Advantages and Disadvantages of Reservation System in India: The reservation system in India is a system of affirmative action in India that provides historically deprived groups representation in the education, employment, and political sectors. Based on the provisions provided in the Indian Constitution, it allows the Indian government to set reserved quotas or seats, which lower the qualifications needed in exams, job openings, etc., for “socially and economically backward citizens.”
Reservation is primarily given to all three groups: Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and Other Backward Classes, also known as SC, ST, and OBC, respectively. Earlier reservation was only given to SCs and STs but was later extended to OBCs in 1992 after implementing the Mandal Commission report.
What is Reservation System in India? Advantages and Disadvantages of Reservation System in India 2022
The reservation system in Indian law is a form of affirmative action wherein a percentage of seats or quotas are reserved in the public sector units (PSUs), union and state civil services, services in the union and state government departments, and all public and private educational institutions, except in the religious or linguistic minority educational institutions. The Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs), and Other Backward Classes (OBCs) or the socially and economically backward communities who were previously inadequately represented in these services and institutions are now provided with the reservation facility. The reservation policy is also implemented for the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes for representation in the Parliament of India.
The reservation issue has remained a cause of disagreement between the reserved and the non-reserved sections of the society. While the unreserved segments keep opposing the provision, the neediest sections from within the reserved segments are hardly aware of how to benefit from the provision or whether there are such provisions.
Hence in this article, we will look at the advantages and disadvantages of the reservation system in India to understand whether we need the reservations or not.
- Advantages of Reservation System in India
- Disadvantages of Reservation System in India
- Comparison Table for Advantages & Disadvantages of Reservation System in India
- FAQs on Pros & Cons of Reservation System in India

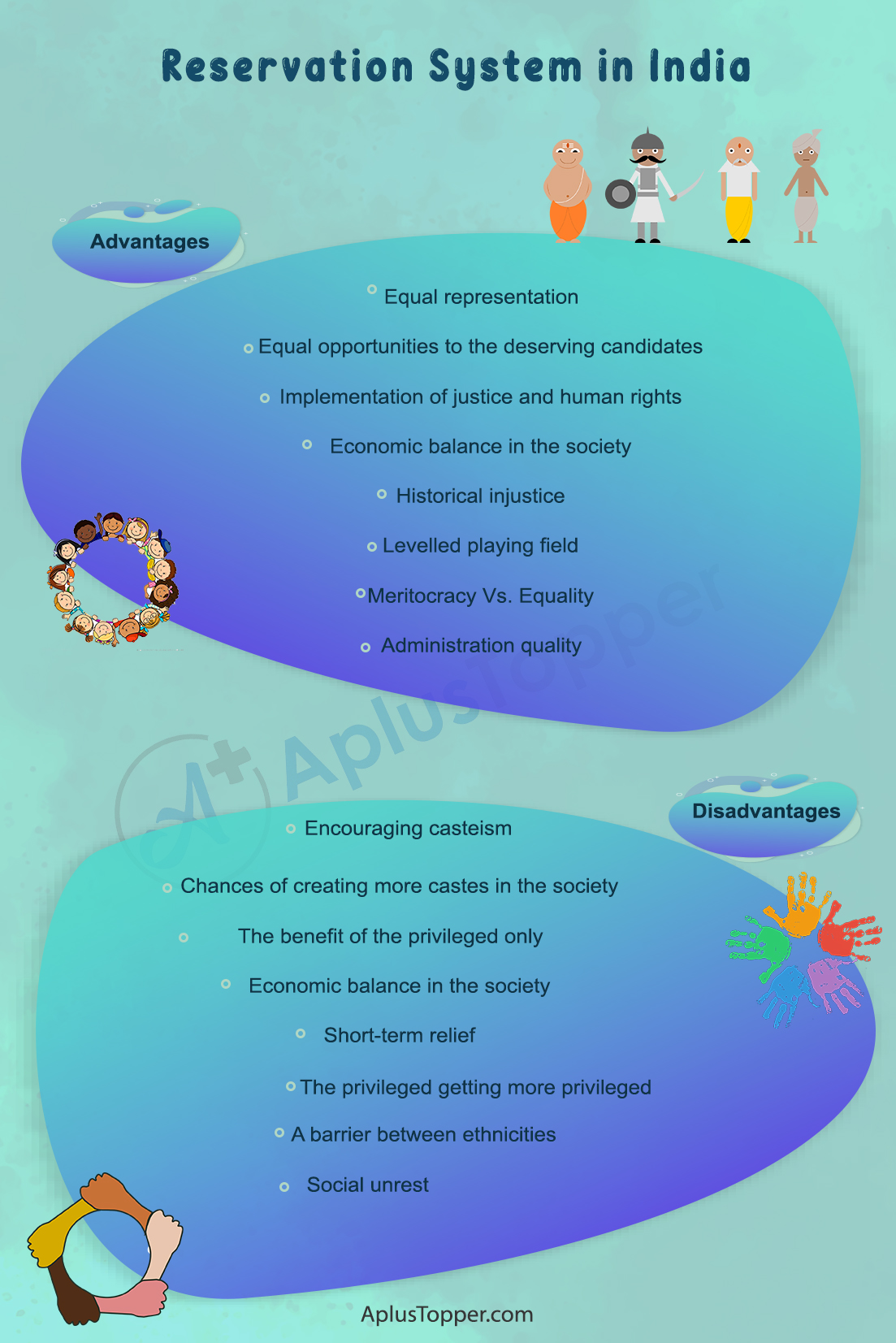
Advantages of Reservation System in India
The advantages of having the Reservation System in India are listed below:
- Equal representation: Increase in the number of people from backward sections in various decision-making procedures, resulting in equal representation from different sections of the society.
- Equal opportunities to the deserving candidates: It has helped some people from backward sections achieve higher posts or services in the public sector and some private institutions as well.
- Implementation of justice and human rights: It has encouraged the people to fight for justice whenever there is a violation of their human rights.
- Economic balance in the society: Reservation has slowed down the process of forward becoming richer and backward becoming poorer.
- Historical injustice: Caste-based reservation is necessary for India because of historical negligence, injustice, and mistreatment caused to the backward communities.
- Levelled playing field: Reservation provides a level playing field as it is difficult for those from the backward sections who were historically disadvantaged of education, skills, and financial or economic mobility to all of a sudden start competing with those who had access to those resources for hundreds of years.
- Meritocracy Vs. Equality: Meritocracy is essential; however, it will have no meaning without equality. People must be brought up to the same level whether it elevates a section or decelerates another regardless of merit. Thus, the caste-based reservation also minimizes the gap between upper and lower castes to a great extent.
- Administration quality: A study had revealed that reservations did not affect the administration efficiency instead enhanced the quality. One of the best examples is the Indian Railways, in which the SC/ST employees are employed in large numbers, and the results have been better.
Disadvantages of Reservation System in India
Along with the good advantages of the Reservation System in India, it has few disadvantages, listed below:
- Encouraging casteism: It’s propagating the notion of caste-based society instead of eliminating it.
- Chances of creating more castes in the society: Poor people from the forward castes still don’t have any social or economic advantage over the rich people from the backward castes. If this situation persists, it may result in the formation of a separate backward caste of people belonging from the poorer section of the forward castes.
- The benefit of the privileged only: Beneficiaries of reservation are primarily from the creamy layer or the dominant class in backward castes. Hence, the marginalized section still remains marginalized.
- Opposing meritocracy: It’s resulting in the degradation of the quality of students and employees enrolled in different institutions if the undeserving candidates get the opportunities.
- Short-term relief: A reservation only provides a limited and short-term solution to the historical injustice issues.
- The privileged getting more privileged: As the reservation grows more prominent, it becomes a mechanism of exclusion rather than inclusion. As we can see nowadays, the previously advantaged communities have becoming disadvantaged to a large extent due to the reservation problem. Many deserving people from the upper castes are still affected by poverty and illiteracy.
- A barrier between ethnicities: It is a form of ethnic discrimination. It works as a barrier for removing casteism and racism and promoting harmony between castes and religions.
- Social unrest: Reservation agitations may cause social unrest, such as during the Mandal Commission (1990).
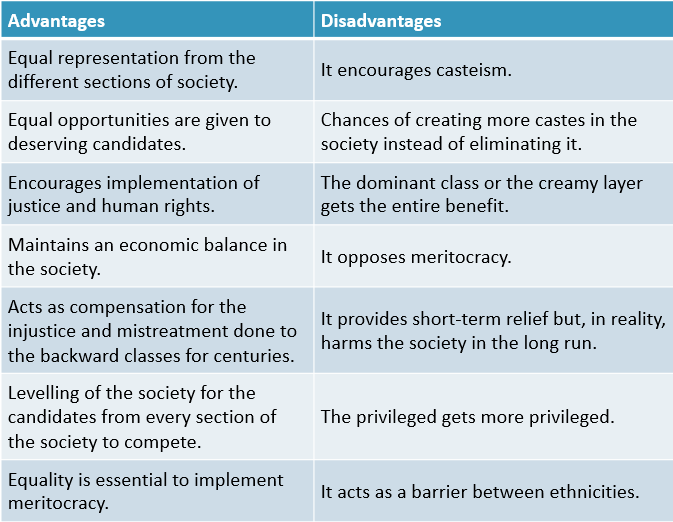
Comparison Table for Advantages & Disadvantages of Reservation System in India
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Equal representation from the different sections of society. | It encourages casteism. |
| Equal opportunities are given to deserving candidates. | Chances of creating more castes in the society instead of eliminating it. |
| Encourages implementation of justice and human rights. | The dominant class or the creamy layer gets the entire benefit. |
| Maintains an economic balance in the society. | It opposes meritocracy. |
| Acts as compensation for the injustice and mistreatment done to the backward classes for centuries. | It provides short-term relief but, in reality, harms society in the long run. |
| Levelling of the society for the candidates from every section of the society to compete. | The privileged get more privileged. |
| Equality is essential to implement meritocracy. | It acts as a barrier between ethnicities. |
| Improvement in administration quality. | It causes social unrest. |
Many times, reservations are the exact opposite of development and equality. Currently, we don’t require reservations based on castes or religion but only to provide support to those with merit but fewer resources. This way, we would successfully eliminate caste discrimination and unite the economically rich to support the economically poor, regardless of their castes.
Reservation is undoubtedly good, as long as it is a method of appropriate positive discrimination for the benefit of the oppressed and economically backward sections of society. Still, when it tends to harm the society and ensures privileges for a few at the cost of other deprived people for narrow political benefits, as it is in the current scenario, it should be revoked as soon as possible.
FAQ’s on Pros & Cons of Reservation System in India
Question 1.
Why is the reservation system needed in India?
Answer:
Reservations are meant to prevent caste supremacists from outright denying the less privileged from the backward classes (SC, ST & OBC) and economically weaker sections (EWS) of the society their right to learn and work altogether.
Question 2.
What is the reservation policy in India?
Answer:
Reservation is provided to Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs) and Other Backward Classes (OBCs) at the rate of 15%, 7.5% and 27%, respectively, in case of direct recruitment on all India basis by open competition.
Question 3.
What is the reservation distribution for the EWS in India?
Answer:
The Union Council of India has approved a 10% reservation in government jobs and educational institutions for the EWS (Economically Weaker Section) in the General category. They have also decided that this would be over and above the existing 50% reservation for SC/ST/OBC categories.
