Advantages and Disadvantages of Biomass Energy: Biomass contains the energy first derived from the sun – the plant absorbs the sun’s energy through photosynthesis and converts carbon dioxide and water into nutrients (carbohydrates).
The energy taken from these organisms is transformed into usable energy through direct and indirect means. Biomass is burned to create heat and converted into electricity (direct means) or processed into biofuel (indirect means).
The use of biomass energy has both advantages and disadvantages for the environment and human lives. This article will discuss the advantages (pros) and disadvantages (cons) of biomass energy.
Students can also find more Advantages and Disadvantages articles on events, persons, sports, technology, and many more.
What is Biomass Energy? Advantages and Disadvantages of Biomass Energy 2022
Biomass is organic, which means it is made from material that comes from living organisms, such as plants and animals. The most common biomass energy materials are plants, wood, and waste. These are also known as biomass feedstocks. Biomass energy is energy generated or produced by living or once-living organisms. The energy from these organisms is burned to create heat or converted into electricity. It is a renewable energy source.
- Advantages of Biomass Energy
- Disadvantages of Biomass Energy
- Comparison Table for Advantages & Disadvantages of Biomass Energy
- FAQs on Pros & Cons of Biomass Energy
Advantages of Biomass Energy
Some advantages of using biomass energy in our daily lives are listed below:
- Clean source of energy: Biomass is a clean and renewable energy source. The initial energy for biomass comes from the sun, animals, and plants. Another form is algae biomass which can regrow in a relatively short period. Trees, crops, wood, municipal waste, and residues from many industries are consistently available and can be used and managed sustainably.
- Environment-friendly energy source: When trees and crops are sustainably farmed, they can balance carbon emissions by absorbing carbon dioxide through respiration. Also, in some bioenergy processes, the amount of carbon re-absorbed even exceeds the carbon emissions released during fuel processing or usage.
- No wastage of valuable land: A lot of biomass feedstocks, such as switchgrass, can be harvested on pastures or marginal lands, where they do not take up the land that can be used for food crops.
- Biomass can be stored and used when required:Unlike other renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind energy, biomass energy is stored within the organism and harvested when needed.
- Biomass reduces the dependency on fossil fuels: Besides the limited supply of fossil fuels, they also have a hazardous impact on the environment, such as the release of large amounts of oxides of carbon and nitrogen and other pollutants into the atmosphere both by burning the fuels and the production and transportation of the same.
- Biomass is cheaper than fossil fuels: The production of fossil fuel requires heavy expenditures such as oil drills, gas pipelines, and fuel collection, production of biomass energy is much cheaper.
- Biomass production adds a revenue source for manufacturers: Waste producers can add value by utilizing the garbage produced to create a more profitable use in the form of biomass energy.
- Reduction of garbage in landfills: By burning solid waste, garbage dumped in landfills gets reduced by around 60 to 90 percent, which reduces the cost of landfill disposal and the amount of land required for landfills.
Disadvantages of Biomass Energy
Though biomass is a renewable source of energy, it has certain disadvantages, which are listed below:
- Can become non-renewable energy: If the biomass feedstocks are not replenished as quickly as used, they can become non-renewable energy. For example, a forest can take hundreds of years to replenish itself. But it is still a much shorter time than fossil fuel. It can take up to 900 years for just a meter of peat to replenish itself.
- Biomass development requires land: Most biomass requires agricultural land to develop. And so, land used for biofuel crops is not available to grow food or provide natural habitats.
- Requires sustainable management of biomass sources:Forested areas that have matured for decades, also known as old-growth forests, can withdraw more carbon than newly planted trees. Hence, if forested areas are not sustainably cut, re-planted, and given time to grow and sequester the trees’ regrowth, the advantages of using the wood for fuel do not offset carbon.
- Economically not so efficient: As most biomass plants require fossil fuels to be economically efficient, a biomass plant under construction will need imported fossil fuels, offsetting some of the enterprise’s sustainability.
- Biomass plants require a lot of space: It’s challenging to find a plant that is in a convenient place in an urban area. So, utilizing onsite hardware like the BioMax® technology will help companies create biomass energy at a small fraction of the space of a large facility.
- Low energy density: Biomass has a lower energy density than fossil fuels as up to 50% of the biomass is water, which is again lost in the energy conversion process. However, converting biomass into pellets rather than wood chips or larger briquettes can increase the fuel’s energy density and make shipping more economical.
- Not completely clean energy source: Burning biomass energy releases carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and other harmful gases, particulates, and pollutants in the atmosphere. If this release of pollutants is not managed carefully, burning biomass can create smog and even exceed the pollution caused by fossil fuels.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Biomass Energy In Tabular Form
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| 1. Renewable energy source | 1. Not a completely carbon-neutral energy source |
| 2. Reduces waste disposal costs | 2. Requires large amounts of land |
| 3. Provides a reliable source of energy | 3. Can compete with food production for resources |
| 4. Can be used to supplement traditional fuels | 4. Harvesting and processing can be labor-intensive |
| 5. Helps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions | 5. Can emit harmful pollutants during combustion |
| 6. Can be produced locally, reducing dependence on foreign oil | 6. Requires specialized equipment for harvesting and processing |
| 7. Provides economic benefits to rural communities | 7. Biomass energy production can lead to deforestation |
| 8. Offers a potential solution to waste management problems | 8. Availability of biomass can be limited |
| 9. Can be used to generate electricity, heat, and fuel | 9. Transportation costs can be high |
| 10. Has a lower environmental impact compared to traditional energy sources | 10. Production can be affected by weather conditions |

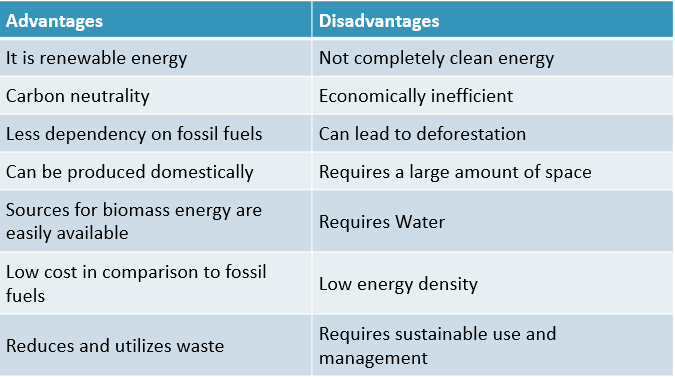
Comparison Table for Advantages & Disadvantages of Biomass Energy
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| It is renewable energy | Not completely clean energy |
| Carbon neutrality | Economically inefficient |
| Less dependency on fossil fuels | Can lead to deforestation |
| Can be produced domestically | Requires a large amount of space |
| Sources for biomass energy are easily available | Requires Water |
| Low cost in comparison to fossil fuels | Low energy density |
| Reduces and utilizes waste | Requires sustainable use and management |
The prospective of biomass energy is there for all of us to see. It is a carbon-neutral fuel source that offers lower costs than fossil fuels and is exceptionally diverse.
However, many issues are holding it back from wider adoption, and hence we have discussed the advantages & disadvantages of biomass energy in this article. Also, more needs to be done to solve the problem of efficiency as fuel, and other issues like space and cost are required to be solved.
FAQ’s on Pros & Cons of Biomass Energy
Question 1.
Where is biomass energy used?
Answer:
Biomass continues to be an essential fuel in many countries, especially for cooking and heating in developing countries. Also, consumption of biomass fuels for transportation and electricity generation is increasing in many developed countries to avoid carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuel use.
Question 2.
Does biomass cause air pollution?
Answer:
Besides carbon dioxide and monoxide emissions, burning biomass in solid, liquid, or gaseous states can emit other hazardous pollutants and particulate matter into the air, including volatile organic compounds and nitrogen oxides.
Question 3.
Can we use biomass energy in homes?
Answer:
Burning biomass energy sources such as wood and garbage – produces heat, which can be used in homes for cooking, heating, and other purposes.
Question 4.
How does biomass affect the economy of a country?
Answer:
Biomass resources provide incredible energy and economic potential for any country. Moreover, the expansion of biofuels technologies will create a stable, domestic energy supply, reducing the vast amount of money spent importing oil from overseas and increasing our country’s national security.
