Advantages and Disadvantages of Prototype Model: A prototype model is a model which develops software. This model builds a prototype of the actual software used for testing and refining until a good prototype is accomplished. The customers interact with these prototypes and give feedback based on which the testing and refining are done. The interaction between the customer and the prototype enables the customer to recognize the required system’s needs better and provides a solid design feel for the customer.
Students can also find more Advantages and Disadvantages articles on events, persons, sports, technology, and many more.
What is Prototype Model? Advantages and Disadvantages of Prototype Model 2021
A prototype model is not a complete system, and there are many missing details in the prototype. It provides a basis for the final product. The best use of the prototype model is when the required system is large and complicated, and no manual process is provided to understand the system’s detailed requirements. It is a trial and error method that takes place between the customer and the developer.
This piece discusses the benefits and drawbacks of a prototype model to understand the model better.
- Advantages of Prototype Model
- Disadvantages of the Prototype Model
- Comparison Table for Advantages and Disadvantages of the Prototype Model.
- FAQs on the Pros and Cons of the Prototype Model
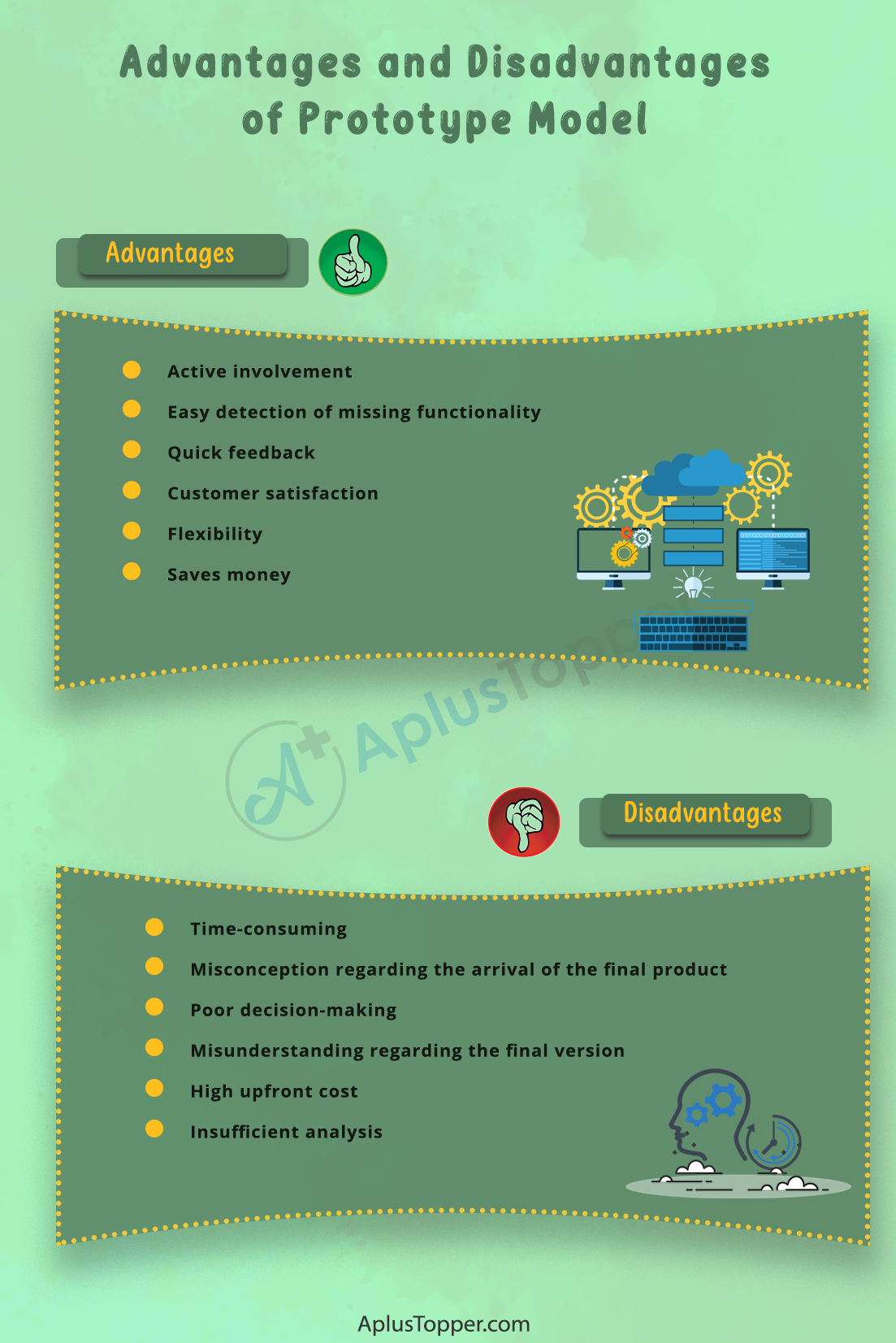
Advantages of Prototype Model
There are various advantages to the prototype model. Some of them are discussed below:
- Active involvement: In this model, the users are involved actively in the development phase and, thus, it is easier to develop the model according to their preferences. Since the users are actively involved, errors are detected in the preliminary stages, making the process easier.
- Easy detection of missing functionality: The missing functionality in the prototype model is easily detectable. As a result of this, the failure risks are reduced.
- Quick feedback: Since the customer has direct interaction with the prototype model, their feedback is much faster. These feedbacks are essential since they are taken into consideration while creating the final system. The customers can quickly provide their thoughts, report the changes required in the project, and then the developers can modify the project accordingly.
- Customer satisfaction: The prototype model provides more significant customer satisfaction. The customer can feel the product and make actual contact with it from a very early stage and can also understand the needs of the product much better. They also enjoy the experience of being a part of developing the operating version of their project.
- Flexibility: The prototype model is flexible. It can be easily changed and modified according to the preferences and needs of the customer or the developer. Furthermore, the developer can reuse the prototype for future use in more complicated projects.
- Saves money: A prototype model can improve the ability to detect errors in the initial stages of the project. As a result, the inclusive cost and time of the project are reduced. Prototype models enable the developer to foresee the areas of expenditure that were not taken into consideration beforehand. It addresses the changes needed in the project before the adjustment process becomes expensive.
Disadvantages of Prototype Model
Unfortunately, no project development model comes without disadvantages. Given below are some of the disadvantages of the prototype model:
- Time-consuming: The prototype model is a time-consuming process. Before developing the final product, multiple prototypes are used for testing, which takes up a lot of time.
- Misconception regarding the arrival of the final product: The customer gets to make direct contact with the prototype at a very early stage. This might lead to a misconception because the customer may think that the actual product will also arrive early. This may be untrue at times.
- Poor decision-making: The developer always wants their product to be of good quality. But while creating the prototype quickly, they might make poor decisions regarding the quality of the prototype, which may affect the actual product.
- Misunderstanding regarding the final version: There is a chance that customers will get irritated and frustrated with the prototype model and lose interest in the last version. Even though the final product is improved and refined, the customers may think that the final version will contain the same failures. Another major problem is that the customer may enjoy a feature present in the initial stages of the prototype model. However, it may happen that later the specific component is removed. In both cases, the customer has a misunderstanding regarding the final version.
- High upfront cost: A prototype model saves money during the final stages of development. But there are upfront costs that are involved in the early stages of developing a prototype model. Also, the cost incurred in developing a prototype might completely go to waste since there might be a chance that the entire prototype will be thrown away.
- Insufficient analysis: There is a chance that the developer may concentrate on a specific prototype, and proper analysis of the entire project may get sidetracked. As a result, the developer will overlook better solutions, incomplete details, and the whole project may be poorly engineered, leading to complex maintenance.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Prototype Model In Tabular Form
| Advantages of Partnership Business | Disadvantages of Partnership Business |
| 1. Opportunity for Sharing of Risk and Reward | 1. Potential for Unequal Contribution of Effort or Investment |
| 2. Flexibility in Management and Operations | 2. Difficulty in Transferring Ownership or Exiting the Partnership |
| 3. Potential for Increased Innovation and Creativity | 3. Lack of Secrecy and Confidentiality |
| 4. Enhanced Access to Markets and Customers | 4. Potential for Loss of Autonomy or Control |
| 5. Ability to Take Advantage of Specialized Knowledge and Networks | 5. Potential for Personal Conflicts or Differences to Affect Business |
| 6. Provides Early and Frequent Feedback from Users | 6. Can Lead to Scope Creep and Lack of Control |
| 7. Enables Detection and Correction of Errors and Defects Early in the Development Cycle | 7. Requires Active Involvement and Availability of Users |
| 8. Allows for Exploration and Experimentation of Design Ideas | 8. Can be Time-consuming and Costly to Develop and Maintain |
| 9. Facilitates Collaboration and Communication between Development Team and Stakeholders | 9. Can Cause Confusion and Misunderstanding about the Final Product |
| 10. Offers Flexibility in Incorporating Changes and Modifications | 10. May Not Be Suitable for Large and Complex Projects |
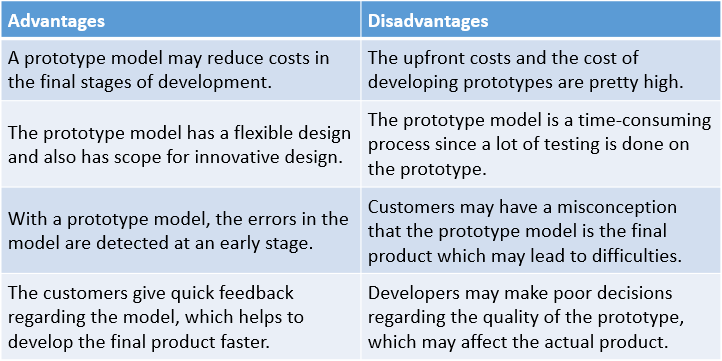
Comparison Table for Advantages and Disadvantages of Prototype Model
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| A prototype model may reduce costs in the final stages of development. | The upfront costs and the cost of developing prototypes are pretty high. |
| The prototype model has a flexible design and also has scope for innovative design. | The prototype model is a time-consuming process since a lot of testing is done on the prototype. |
| With a prototype model, the errors in the model are detected at an early stage. | Customers may have a misconception that the prototype model is the final product which may lead to difficulties. |
| The customers give quick feedback regarding the model, which helps to develop the final product faster. | Developers may make poor decisions regarding the quality of the prototype, which may affect the actual product. |
FAQs on Pros and Cons of the Prototype Model
Question 1.
Can a homemade sample be considered an official prototype?
Answer:
Yes, absolutely. In simpler words, a prototype is a working model of your product. If the functions of your homemade sample are similar to the finished design, then it can be considered as an official prototype. Your piece doesn’t need to be perfect. If the looks and the functions are similar, then that is enough. For further development, technical designers and factories can help you produce a more advanced version. Nevertheless, having a rough prototype can help safeguard initial quotes and minimums.
Question 2.
What is the minimum required to make a prototype?
Answer:
Unfortunately, no definite answer is available for this question. The cost will entirely depend on your idea of the prototype. It will depend on the cost of materials you want to use in your prototype, the intricacy of your design, and the person making the prototype. Usually, an estimation of $1,500 to $5,000 is made to develop a prototype, including everything from sketches to ultimate samples. But depending on your design, the price may vary widely.
Question 3.
How is a prototype model used?
Answer:
Prototypes are sample models of the existing system. It provides the main functionalities of the proposed system. It has limited capabilities and is not detailed. It helps to determine the actual product’s objectives and develop and refine the actual product. It is used for demonstration and implementation processes and is also used for testing.
