Advantages and Disadvantages of Rain: Vapour, or microscopic droplets of water, is present in the atmosphere at all points of time. Water vapor may be retained in massive amounts by warm air.
Air soars when it is heat is applied. It gets cooler as the air ascends. Water begins to condense and convert into a liquid form. Clouds are characterized by a large concentration of liquid droplets that have clustered together.
Mountain ranges may induce air to ascend and liquid droplets to condense in the air.
If the clouds are enormous sufficiently, water drops collide and expand even significantly larger. When the drops develop heavily sufficiently, they create rain and descend to the earth.
Students can also find more Advantages and Disadvantages articles on events, persons, sports, technology, and many more.
What is Rain? Advantages and Disadvantages of Rain 2021
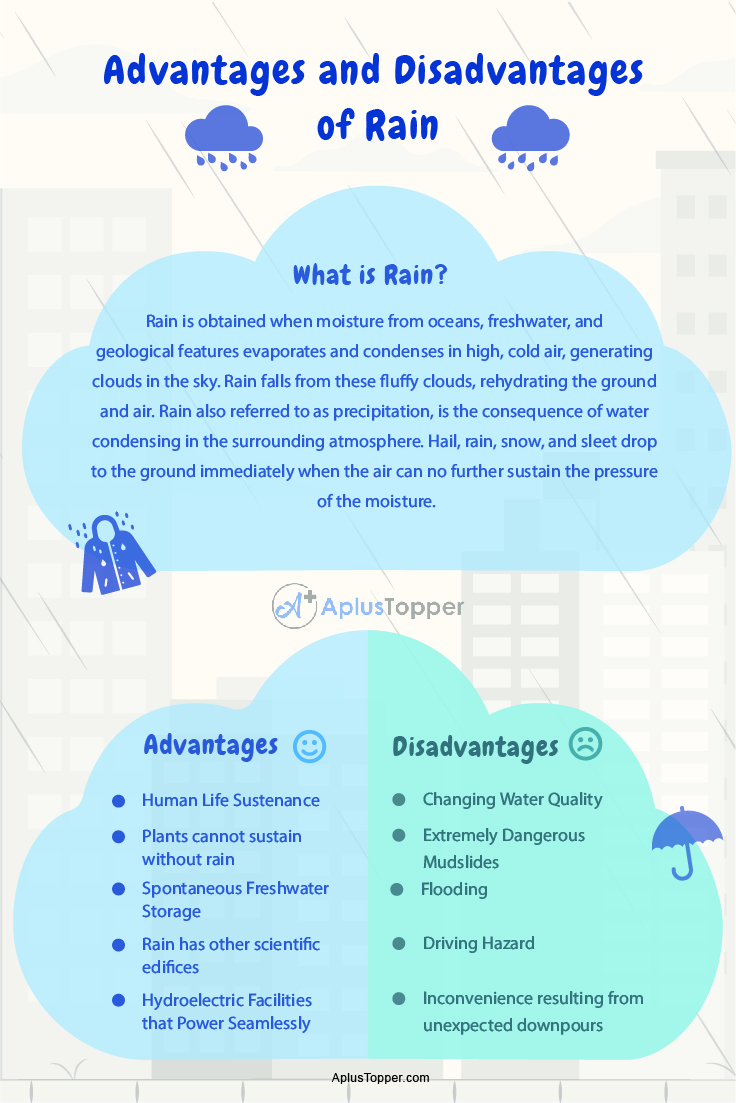
Rain is obtained when moisture from oceans, freshwater, and geological features evaporates and condenses in high, cold air, generating clouds in the sky. Rain falls from these fluffy clouds, rehydrating the ground and air. Rain also referred to as precipitation, is the consequence of water condensing in the surrounding atmosphere. Hail, rain, snow, and sleet drop to the ground immediately when the air can no further sustain the pressure of the moisture.
Rain is a significant component of the never-ending water cycle, in which rain descends to the earth, evaporates, is absorbed by clouds, and afterward pours again to resume the loop. Precipitation actually aids the earth’s atmospheric conditions, seasonal changes, and the sustainability of all plant and animal life on earth.
- Advantages of Rain
- Disadvantages of Rain
- Comparison Table for Advantages and Disadvantages of Rain
- FAQs on Pros and Cons of Rain
Advantages of Rain
Rain has numerous implications for the environment, notably replenishing wild vegetation, moistening the air, forming streams and rivers, refilling the water table, and creating extremely beneficial negative ions. The redistribution of clean, fresh water in the water cycle is by far the most significant benefit of rainfall.
- Human Life Sustenance: Human body needs a consistent availability of freshwater to help support its continued existence, which is made available by plenty of precipitation. To disintegrate solids, the human digestive system necessitates water. Sweat, urine, and feces all assist to completely eliminate hazardous toxins from the human system.
- Plants cannot sustain without rain: Vegetation, plants and trees, grass, and blossoming flowering shrubs all necessitate water to survive and flourish. From see4f gcbbsds through adult stages of growth, plant roots soak up moisture and transmit it to the stems and leaves, promoting nourishment. As a direct consequence of photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, providing the essential oxygen to the atmosphere for animal respiration.
- Rain is a vitality resource for all components of the environment: Plant species get the water they require to convert solar energy into nutrition from rainwater-soaked soil, and animals derive their hydration from that watered vegetation as well as static and running water. Rain cools the air, which has already been scorched by the sun, rehydrating and replenishing parched leaves and grasslands. It retains rivers, waterways, and marshes, which in turn helps to furnish fresh water to fish and amphibians.
- Spontaneous Freshwater Storage: Rainwater falls to the surface and is soaked into the topsoil, ultimately hitting aquifers in the bedrock. The water table in aquifers maintains high levels of concentration of water. Many man-made water wells serve to drink and to bathe water by pulling straight from the water table. Aquifer water penetrates through sedimentary rock to other regions, giving plants and trees a steady and consistent inflow of water.
- Hydroelectric Facilities that Power Seamlessly: Hydroelectric facilities leverage an archaic manner of energy generation: they leverage the fluid motion of fast-moving rivers or the gravity of reservoirs to propel gigantic wind turbines. Rain furnishes all of the water capacity necessary to drive hydroelectric plants, rendering them pollution-free. As a source of energy, rain is completely complimentary. All of our hydroelectric plants are kept on running by a constant stream of precipitation.
- Rain has other scientific edifices: Humans have recognized advanced functionality for rain. Rainwater-produced spontaneous lightning is now being studied by various researchers and see whether its electricity can actually be captured and stored separately. Scientists are also trying to investigate cloud seeding as a means of producing rain.
Disadvantages of Rain
Rain is absolutely lovely, but there is no such thing as too much of which is always wonderful in the world. Rain gets a terrible reputation a lot more these days. As with weather-sensitive activities, the unnecessary burden aspect is well-known and clearly evident.
- Changing Water Quality: Rainwater is generally preferable to synthetic agricultural technologies since it eliminates the increased contaminants that artificial irrigation methods commonly incorporate, such as chlorine. However, there is one complicating factor: when a polluted atmosphere yields acid rain, it is severely detrimental to the environment and human health, rainwater’s blessings are curtailed.
- Extremely Dangerous Mudslides: When there is a considerable amount of precipitation after a drier season, mudslides can strike, and they can be catastrophic. They not only erode away rich soil, but they can also potentially damage dwellings and endanger human life. They normally occur on hillsides, and even if there aren’t any dwellings on the mountainside, there’s the possibility of devastating mayhem on the roads, businesses, and dwellings at the foot.
- Flooding: Major flooding wrecks residences, industries, and individual lives under the worst cases. When the origin of the inundation is extended days of heavy downpour, the flooding might be incremental. Flash floods, on the other contrary, are arguably even more dangerous and deadly since they can overwhelm individuals who are either unprepared for them or misjudge their serious threat. Cities and towns are obliged to rebuild, which has detrimental financial consequences.
- Driving Hazard: One major drawback of rain is that it takes longer to slow down on moist roads; hence if people are driving as if the highways are not damp, tragedies can happen.
- Inconvenience resulting from unexpected downpours: Rain may be inconvenient for individuals who have left home without suitable attire (raincoats, rain boots, etc.). They will be woefully underprepared to deal with the problem.

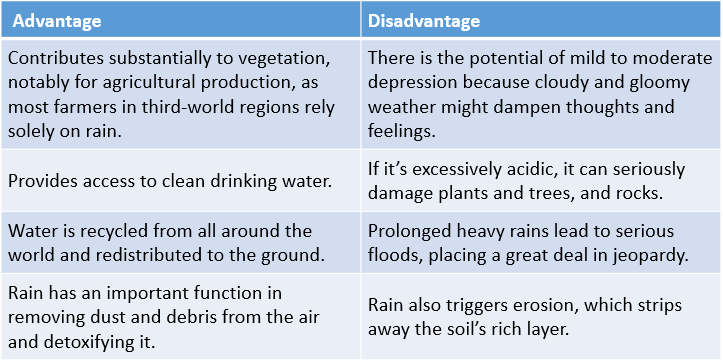
Comparison Table for Advantages and Disadvantages of Rain
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
| Contributes substantially to vegetation, notably for agricultural production, as most farmers in third-world regions rely solely on rain. | There is the potential of mild to moderate depression because cloudy and gloomy weather might dampen thoughts and feelings. |
| Provides access to clean drinking water. | If it’s excessively acidic, it can seriously damage plants and trees, and rocks. |
| Water is recycled from all around the world and redistributed to the ground. | Prolonged heavy rains lead to serious floods, placing a great deal in jeopardy. |
| Rain has an important function in removing dust and debris from the air and detoxifying it. | Rain also triggers erosion, which strips away the soil’s rich layer. |
FAQs on Pros and Cons of Rain
Question 1.
What causes rain to form?
Answer:
Rain is composed up of water particles that have gotten heavy enough to fall under gravitational force as a result of the decrease of water vapor in the surrounding air.
Question 2.
What is the maximum amount of rain that may be reasonably expected?
Answer:
There is no method of determining a sizable portion. It depends on a combination of basic parameters, including location, temperature, and other meteorological conditions. Flooding occurs when there is way too much rain, while drought occurs when there is not enough rain. In Mt. Waialeale, Kauai, Hawaii, for example, the rain seldom ceases, with up to 350 wet days per year.
Question 3.
What exactly is acid rain?
Answer:
Acid rain is rain that includes a large amount of acid or hydrogen ions (low pH). The presence of gases like Sulphur Dioxide and Nitrogen Oxides in the air triggers the formation of acid rain.
Question 4.
What effect does acid rain have on plants?
Answer:
Acid rain has a secondary effect on plants since it depletes the soil’s vital nutrients. Acid rain dissolves and washes away all of the soil’s vitamins and minerals, which are absolutely necessary for plant growth and development.
