Self-Pollination is a type of Pollination wherein dust from a similar plant shows up at the disgrace of a blossom or at the ovule. There are two kinds of self-Pollination: in autogamy, dust is moved to the shame of a similar blossom; in geitonogamy, dust is moved from the anther of one bloom to the disgrace of one more blossom on a similar blossoming plant, or from microsporangium to ovule inside a solitary gymnosperm. A few plants have instruments that guarantee autogamy, for example, blossoms that don’t open (cleistogamy), or stamens that transition to come into contact with the shame. The term selfing that is regularly utilized as an equivalent word, isn’t restricted to self-Pollination, yet additionally applies to different sorts of self-preparation.
- Advantages Of Self Pollination
- Disadvantages Of Self Pollination
- Comparison Table for Advantages And Disadvantages Of Self Pollination
- FAQs on Pros and Cons of Pollination
Advantages Of Self Pollination
- Self-Pollination assists with keeping up with parental characters or immaculateness of the species.
- The plant doesn’t have to rely upon pollinating specialists.
- No need of creating an enormous number of dust grains.
- Blossoms don’t have to foster gadgets for drawing in bug pollinators.
- It guarantees seed creation. Maybe it is utilized as a safeguard gadget for cross-pollinated blossoms.
- It kills a few awful latent characters.
- The immaculateness of the race is kept up with
- There is no wastage of dust grains
- Self-Pollination guarantees that passive characters are killed
- The plants don’t rely upon outside factors or pollinating specialists for Pollination.
Disadvantages Of Self Pollination
- Self-Pollination doesn’t permit new adaptions as indicated by the adjustment of the conditions.
- It can prompt the diminished soundness of the species, because of the reproducing of related examples.
- Insusceptibility to sicknesses diminishes.
- The seeds are less in numbers
- Can’t be delivered new assortments of plants
- Delivered seeds are frail because of the moment size of the endosperm
- Without new characters presented, the resultant offsprings’ resistance to sicknesses lessens.
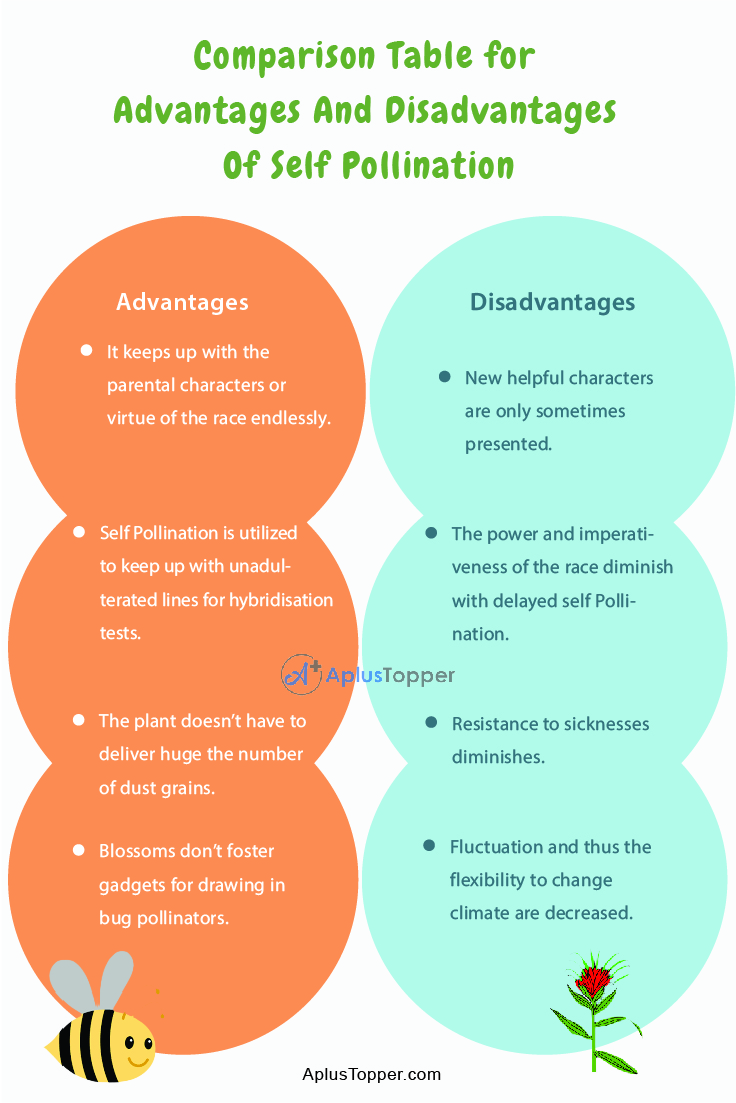
Comparison Table for Advantages And Disadvantages Of Self Pollination
| Advantages of Self Pollination | Disadvantages of Self Pollination |
| It keeps up with the parental characters or virtue of the race endlessly. | New helpful characters are only sometimes presented. |
| Self Pollination is utilized to keep up with unadulterated lines for hybridisation tests. | The power and imperativeness of the race diminish with delayed self Pollination. |
| The plant doesn’t have to deliver huge the number of dust grains. | Resistance to sicknesses diminishes. |
| Blossoms don’t foster gadgets for drawing in bug pollinators. | Fluctuation and thus the flexibility to change climate are decreased. |
| It guarantees seed creation. Maybe it is utilized as a safeguard gadget for cross-pollinated blossoms. | Seeds are less in numbers |
FAQs on Pros and Cons of Pollination
Question 1.
What are the characteristics of self-pollination?
Answer:
The features of self-pollination are:
- Self-Pollination happens among anther and pistils of similar blossom or various blossoms of a similar plant.
- The presence of sexually open blossom or monoecious plants is a must for self-Pollination.
- Blossoms are by and large little, less appealing and without nectar.
- Less number of dust grains are required.
- Seed Produced through self-Pollination is little, light in weight and less in number.
- Descendants of self-rearing plants show less power. At times they are frail.
- More current characteristics other than guardians won’t ever create.
Question 2.
What are the pros of self-pollination?
Answer:
The benefits of self-pollination are;
- Not very many dust grains can fertilize the blossom.
- Immaculateness of the race is kept up with.
- Self-Pollination keeps away from the wastage of dust grains.
- Fewer possibilities of disappointment in Pollination.
Question 3.
What are the cons of self-pollination?
Answer:
The benefits of self-pollination are:
- Self-pollinated blossoms have little, light weighted and fewer quantities of seeds.
- Nonstop self-Pollination brings about the development of more fragile descendants.
- there are no possibilities of the development of new species and assortments of plants.
- The possibilities of development are likewise decreased.
