Advantages and Disadvantages of Optical Fiber: Correspondence through optical fiber cable may be considered a technique of transferring data from one point to another while sending light pulses. At the moment, these connections are implemented for data transmission, such as sharing photos, voice messages, and so on. These cables can be constructed using plastic or glass to transfer data more reliably and promptly than copper wires.
An optical fiber is a long, narrow strand of plain substance. This wire has the look of a cylinder. The core of this wire is known as the core, and the exterior walls of the core are referred to as the cladding. Cladding functions as a barrier protection shell in this case. These two are comprised of a wide assortment of plastic, as contrasted to glass.
Students can also find more Advantages and Disadvantages articles on events, persons, sports, technology, and many more.
Let’s go through some of the most frequent fiber optic cable benefits and drawbacks.
- Advantages of Optical Fiber
- Disadvantages of Optical Fiber
- Comparison Table for Advantages & Disadvantages of Optical Fiber
- FAQs on Pros & Cons of Optical Fiber
What is Optical Fiber? Advantages and Disadvantages of Optical Fiber 2021
Optical fiber sends information using light pulses instead of electrical signals, possibly yielding in numerous times higher bandwidth than conventional electrical systems. Exterior sheathing and armor can be applied to help protect fiber optic cable from adverse weather conditions.
An optical fiber’s sheathing, or outside reflecting layer, is a hair-thin glass or plastic fiber with an average diameter of 125 micrometers (μm). The inner core, or inner transmission route, might be just as little as 10m. As a consequence, it is pretty extensively deployed for voice in commercial businesses, governments around the world, the armed forces, and a wide variety of other domains.
These wires are required for LANs. As a result, telecommunications firms are using these wires to replace telephone lines. Optical fiber has become more prominent in telecommunications and data transmission due to its unparalleled pluses: the quicker speed with less attenuation and reduced susceptibility to electromagnetic interference (EMI), compact size, and enough information carrying potential. On the other side, the ever-increasing bandwidth requirements are fuelling a sharp rise in optical fiber usage.
Although optical fiber offers superior bandwidth and speed than copper cable, it also has significant drawbacks.
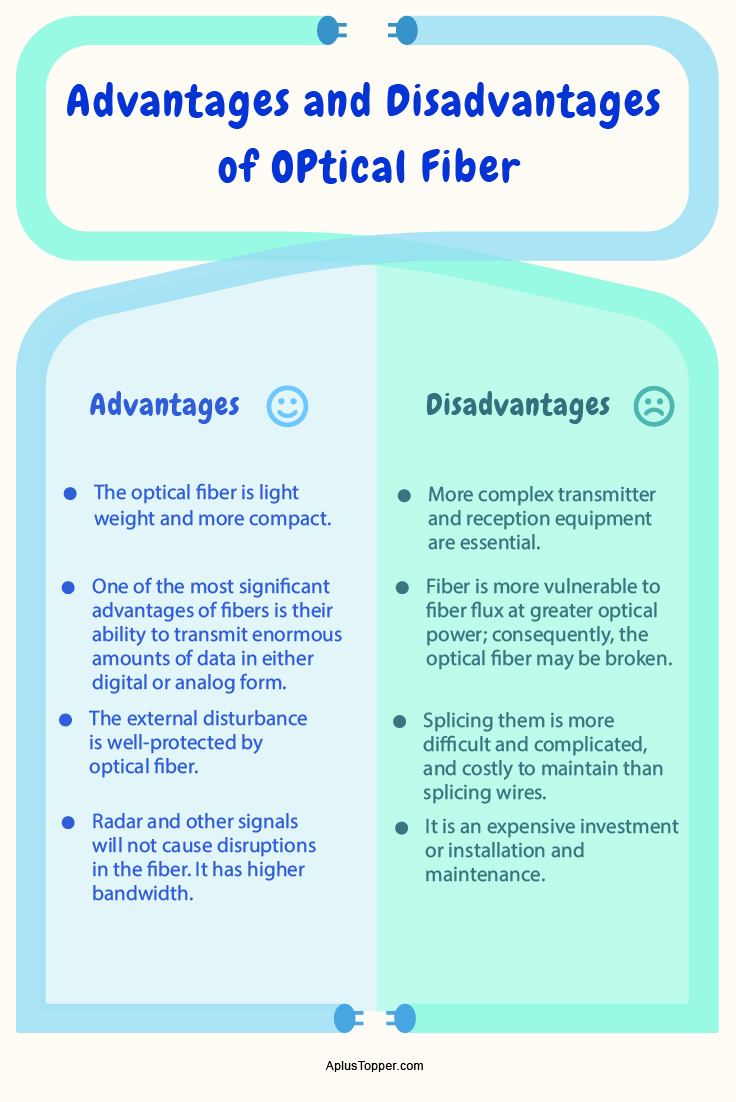
Advantages of Optical Fiber
Enhanced bandwidth and speed—Optical fiber cable can accommodate exceedingly high bandwidth and speed. The huge large amount of data that can be sent per unit of optical fiber cable is perhaps the most important advantage.
- Reasonable Cost of investment: As the market for optical fiber has dramatically increased, so has the competitive environment; consequently, Capital expenditures prices have dropped enormously as the number of fiber producers manufacturing this item has continued to increase owing to the increased need for optical fiber.
- Less signal degradation: Signal loss in fiber optic cables is significantly lower than in copper cables. Unlike copper connections, optical fiber has no cross-talk distortion. Less power dissipation and extended data transfer average distance are feasible.
- Slimmer and lighter: Optical fiber is lighter in weight than copper cable and might even be developed to significantly lower dimensions. They are thinner and lightweight than corresponding copper wire connections, making them a better complement for settings where space is at a premium.
- Longevity: The useful life of a fiber optic cable is normally approximately 100 years, making it a convenient Return on investment.
- Light impulses: Unlike electrical communications sent through the copper cables, light signals from one fiber do not overlap with those from other fibers in the very same fiber cable. This equates to crisper phone calls or enhanced TV coverage.
- Data protection: Optical fiber cables do not generate electromagnetic radiation, so they are exceedingly complex to intercept. When transmitting or sending information, these wires are tamper-proof.
- Versatility is doubled: Optical fiber is much more flexible and adaptable than copper wires of the very same dimension. A fiber optic cable is extremely configurable, bends effortlessly, and withstands most acidic components that come into contact with copper wire. Since these optical fibers are so slender, they do not actually break when wound around angles with only a few centimeters in size.
- The convenience of installation: Because of the less lightness, the installation process is fairly straightforward.
Disadvantages of Optical Fiber
Even though optical fiber has many virtues, it also has some significant shortcomings.
- Reduced power: The power of light-emitting sources is severely restricted. Although high-power emitters are obtainable to boost power delivery, they come at an incremental cost.
- Resilience: Compared to other metal cables, optical fiber is more delicate and particularly susceptible to breakage. Despite its additional agility, optical fiber is more frail and prone to damage than copper cables. Dealing and maintenance of optical fiber should be done with extreme care.
- Average distance between transmitter and receiver: The length between the transmitter and receiver should be reduced to a minimum, or repeaters will be considered necessary to maximize the signal strength.
- Fusing or Jointing: Optical fibers necessarily require the employment of professional, competent specialists for optical fusion splicing as well as inspection and evaluation when joining optical fibers together.
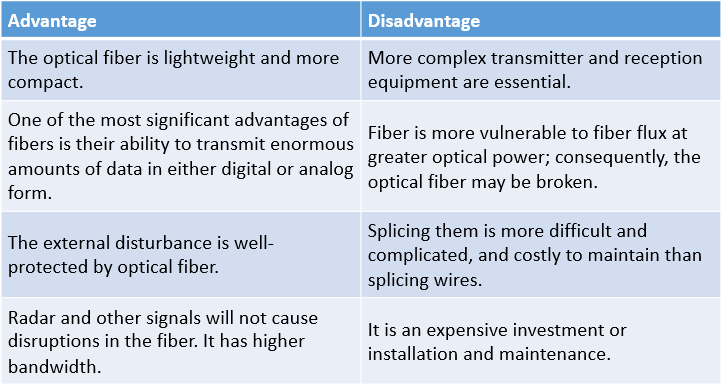
Comparison Table for Advantages & Disadvantages of Optical Fiber
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
| The optical fiber is lightweight and more compact. | More complex transmitter and reception equipment are essential. |
| One of the most significant advantages of fibers is their ability to transmit enormous amounts of data in either digital or analog form. | Fiber is more vulnerable to fiber flux at greater optical power; consequently, the optical fiber may be broken. |
| The external disturbance is well-protected by optical fiber. | Splicing them is more difficult and complicated, and costly to maintain than splicing wires. |
| Radar and other signals will not cause disruptions in the fiber. It has higher bandwidth. | It is an expensive investment or installation and maintenance. |
FAQs on Pros & Cons of Optical Fiber
Question 1.
How Do You Pick the best and most efficient Optical Fiber Cable?
Answer:
Optical fiber cable has attracted attention in communication networks, and a staggering number of businesses are seeking to develop and facilitate fiber optic cables. When purchasing optical fiber, you should begin with a trusted brand and critically evaluate the selection criteria.
- Verify the professional competence of the Manufacturing company.
- Single-mode optical fiber is typically implemented for lengthy ranges, but multimode optical fiber is usually employed for short distances. Furthermore, the equipment and installation expenses differ considerably on the fiber mode. Keep your options open and reach a choice.
- There are three variants of optical cable jackets: OFNR, OFNP, and LSZH. Before selecting the right jacket type, consult the local fire code authorities to understand the design criteria.
Question 2.
What is the Optical Fiber Principle Of operation?
Answer:
The process of transfer of data in the form of light atoms, or photons, is the basic mechanism of optical fiber.
The fiber optical cable incorporates the total internal reflection of light. The fibers are manufactured in such a manner that light can propagate together with the optical fiber-based on the power and range of transmission deemed necessary.
Question 3.
What are the most prevalent varieties of Fiber Optic Cable?
Answer:
In practice, there are three main types of fiber optic cables: glass optical fiber (single-mode fiber optic cable and multimode optical fiber) and plastic optical fiber (POF).
Question 4.
Identify the aspects that contribute to optical power attenuation in fiber.
Answer:
The variables accountable for optical power attenuation in fiber are as follows:
- Absorption.
- Scattering.
- The waveguide effect
